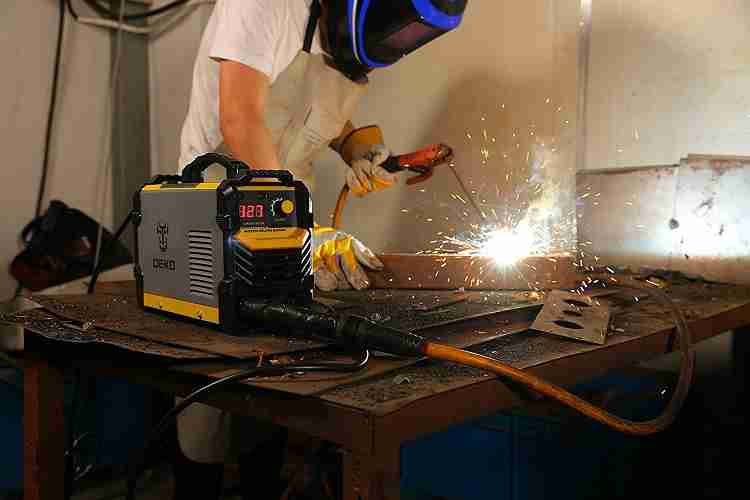
Welding electrodes are an essential component in the welding process, but understanding how to store and handle them correctly can maximize their effectiveness and lifespan. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting out, proper storage and handling techniques can ensure that your electrodes remain in optimal condition, resulting in better welds and cost savings. In this article, we will explore some valuable tips and guidelines for storing and handling welding electrodes correctly, allowing you to achieve the best possible results in your welding projects.
Selection of Welding Electrodes
Understanding Different Types of Electrodes
When it comes to welding, not all electrodes are created equal. There are various types of electrodes available, each with its unique composition and characteristics. Understanding the different types of electrodes is crucial in selecting the right one for your welding project.
Electrodes can be categorized based on their coating and core materials. The coating of an electrode plays a significant role in determining its performance and properties. Common coating types include rutile, cellulose, and basic coatings. Each coating offers distinct benefits, such as enhanced arc stability or improved resistance to moisture.
The core material of an electrode also varies, with options like mild steel, stainless steel, and cast iron. Choosing the appropriate core material is essential to ensure compatibility with the base metal and achieve the desired weld quality.
Choosing the Right Electrode for the Job
Selecting the right electrode for a welding job requires careful consideration of several factors. One crucial aspect is the type of base metal being welded. Various base metals have different properties and require compatible electrodes for optimal results. For instance, stainless steel electrodes are suitable for welding stainless steel, while carbon steel electrodes are a better choice for carbon steel.
Another consideration is the welding position. Not all electrodes perform equally well in different positions. Some electrodes may be ideal for flat or horizontal welding, while others are better suited for vertical or overhead welding. Understanding the intended welding position and selecting an electrode that performs well in that position can greatly improve the efficiency and quality of the weld.
Other factors to consider when choosing electrodes include the required penetration, joint configuration, and the presence of any specific welding codes or standards that need to be followed. Consulting with welding experts or referring to manufacturer guidelines can help in making informed decisions.
Considerations for Specific Welding Processes
Different welding processes, such as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW), may have specific requirements when it comes to electrode selection.
For SMAW, commonly known as stick welding, electrodes with various coating types and core materials are available to cater to different applications. Some electrodes are designed specifically for SMAW in mild steel, while others are suitable for high-strength steels or alloys. Considering the specific welding process and its requirements can greatly impact the final weld quality and productivity.
Similarly, choosing the appropriate electrode for GMAW or FCAW involves considering factors such as wire diameter, shielding gas composition, and base metal compatibility. Taking into account the unique requirements of each welding process ensures optimal electrode selection and ultimately results in successful welds.
Proper Storage of Welding Electrodes
Importance of Proper Storage
Proper storage of welding electrodes is essential in maintaining their integrity and performance. Failing to store electrodes correctly can lead to various issues, including degraded welding performance, decreased electrode life, and even weld defects.
Electrodes are sensitive to moisture, high temperatures, and certain gases or contaminants. Inadequate storage conditions can cause moisture absorption, which leads to hydrogen-induced cracking and porosity in the weld. Extreme temperatures can affect the coating integrity and the core material, rendering the electrodes ineffective.
Moreover, exposure to contaminants like oil, grease, or dirt can impair the electrode’s ability to create a clean and strong weld. Thus, proper storage practices are vital to ensuring the reliability and quality of welding electrodes.
Ideal Storage Conditions
To maintain the integrity of welding electrodes, it is crucial to store them in an environment that meets the recommended conditions. The ideal storage conditions for electrodes typically include a dry, clean, and temperature-controlled area.
The storage area should have low humidity to prevent moisture absorption by the electrodes. Ideally, the relative humidity should be kept below 50% to minimize the risk of hydrogen-induced cracking. If the moisture content exceeds the recommended level, the electrodes may require redrying before use, which can be time-consuming and reduce productivity.
Additionally, the storage area should be clean and free from contaminants. It is important to keep electrodes away from substances like oil, grease, or dust, as these can contaminate the coating and ultimately affect the weld quality.
Maintaining a temperature-controlled environment is also crucial. Extreme temperatures can negatively impact the electrode’s performance and shelf life. It is generally recommended to store electrodes at temperatures between 50°F and 120°F (10°C and 49°C) to ensure their stability and prevent any degradation.