When it comes to MIG welding, there’s one crucial component that plays a vital role in the process: the wire feeder. But have you ever wondered what exactly its purpose is? Well, in this article, we’ll shed some light on that very question. Join us as we explore the world of MIG welding and uncover the importance of the wire feeder in ensuring efficient and precise welds. Get ready to discover how this small but mighty device facilitates the smooth feeding of the welding wire, making all the difference in achieving high-quality welds. So, let’s dive in and uncover the purpose of a wire feeder in MIG welding!
This image is property of www.mig-welding.co.uk.
Introduction to MIG welding
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a widely used welding process that utilizes a wire electrode and a shielding gas to create a strong and durable weld. This process is commonly used in various industries, including automotive manufacturing, construction, and metal fabrication.
Understanding wire feeders
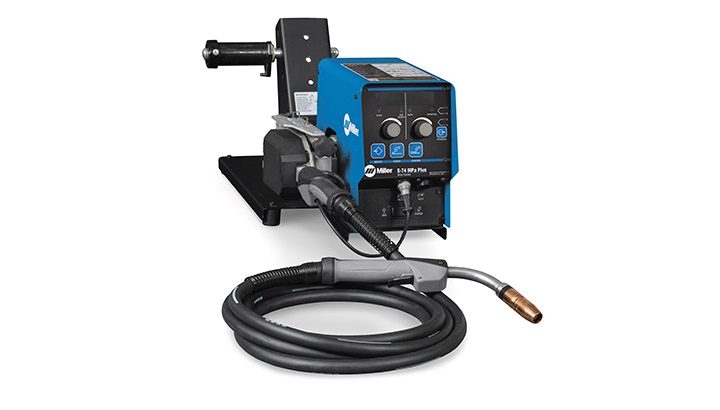
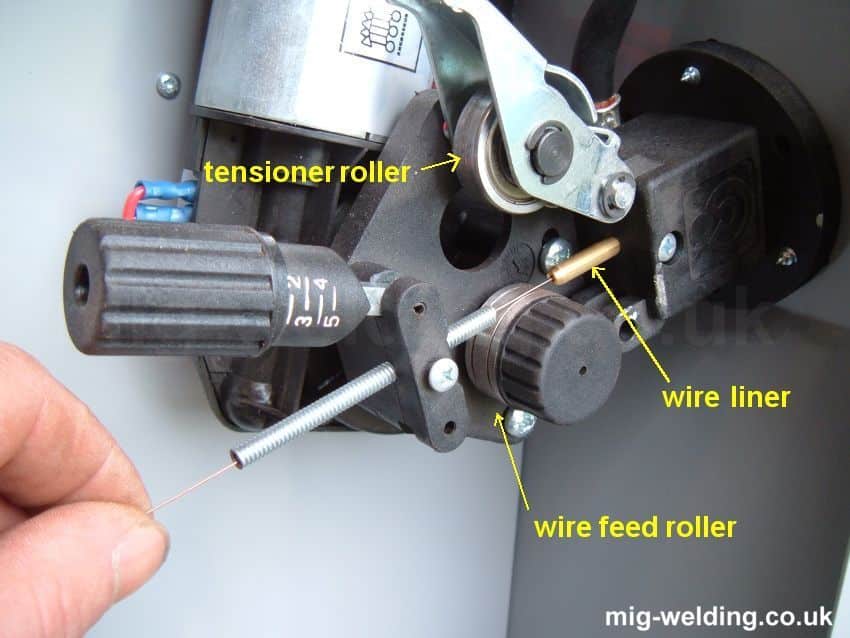
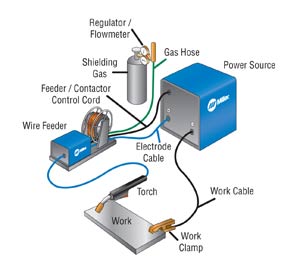
A wire feeder is an integral part of the MIG welding process. It is a device that continuously feeds the electrode wire through the welding gun, allowing the welder to maintain a consistent arc length and control the deposition rate of the filler metal.
This image is property of ars.els-cdn.com.
