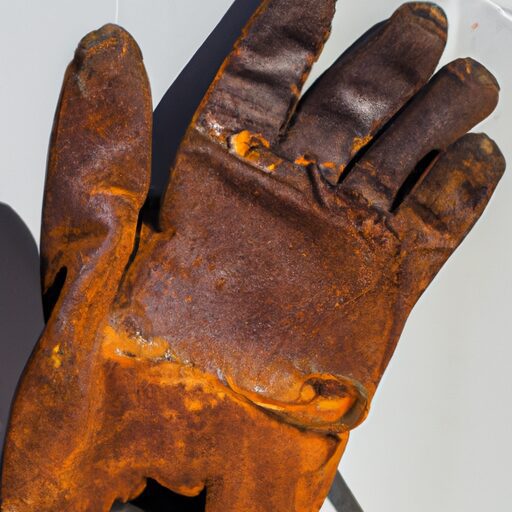
Everyone who has worked with welding tools knows how frustrating it can be to find them covered in rust. Not only does it affect their appearance, but it can also compromise their performance and durability. That’s why we have put together a helpful guide on preventing rust on welding tools. From proper storage techniques to necessary maintenance routines, we will provide you with practical tips to ensure your tools stay rust-free and in excellent working condition. Say goodbye to rusty tools and hello to smooth, efficient welding!
Understanding Rust on Welding Tools
Before diving into the preventive measures, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what rust is and why it occurs on welding tools. Rust, scientifically known as iron oxide, forms when iron or metal alloys come into contact with moisture and oxygen. This chemical reaction weakens the structure of the metal, making it more prone to corrosion and decay over time.
Causes of Rust on Welding Tools
While rust can occur on any metal surface, welding tools are particularly susceptible due to their exposure to heat, moisture, and various environmental factors. The primary causes of rust on welding tools include:
-
Oxidation: The combination of oxygen and metal in the presence of moisture leads to oxidation, which in turn causes rusting.
-
Moisture and Humidity: Welding tools that are not properly dried after use or stored in areas with high humidity can quickly accumulate moisture, creating an ideal environment for rust formation.
-
Exposure to Chemicals: Welding tools can come into contact with various chemicals during the welding process, especially fluxes and cleaning agents. If not cleaned promptly and thoroughly, these chemicals can accelerate rusting.
-
Environmental Factors: Factors such as rain, salt air, acidic environments, and direct sunlight can all contribute to rust formation on welding tools.
Importance of Preventing Rust on Welding Tools
Preventing rust on welding tools is crucial for maintaining their longevity, performance, and overall safety. Rust weakens the structural integrity of the tools, making them more prone to breakage and failure. This can lead to hazardous welding conditions and potentially cause accidents or injuries.
Additionally, rust particles can contaminate the welding process, affecting the quality of welds and compromising their durability. Rust prevention measures not only preserve the tools but also ensure the precision and reliability of the welding work.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to prevent rust formation on welding tools. By following these simple practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your tools:
Regular Cleaning of Welding Tools
After each use, make it a habit to clean your welding tools thoroughly. Use a wire brush or abrasive pad to remove any residue, flux, or spatter. Pay particular attention to hard-to-reach areas and ensure all surfaces are clean and dry.
Proper Storage Conditions
Store your welding tools in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area. Avoid storing them on the ground or in damp places that are prone to moisture and humidity. Use designated tool racks or cabinets to keep them organized, protected, and easily accessible.
Oil or Lubricate
Apply a thin layer of oil or lubricant to the metal surfaces of your welding tools. This helps form a protective barrier against moisture and oxygen. Be sure to wipe off any excess oil to prevent attracting dust or debris.
Keep Tools Dry
After cleaning and before storage, ensure that your welding tools are completely dry. Moisture trapped in crevices or between moving parts can lead to rust formation, so take the time to thoroughly dry the tools using compressed air or a soft cloth.
Avoid Exposure to Moisture and Humidity
When using welding tools outdoors or in high-humidity environments, take extra precautions to protect them from moisture. Consider using moisture-resistant covers or tarps and always dry them thoroughly after each use.
Protective Coatings
Applying protective coatings to welding tools provides an additional layer of defense against rust. Some commonly used protective coatings include:
Anti-Rust Paint
Anti-rust paints are specially formulated to inhibit rust formation on metal surfaces. They contain rust inhibitors that create a barrier, preventing moisture and oxygen from coming into contact with the metal.
