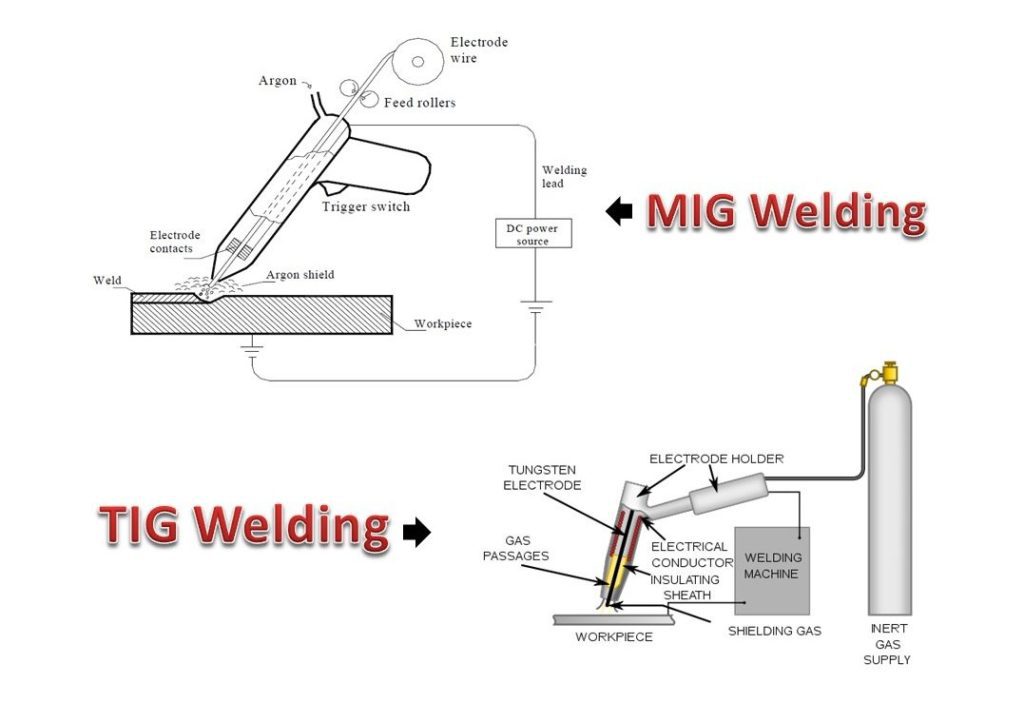
Let us take a closer look at the world of welding, where sparks fly and metal is joined together with precision and skill. In our article today, we explore the fascinating question: What is the difference between MIG and TIG welding? Two popular methods used in the welding industry, MIG and TIG each have their own unique characteristics and purposes. From the way they work to the types of materials they are best suited for, we uncover the distinctions between these two techniques. So, if you’ve ever wondered about the nuances of welding, get ready to dive into the world of MIG and TIG!
What is MIG Welding?
Definition
MIG welding, also known as Metal Inert Gas welding, is a welding process that utilizes a continuous wire electrode to produce the weld. The wire electrode is fed through a welding gun and is melted by an electric arc, creating the weld joint between the base material and the filler material. In MIG welding, an inert gas, such as argon or helium, is used to shield the weld from atmospheric contamination, ensuring a clean and strong weld.
Process
In MIG welding, the wire electrode is continuously fed into the weld pool through a wire feeder. As the wire electrode is fed, an electric arc is created between the wire electrode and the base material, causing the wire to melt and join the metal together. The inert gas shield protects the molten weld pool from reacting with the surrounding air, preventing impurities and defects in the weld.
Equipment
To perform MIG welding, several equipment components are required. These include a power source, a wire feeder, a welding gun, a welding table or workpiece, and a shielding gas cylinder. The power source provides the electrical current necessary to create the welding arc, while the wire feeder feeds the wire electrode at a controlled speed. The welding gun is connected to the wire feeder and is used to guide the wire electrode into the weld joint. Additionally, a shielding gas cylinder, regulator, and flow meter are needed to supply the inert gas for shielding the weld.