Components of a wire feeder
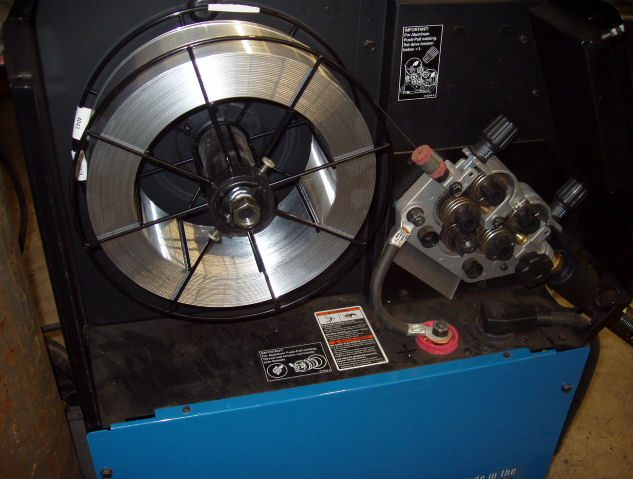
A typical wire feeder consists of several important components. These include a wire spool holder, a drive system, a wire feed motor, and a control mechanism. The wire spool holder securely holds the spool of welding wire, while the drive system pulls the wire from the spool and pushes it through the hose assembly. The wire feed motor is responsible for controlling the speed at which the wire is fed, and the control mechanism allows the welder to adjust the wire feed rate.
This image is property of www.fabricatingandmetalworking.com.
Controlling wire feed speed
The speed at which the wire is fed through the welding gun, known as the wire feed speed, is a crucial parameter in MIG welding. It determines the deposition rate of the filler metal and affects the penetration and bead shape of the weld. Controlling the wire feed speed is achieved by adjusting the wire feed rate using the control mechanism on the wire feeder.
This image is property of www.millerwelds.com.
Advantages of using a wire feeder in MIG welding
Using a wire feeder in the MIG welding process offers several advantages that contribute to improved efficiency, productivity, and safety. Let’s explore some of these advantages in more detail.
Improved efficiency and productivity
One of the main benefits of using a wire feeder in MIG welding is the consistent and uninterrupted feed of the electrode wire. This allows the welder to maintain a steady and stable arc, resulting in a more efficient welding process. Additionally, the automatic wire feeding mechanism eliminates the need for manual feeding, saving time and effort for the welder.
Reduction in material waste
A wire feeder ensures precise control over the wire feed rate, preventing excessive or insufficient deposition of filler metal. This helps minimize material waste by optimizing the amount of wire used to produce a sound weld. By reducing material waste, using a wire feeder can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
Increased safety
In MIG welding, the wire feeder acts as a remote control for the welding process. The welder can position themselves in a safe and comfortable location, away from any potential hazards. This distance also helps minimize exposure to harmful welding fumes and reduces the risk of accidents.
Precise control of wire feed rate
A wire feeder allows for precise control of the wire feed rate, resulting in consistent welds with accurate bead size and shape. This level of control enables welders to produce high-quality welds with minimal defects, improving the overall strength and durability of the weld joint. The ability to adjust the wire feed rate also facilitates welding different materials and varying thicknesses with ease.
Suitability for automation
Wire feeders are commonly used in automated welding systems due to their ability to consistently feed the electrode wire. In industrial settings where large-scale welding operations are required, automation offers enhanced efficiency and productivity. By incorporating wire feeders into automated welding systems, manufacturers can achieve higher production rates and more consistent weld quality.
This image is property of gowelding.org.
Common issues with wire feeders and troubleshooting tips
While wire feeders are generally reliable, they can sometimes encounter issues that affect the welding process. Here are a few common problems and some troubleshooting tips:
-
Wire feeding problems: If the wire is not feeding properly or is getting stuck, check for any obstructions or debris in the wire feeding system. Ensure the drive rolls are aligned correctly and inspect the wire for any kinks or bends.
-
Erratic wire feed: If the wire feed is inconsistent, it may be due to improper tension in the wire feed system. Adjust the tension according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and ensure the wire spool is properly aligned.
-
Burnback: Burnback occurs when the wire fuses to the contact tip, causing it to become stuck and preventing the wire from feeding properly. This issue can be resolved by cleaning or replacing the contact tip and adjusting the wire feed speed.
-
Excessive splatter: Excessive spatter can occur if the wire feed speed is too high or if the contact tip is dirty or worn out. Verify that the wire feed speed is appropriate for the welding parameters and clean or replace the contact tip if necessary.
Remember, if you encounter any issues with your wire feeder that you are unsure how to resolve, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek assistance from a qualified welding professional.
In conclusion, a wire feeder plays a crucial role in the MIG welding process by ensuring a consistent and controlled feed of the electrode wire. It offers several advantages, including improved efficiency, reduced material waste, increased safety, precise control of the wire feed rate, and suitability for automation. By understanding the components and functionality of a wire feeder, welders can optimize their welding process and achieve high-quality welds.