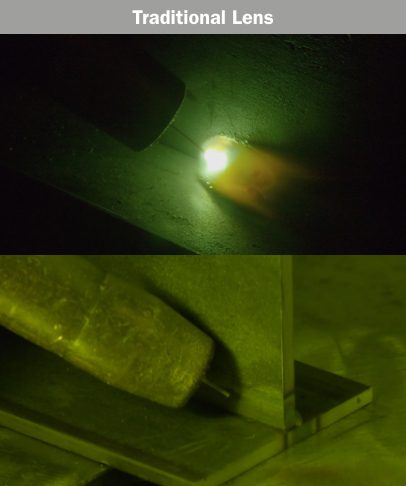
In the world of welding, a fundamental question has sparked an ongoing debate: should you be able to see through a welding helmet? This seemingly simple query has generated a diverse range of opinions across the industry. On one end of the spectrum, some argue that the ability to see through the helmet would enhance safety and precision, allowing welders to have better visibility of their surroundings. However, others maintain that a darkened lens is essential to protect the eyes from intense light and harmful radiation. Let’s explore this intriguing dilemma and uncover the pros and cons of being able to see through a welding helmet.
Benefits of Seeing Through a Welding Helmet
Improved visibility
One of the key benefits of being able to see through a welding helmet is improved visibility. Traditional welding helmets without auto-darkening capabilities often have a narrow field of vision, making it challenging for welders to have a clear view of their workpiece. By being able to see through a welding helmet, welders can have a wider field of vision and better visibility of the welding area and surrounding environment. This improved visibility allows for more precise and accurate welding, resulting in better quality welds.
Better accuracy
A welding helmet that allows for seeing through can greatly enhance accuracy during the welding process. With a clear and unobstructed view of the workpiece, welders can better align their welding torch or electrode with the intended welding line. This increased accuracy leads to more precise welds and reduces the need for rework or repairs. In industries where precision is crucial, such as aerospace or automotive, being able to see through a welding helmet can greatly improve welding accuracy.
Enhanced safety
Contrary to what one might assume, being able to see through a welding helmet can actually enhance safety. With a clear view of the workpiece and surroundings, welders can better assess potential hazards or dangerous situations. For example, they can quickly identify any flammable materials near the welding area and take appropriate precautions. Additionally, better visibility enables welders to detect any faulty equipment or potential welding defects, ensuring proactive measures are taken to address them. Ultimately, the enhanced safety provided by being able to see through a welding helmet reduces the risk of accidents and injuries in the welding environment.
Drawbacks of Seeing Through a Welding Helmet
Increased risk of eye damage
One of the main drawbacks of seeing through a welding helmet is the increased risk of eye damage. Welding generates a significant amount of bright light, intense heat, and harmful radiation, which can be detrimental to the eyes if not properly protected. Traditional welding helmets with a fixed shade lens provide a constant level of protection against these hazards. However, if a welding helmet allows for seeing through, there is a chance that the eyes could be exposed to the harmful effects of welding radiation, leading to eye injuries or vision problems if proper precautions are not taken.
Reduced protection from harmful radiation
Welding involves various types of radiation, including ultraviolet (UV) light, infrared (IR) radiation, and intense visible light. Welding helmets with a fixed shade lens are designed with specific optical filters to block out a certain level of radiation, ensuring the welder’s eyes are protected. However, when a welding helmet allows for seeing through, the level of radiation protection may be compromised. Even with the presence of auto-darkening features in some welding helmets, there may still be a risk of inadequate protection from harmful radiation. This reduced protection can result in long-term health issues for welders who are consistently exposed to welding radiation.
Inability to gauge the welding arc intensity
Another drawback of seeing through a welding helmet is the difficulty in accurately gauging the intensity of the welding arc. The brightness of the welding arc provides valuable information to welders, indicating the condition of the welding process and whether adjustments need to be made. With a welding helmet that allows for seeing through, there may be a lack of clarity or distortion when perceiving the welding arc’s intensity. This can make it challenging to determine if the welding parameters are set correctly, potentially leading to subpar weld quality or even welding defects.
This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Factors to Consider
Type of welding
The type of welding being performed is an essential factor to consider when deciding whether to see through a welding helmet. Different welding processes, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), or tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, produce varying levels of brightness and heat. Welders engaging in processes that generate a higher intensity of light and heat may need to prioritize a welding helmet with maximum protection, even if it means sacrificing the ability to see through. However, for processes with lower levels of brightness or when working on intricate projects, the option to see through a welding helmet can be beneficial.