Advantages
MIG welding offers several advantages that make it a popular choice in various industries. Firstly, it is a relatively fast welding process, allowing for high productivity and efficiency. Additionally, MIG welding provides good control over the welding parameters, such as current and wire speed, resulting in consistent and high-quality welds. Moreover, MIG welding can be used on a wide range of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Disadvantages
Although MIG welding has numerous advantages, it also has a few drawbacks to consider. One disadvantage is that it requires a shielding gas, which adds to the overall cost and complexity of the welding setup. Additionally, MIG welding may not be suitable for welding in outdoor or windy conditions, as the shielding gas can easily be blown away, affecting the weld quality. Furthermore, MIG welding may not be suitable for welding thin materials, as the high heat input can lead to distortion or burn-through.
This image is property of 3.bp.blogspot.com.
What is TIG Welding?
Definition
TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, is a welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the weld joint. Unlike MIG welding, TIG welding does not require a continuous wire electrode. Instead, a filler wire may be used separately if additional material is needed. TIG welding also utilizes an inert gas, such as argon, to protect the weld pool and ensure a clean weld.
Process
In TIG welding, a non-consumable tungsten electrode is held in a TIG torch, which is connected to a power source. The tungsten electrode creates an electric arc with the base material, melting the base material and creating the weld pool. If necessary, a separate filler wire can be added manually to the weld pool to increase the weld size. The inert gas shield protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, ensuring a high-quality weld.
Equipment
TIG welding requires specific equipment for the welding process. The equipment includes a power source, a TIG torch, a tungsten electrode, a filler wire (if required), and a shielding gas cylinder. The power source provides the electrical current needed to generate the welding arc, while the TIG torch holds the tungsten electrode and delivers the shielding gas. The tungsten electrode is non-consumable and remains constant during the welding process. Additionally, a filler wire may be used for adding additional material to the weld pool.
Advantages
TIG welding offers various advantages that make it suitable for specific applications. One advantage is the high precision and control it provides, allowing for the welding of intricate and critical joints. TIG welding also produces high-quality welds with minimal spatter and distortion. Furthermore, TIG welding can be used on a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. Additionally, the absence of a consumable electrode in TIG welding eliminates the need for post-weld clean-up.
Disadvantages
Despite its advantages, TIG welding does have a few disadvantages. One drawback is that it is a slower welding process compared to MIG welding, resulting in lower productivity for certain applications. Additionally, TIG welding requires a higher skill level due to the need for manual control of the filler wire and tungsten electrode. This can make the learning curve steeper for beginners. Moreover, TIG welding may not be suitable for thick materials or heavy-duty applications, as the process may be time-consuming and costly.
This image is property of www.difference.minaprem.com.
Comparison between MIG and TIG Welding
Process
The key difference between MIG and TIG welding lies in the process. MIG welding utilizes a continuous wire electrode that is fed through a welding gun, while TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. This difference in process affects the ease of use, productivity, and overall weld quality.
Speed and Productivity
In terms of speed and productivity, MIG welding is generally faster than TIG welding. The continuous wire electrode in MIG welding allows for higher deposition rates, resulting in quicker welds. This makes MIG welding more suitable for projects that require high productivity, such as industrial manufacturing or fabrication. On the other hand, TIG welding is a slower process, as it requires manual control of the filler wire and tungsten electrode. This slower speed makes TIG welding ideal for precision welding and applications where weld quality is crucial.
Precision and Control
When it comes to precision and control, TIG welding takes the lead. The manual control of the filler wire and tungsten electrode in TIG welding allows for fine-tuning and precise weld bead placement. This level of control is essential for welding delicate or intricate joints, such as in aerospace or medical applications. In contrast, MIG welding offers less control and precision, as the wire electrode is continuously fed through the welding gun. However, MIG welding is still capable of producing strong and reliable welds for many applications.