Galvanization
Galvanization involves applying a layer of zinc to the surface of the metal. Zinc acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding before the underlying metal. This process effectively protects the metal from rust formation.
Powder Coating
Powder coating involves electrostatically applying a dry powder to the metal surface, which is then cured under heat. This creates a protective and durable finish that resists rust and other forms of corrosion.
Electroplating
Electroplating is the process of depositing a thin layer of metal, such as nickel or chromium, onto the surface of the tools. This not only enhances their appearance but also provides excellent corrosion resistance.
Applying Protective Films
Protective films, such as adhesive-backed plastic or wax coatings, can be applied to welding tools to create a barrier against moisture and humidity. These films are easily removable and offer temporary protection during storage or transportation.
Preventing Rust during Welding
Preventing rust during the welding process requires attention to both the welding consumables and environmental conditions. By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the chances of rust formation:
Use Stainless Steel Welding Consumables
Using stainless steel welding consumables, including electrodes and filler wires, can significantly reduce the risk of rust contamination during the welding process. Stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance properties, making it ideal for welding applications.
Avoid Contamination
Ensure that the welding equipment, including wire feeders, torches, and surfaces, are free from contaminants such as oil, dirt, and rust. Contamination can compromise the quality of the weld and lead to rust formation.
Protective Gases and Fluxes
Using protective gases, such as argon or carbon dioxide, shields the welding area from oxygen, preventing rust formation. Additionally, fluxes can be used to remove impurities and provide a protective layer on the molten metal, further minimizing the risk of rusting.
Weld in Dry Conditions
Whenever possible, choose dry conditions for welding to minimize the presence of moisture. Wet or humid conditions increase the chances of rust formation, especially on freshly welded surfaces.
Maintain Proper Welding Currents
Maintain the correct welding current and voltage settings as specified by the welding procedure. Improper settings can lead to excessive heat, which can contribute to accelerated oxidation and rusting.
Post-Welding Cleaning
After completing the welding process, promptly clean the welded joints and surrounding areas to remove any slag, spatter, or flux residue. Thorough cleaning prevents the accumulation of contaminants that could eventually lead to rust formation.
Regular Inspection and Repair
Regular inspection and immediate repair of welding tools are crucial for rust prevention. By following these practices, you can address any signs of rust or damage before they escalate:
Frequent Tool Inspection
Regularly inspect your welding tools for any signs of rust, wear, or damage. Look for pitting, discoloration, or flaking on the metal surfaces, and check for loose or damaged coatings.
Immediate Repair of Damaged Coatings
If you notice any damaged or deteriorated coatings on your welding tools, repair them promptly. Use appropriate techniques to remove the damaged area, apply a new coating, and ensure proper adhesion.
Replacing Severely Affected Parts
In cases where rust damage is extensive or affects critical components of the welding tools, consider replacing the affected parts entirely. This ensures that the tools remain in optimal condition and ensures the safety of the welding operation.
Avoiding Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in rust formation on welding tools. By taking the following precautions, you can effectively reduce the exposure to these factors:
Avoid Welding in Rain or High Humidity
Welding in wet conditions greatly increases the risk of rust formation. Whenever possible, avoid welding outdoors during rainfall or in areas with high humidity. If working indoors, ensure proper ventilation to control humidity levels.
Protect Tools from Acidic Environments
Acidic environments, such as battery charging or pickling areas, can accelerate rust formation. Keep welding tools away from these areas and properly clean and dry them if accidental exposure occurs.
Shield Tools from Direct Sunlight
Direct sunlight can contribute to rust formation, especially when combined with high temperatures. Store and work with welding tools in shaded areas to minimize exposure to sunlight, and consider using protective covers or shades.
Minimize Exposure to Salt Air
If you work in coastal regions, the presence of salt air can significantly increase the chances of rust formation. Take extra precautions by regularly cleaning and drying your welding tools, and consider applying additional protective coatings.
Protect Against Chemical Exposure
Various chemicals encountered during welding, such as cleaning agents, acids, or fluxes, can accelerate rusting. Always clean and wipe down the tools thoroughly after each use to remove any chemical residues and prevent their corrosive effects.
Proper Handling and Usage
Proper handling and usage of welding tools are vital not only to prevent rust but also to ensure their overall performance and longevity. Follow these guidelines for optimal tool care:
Wear Appropriate Gloves
Protect your welding tools from the corrosive effects of sweat and oils by wearing appropriate gloves while handling them. This prevents direct contact with the metal surfaces and helps maintain the integrity of any protective coatings.