Welding environment
The welding environment also plays a significant role in determining whether seeing through a welding helmet is advantageous. Some welding tasks may require welders to have a clear view of their surroundings while others may involve working in confined spaces or in the presence of hazardous materials. Understanding the specific requirements of the welding environment can help welders make an informed decision about the need for enhanced visibility through a welding helmet.
Personal preference
Lastly, personal preference should be considered when deciding whether to see through a welding helmet. Some welders may find that the benefits of improved visibility outweigh the potential drawbacks, while others may prioritize maximum protection and opt for a traditional welding helmet. It is important for each individual welder to assess their own comfort level, welding expertise, and the specific demands of their welding projects before choosing a welding helmet.
Regulations and Standards
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States provides regulations and guidelines for workplace safety, including those related to welding. OSHA mandates that employers ensure the use of appropriate eye protection, including welding helmets, to protect workers from welding hazards. OSHA-approved welding helmets must meet specific requirements, such as adequate protection against ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. Welders should consult OSHA standards and regulations to ensure compliance and prioritize safety in their welding practices.
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) develops and promulgates voluntary safety standards for various industries, including welding. ANSI standards, such as ANSI Z87.1, provide specifications and testing requirements for eye and face protection, including welding helmets. Welders can look for welding helmets that meet or exceed ANSI standards to ensure they are using reliable and trustworthy protective equipment.
European Norm (EN)
In Europe, the European Norm (EN) standards regulate and assess various aspects of personal protective equipment, including welding helmets. The EN standards provide guidance on the performance requirements and test methods necessary for welding helmets to be deemed safe and effective. Compliance with EN standards ensures that welding helmets meet the necessary safety criteria for use in European countries.
This image is property of www.millerwelds.com.
Technological Advances in Welding Helmets
Auto-darkening helmets
Auto-darkening welding helmets have become increasingly popular due to their ability to automatically adjust their lens shade to the appropriate level of darkness. These helmets use sensors to detect the presence of the welding arc and instantly darken the lens to protect the welder’s eyes. This feature eliminates the need for repeatedly flipping the helmet up and down, providing continuous visibility during the welding process. Auto-darkening helmets can offer the benefits of improved visibility while still maintaining adequate protection against welding radiation.
Tint control features
Some welding helmets with the ability to see through offer tint control features. This allows welders to adjust the level of darkness in the lens according to their preference or the specific welding task at hand. By having control over the tint, welders can optimize their visibility without compromising their safety. This feature can be particularly useful in situations where the brightness of the welding arc varies, such as when working with different materials or using different welding processes.
Camera-equipped helmets
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of welding helmets equipped with cameras. These helmets have a built-in camera that provides a real-time view of the welding area, allowing welders to have a clear visual of their workpiece without removing the helmet. The camera display is often positioned inside the helmet near the lens, ensuring an unobstructed view. Camera-equipped welding helmets can offer the benefits of seeing through while also enhancing accuracy and reducing the risk of eye fatigue.
Safety Measures for Welding
Proper welding technique
Regardless of whether a welding helmet allows for seeing through or not, practicing proper welding technique is crucial for safety. Welders should ensure they are following recommended welding procedures and using appropriate welding practices. This includes maintaining the correct distance between the welding torch or electrode and the workpiece, using the appropriate welding parameters, and consistently monitoring the welding process for any potential issues. By adhering to proper technique, welders can minimize the risk of accidents or injuries and ensure the best possible weld quality.
Selection of appropriate lens shades
For welding helmets that allow for seeing through, it is important to select the appropriate lens shades to provide adequate protection against welding radiation. Lens shades determine the darkness of the lens during welding, with higher numbers indicating darker shades. The choice of lens shade should be based on the welding process, type of material being welded, and the welding current used. Consulting welding charts or recommendations from manufacturers can help welders determine the appropriate lens shade for their specific welding requirements.
Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
In addition to a welding helmet, welders should always wear the necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure their safety. This includes wearing a welding apron, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing that covers the entire body. Depending on the specific welding task and environment, additional PPE such as welding curtains, face shields, or fire-resistant boots may be required. The use of proper PPE further protects welders from potential hazards, even if a welding helmet allows for seeing through.
This image is property of waterwelders.com.
Alternatives to Seeing Through a Welding Helmet
Welding curtains and screens
Welding curtains and screens are alternatives to seeing through a welding helmet that can provide protection and create a safe welding environment. These curtains and screens are made from fire-resistant materials and are designed to prevent sparks, welding spatter, and UV radiation from reaching areas outside the welding zone. By setting up welding curtains or screens, welders can protect nearby workers or passersby from potential hazards while maintaining their own safety.