Skill Level
In terms of skill level, MIG welding is considered easier to learn and master than TIG welding. The continuous wire electrode in MIG welding simplifies the welding process, making it more beginner-friendly. MIG welding can be mastered relatively quickly, allowing beginners to produce acceptable welds with minimal training. On the other hand, TIG welding requires a higher skill level due to the need for manual control of the filler wire and tungsten electrode. It may take more time and practice to achieve the desired level of skill and precision in TIG welding.
Applications
Both MIG and TIG welding have their own set of applications. MIG welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing, where high productivity and speed are essential. It is suitable for welding thicker materials and large structures. TIG welding, on the other hand, finds its applications in industries that require high precision and quality welds, such as aerospace, nuclear, and food processing. It is commonly used for welding thin materials, intricate joints, and critical components.
This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Which Welding Method Should You Choose?
Considerations
Choosing the right welding method depends on several factors. It is important to consider your budget, skill level, and the specific job requirements before making a decision.
Budget
If budget is a significant consideration, MIG welding may be the more cost-effective option. MIG welding equipment and consumables tend to be less expensive compared to TIG welding. Additionally, MIG welding requires fewer accessories and can be set up quickly, reducing initial costs. However, it is important to factor in the long-term costs, such as the need for shielding gas, when considering the overall budget.
Skill Level
For beginners or individuals with limited welding experience, MIG welding is generally easier to learn and master. The continuous wire electrode and automatic feeding make the process more forgiving and less dependent on manual dexterity. TIG welding, on the other hand, requires a higher skill level and manual control of both the filler wire and tungsten electrode. It may take more time and practice to develop the necessary skills for TIG welding.
Job Specifications
The specific requirements of the welding job also play a crucial role in selecting the welding method. If the job involves thick materials, high productivity, or large-scale welding, MIG welding may be the better choice. MIG welding’s fast deposition rates and suitability for thicker materials make it ideal for such applications. On the other hand, if the job requires precision welding, high-quality welds, or welding of thin materials, TIG welding is the more suitable option. TIG welding’s fine control and limited heat input make it ideal for such applications.
This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
Safety Measures for Welding
Protective Equipment
Safety should always be a top priority when engaging in welding operations. Using appropriate protective equipment is essential to prevent injuries and ensure a safe working environment. Welders should wear protective clothing, including flame-resistant jackets, pants, and gloves, to protect against heat and sparks. Additionally, safety glasses or a welding helmet with a proper shade level should be worn to shield the eyes from harmful UV radiation. Respiratory protection, such as a respirator or respirator mask, may also be necessary to protect against fumes and gases.
Work Environment
Creating a safe work environment is crucial for welding operations. Ensure proper ventilation in the workspace to prevent the accumulation of welding fumes and gases, which can be hazardous to health. Adequate lighting should also be provided to ensure clear visibility of the work area. Clear the workspace of any flammable materials or clutter that may pose a fire hazard. Additionally, ensure that the welding equipment is set up on a stable surface and that all electrical connections are secure.
Fire Safety Precautions
Fire safety is an important aspect of welding operations. Have a fire extinguisher readily available and ensure that it is in working condition. Familiarize yourself with the correct usage of the fire extinguisher and train others in the vicinity. Remove any combustible materials from the immediate vicinity of the welding area. It is also advisable to have a fire-resistant blanket or welding curtain to protect nearby surfaces from sparks and splatter. Regularly inspect the welding equipment for potential fire hazards, such as frayed cables or faulty connections.
This image is property of mechanical-engineering.s3.amazonaws.com.
Conclusion
MIG welding and TIG welding are two widely used welding processes that offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. MIG welding excels in terms of speed, productivity, and ease of use, making it suitable for various industrial applications. TIG welding, on the other hand, provides superior precision, control, and weld quality, making it ideal for critical and intricate welding projects. When choosing between MIG welding and TIG welding, consider factors such as budget, skill level, and job specifications to make an informed decision. Always prioritize safety by wearing appropriate protective equipment, maintaining a safe work environment, and following fire safety precautions. Whether you choose MIG or TIG welding, both methods have their own strengths and can deliver excellent welds when used correctly.