Avoid Dropping or Impacting Tools
Avoid dropping or subjecting your welding tools to unnecessary impacts or shocks. Dropping tools can chip or damage protective coatings, leaving the metal surface vulnerable to rust. Handle tools with care, and store them securely after each use.
Store Tools Properly During and After Use
During breaks in welding or when not in use, store your tools in a designated place, such as a tool chest or cabinet. Avoid leaving tools on the ground or in damp areas, as this can lead to moisture accumulation and rust formation.
Use Tools for their Intended Purposes
Each welding tool has a specific purpose and usage. Avoid using tools for tasks they were not designed for, as this can lead to damage or accelerated wear, making them more prone to rusting.
Avoid Excessive Heat or Cold
Extreme temperatures, whether excessive heat or cold, can affect the durability and performance of welding tools. Avoid exposing your tools to extreme temperature conditions, as this can lead to warping, cracking, or accelerated rust formation.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Creating and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule is essential to ensure the continued performance and longevity of welding tools. Follow these steps to implement an effective maintenance plan:
Create a Maintenance Plan
Develop a maintenance plan that outlines the cleaning, inspection, and repair procedures for your welding tools. Determine how often each task should be performed, taking into consideration usage frequency and environmental factors.
Implement Routine Inspections and Cleaning
Follow a routine inspection schedule to regularly assess the condition of your welding tools. This should involve visual inspections, cleaning, and lubrication where necessary. Regular maintenance prevents rust formation and identifies any issues early on.
Keep Records of Maintenance
Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities performed on your welding tools. This includes the dates of inspections, cleaning, repairs, and any replacement parts used. These records serve as a valuable reference for future maintenance and help track tool lifespan.
Schedule Professional Servicing
Alongside regular maintenance, consider scheduling professional servicing for your welding tools. Professional technicians can provide specialized cleaning, repair, and calibration services that extend the life and performance of your equipment.
Rust Removal Techniques
Despite taking preventive measures, rust may still occur on welding tools over time. In such cases, it’s important to promptly address the issue and remove rust using appropriate techniques:
Wire Brushing
Mechanically remove rust using a wire brush or abrasive pad. This technique is effective for surface rust or light corrosion. Be sure to clean and dry the tool thoroughly after wire brushing to prevent any residual rust from reoccurring.
Chemical Rust Removers
Chemical rust removers, such as phosphoric acid-based solutions, can dissolve rust and convert it into a protective coating. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using these products, and be cautious as they can be corrosive to the skin.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis involves using an electrolyte solution and a direct current to remove rust from metal surfaces. This method is particularly effective for heavily rusted or intricate parts, but it requires careful handling and adequate safety precautions.
Sanding and Polishing
For more stubborn rust or pitting, sanding the affected areas with sandpaper or a sanding disc can help remove the rust. Follow up with polishing to restore the surface to its original shine and apply a protective coating as necessary.
Use of Rust Converters
Rust converters contain chemicals that react with rust, converting it into a more stable compound. These products are typically brushed or sprayed onto the rusted surface and form a protective layer. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and drying time.
Educating and Training Welders
Lastly, educating and training welders on rust prevention practices is essential for maintaining a rust-free environment and prolonging the lifespan of welding tools. Consider the following steps to promote awareness:
Providing Rust Prevention Training
Ensure that welders are educated on the causes of rust and the importance of preventive measures. Offer training sessions or workshops to familiarize them with proper cleaning, maintenance, and storage practices specific to welding tools.
Familiarize with Proper Handling and Care
Highlight the significance of proper handling and care of welding tools during training sessions. Emphasize the use of appropriate gloves, avoiding impacts, and proper storage techniques to prevent rust formation.
Emphasize on Maintenance Practices
Incorporate regular maintenance practices, such as cleaning, inspection, and recording, into the training curriculum. Stress the importance of following a maintenance plan and the benefits it brings in terms of tool longevity and consistent welding performance.
In conclusion, preventing rust on welding tools is crucial for maintaining their performance, safety, and durability. By understanding the causes of rust, implementing regular cleaning and maintenance practices, applying protective coatings, following preventive measures during welding, and adhering to proper handling and usage guidelines, welders can ensure their tools remain rust-free and in optimal condition. Regular inspection, immediate repair, and avoidance of environmental factors that contribute to rust formation further contribute to the longevity of welding tools. Lastly, proper rust removal techniques, educating welders on rust prevention, and promoting maintenance practices create a comprehensive approach to tackle rust and ensure the consistency and quality of welding work.