Remote viewing technology
Remote viewing technology offers an innovative solution for welders who desire enhanced visibility without the need to see through a welding helmet. This technology involves the use of external cameras placed near the welding area, which transmit real-time video footage to a display or monitor located outside the immediate welding zone. By utilizing remote viewing technology, welders can have a clear view of their workpiece and welding process without compromising their safety or eye protection.
Welding goggles
Welding goggles are another alternative to seeing through a welding helmet. These goggles provide eye protection from welding radiation and flying debris while allowing for a direct, unobstructed view of the welding area. Welding goggles are typically used for specific welding tasks, such as gas welding or brazing, where a welding helmet may be impractical or unnecessary. Welders considering using welding goggles should ensure they provide the appropriate level of protection based on the specific welding process and potential hazards involved.
Effectiveness of Seeing Through a Welding Helmet
Subjective experiences from welders
The effectiveness of seeing through a welding helmet can vary depending on individual welder experiences. Some welders may find that the benefits of improved visibility outweigh any potential drawbacks in their specific welding tasks. Welders who require a high level of precision, work on intricate projects, or frequently need to assess their surroundings may find that seeing through a welding helmet significantly enhances their performance. However, it is important to note that individual experiences may differ, and welders should prioritize their own safety and comfort when deciding whether to see through a welding helmet.
Scientific studies and research
Scientific studies and research have been conducted to assess the effectiveness of seeing through a welding helmet. These studies often evaluate factors such as visibility, accuracy, eye fatigue, and overall weld quality when using welding helmets that allow for seeing through. While some studies have shown positive results in terms of improved visibility and accuracy, others have raised concerns about the potential risks associated with reduced protection from welding radiation. As with any safety-related matter, welders should consider the findings of scientific research and make informed decisions based on their specific requirements and comfort levels.
This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Training and Education
Importance of proper training
Proper training is crucial for welders to safely and effectively perform their welding tasks, regardless of whether they are using a welding helmet that allows for seeing through. Training ensures that welders understand the potential risks associated with welding and are knowledgeable about the appropriate safety measures to follow. Additionally, training provides valuable information on selecting and using the proper personal protective equipment, including welding helmets, to mitigate workplace hazards. Welders should prioritize obtaining proper training from qualified instructors or participating in recognized welding education programs to enhance their skills and ensure their safety.
Educational programs for welders
Educational programs specifically designed for welders are available to provide in-depth knowledge and practical training. These programs offer comprehensive courses that cover welding techniques, welding safety, inspection procedures, and the use of protective equipment. By enrolling in welding education programs, welders can gain a deeper understanding of welding principles and best practices, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding the use of welding helmets and the balance between visibility and safety.
Continuing education and skill enhancement
Continuing education and skill enhancement opportunities are essential for welders to stay updated on the latest advancements in welding technology and safety practices. These opportunities can include attending workshops, seminars, or industry conferences, as well as obtaining certifications in specific welding processes. By actively seeking out continuous learning, welders can ensure that they are aware of any new developments or regulations related to welding helmets and keep their skills and knowledge up to date.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision of whether to see through a welding helmet or opt for a traditional helmet with fixed shade lenses ultimately depends on various factors. While seeing through a welding helmet can offer benefits such as improved visibility, better accuracy, and enhanced safety, it also comes with drawbacks such as an increased risk of eye damage and reduced protection from harmful radiation. Welders need to consider the type of welding they perform, the welding environment, and their personal preferences when making this decision.
Regulations and standards set by organizations such as OSHA, ANSI, and EN provide guidelines for selecting and using appropriate welding helmets to ensure safety in the workplace. Technological advances in welding helmets, such as auto-darkening helmets, tint control features, and camera-equipped helmets, offer alternatives for welders who desire enhanced visibility without compromising safety.
Safety measures, including proper welding technique, selection of appropriate lens shades, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), are crucial for welders’ safety regardless of the type of welding helmet used. Alternative options to seeing through a welding helmet, such as welding curtains and screens, remote viewing technology, and welding goggles, provide additional choices to meet specific welding requirements.
The effectiveness of seeing through a welding helmet can vary based on welder experiences and scientific studies. Individual preferences and requirements should be considered when deciding whether to see through a welding helmet. Proper training, education, and continuing skill enhancement are vital for welders to safely and proficiently perform their welding tasks and make informed decisions regarding the use of welding helmets.
Ultimately, the key lies in balancing visibility and safety, ensuring welders have a clear view of their workpiece and surroundings while adequately protecting their eyes from welding hazards. Each welder should assess their specific requirements and comfort levels to make the best decision regarding the use of welding helmets and achieve optimal results in their welding endeavors.
This image is property of cdn.thefabricator.com.