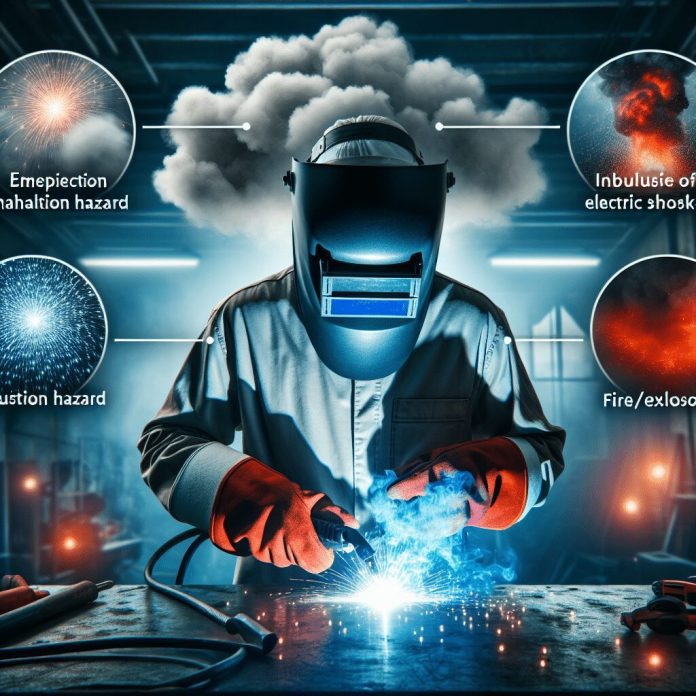
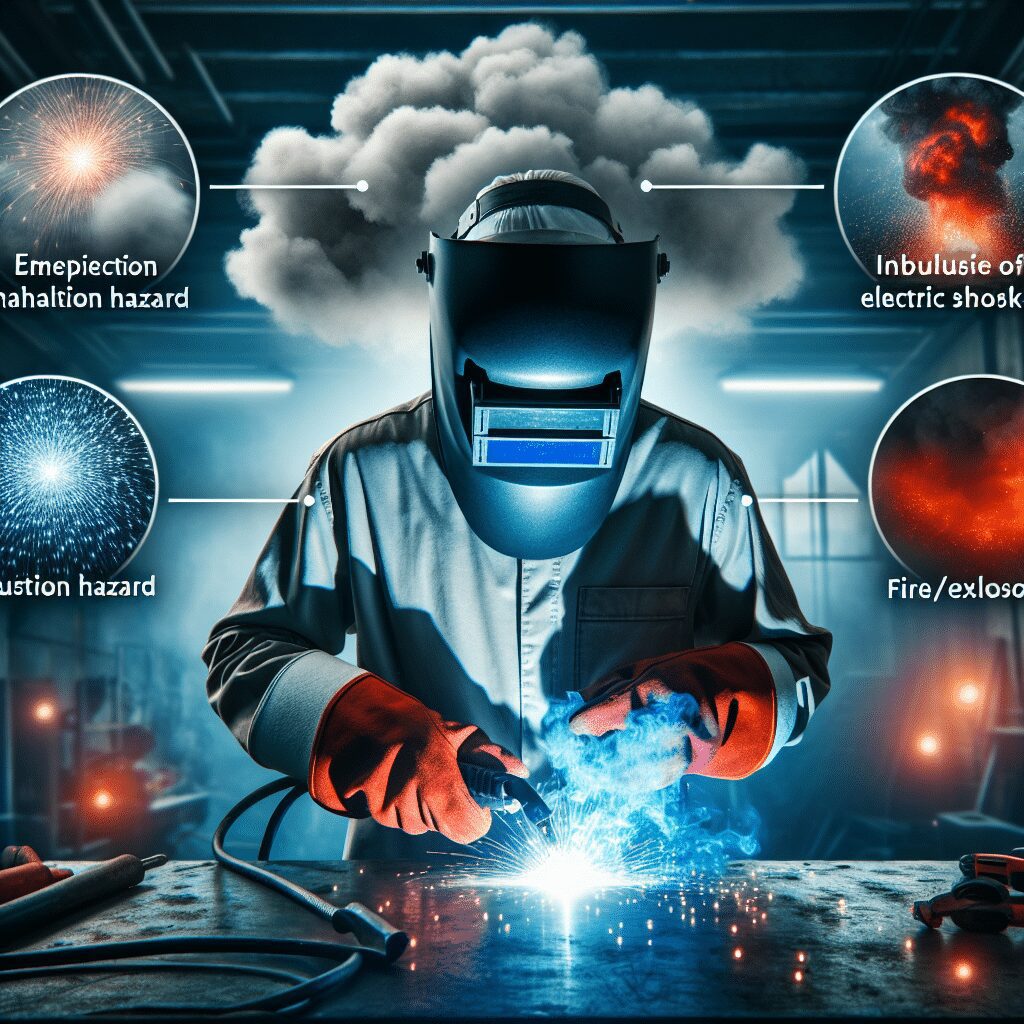
Welding is an essential technique used in various industries, but have you ever wondered what health and safety risks come with this process? From the potential exposure to harmful fumes and gases, to the risk of burns and eye injuries, welding presents a range of hazards that need to be understood and managed. In this article, we will explore the importance of prioritizing health and safety measures in welding and delve into the various risks that welders face on a daily basis. So, let’s put on our safety gear and embark on this informative journey together! Welding is a common and important process in many industries, but it also poses several health and safety risks that need to be taken seriously. In this article, we will explore the various health risks associated with welding, as well as the safety risks involved in this profession. We will also discuss some preventive measures that can be taken to mitigate these risks and ensure a safe working environment.
Health Risks of Welding
1.1 Eye Injuries
One of the most significant health risks of welding is eye injuries. The intense arc created during the welding process emits powerful ultraviolet and infrared rays that can damage the eyes. This can lead to a condition called arc eye, which is similar to severe sunburn of the eyes. Symptoms of arc eye include redness, pain, tearing, and sensitivity to light. Prolonged exposure to such rays can also cause long-term damage to the eyes, including cataracts or even permanent blindness.
To protect your eyes while welding, it is crucial to wear appropriate eye protection, such as welding helmets or goggles with shaded lenses. These protective devices block harmful radiation and prevent debris or sparks from entering your eyes.
1.2 Respiratory Issues
Another significant health risk in welding is respiratory issues. The fumes and gases released during the welding process can contain toxic substances, such as zinc, lead, chromium, and cadmium. Inhaling these harmful substances regularly can lead to various respiratory problems, including bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia, and even lung cancer.
To minimize the risk of respiratory issues, welders should always work in well-ventilated areas. Ventilation systems, such as fans or exhaust systems, can help remove the fumes and gases from the workspace. Additionally, wearing respiratory protection, such as a properly fitted respirator, can further reduce the inhalation of hazardous substances.
1.3 Skin Disorders
Welding can also pose risks to the skin. The intense heat and sparks produced during the welding process can cause burns, skin irritation, and other skin disorders. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the arc can also lead to sunburn-like symptoms and increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
To protect your skin during welding, it is crucial to wear appropriate protective clothing, such as flame-resistant gloves, long-sleeved shirts, and pants. Additionally, regularly applying a high SPF sunscreen and working in shaded areas can minimize the risk of skin damage caused by ultraviolet radiation.
1.4 Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Exposure to excessive noise is another health risk that welders face. The noise generated by the welding process, especially when using high-powered equipment, can exceed safe levels and cause irreversible damage to the ears. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can result in noise-induced hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and other hearing disorders.
To protect your hearing, always wear appropriate hearing protection, such as earmuffs or earplugs, while welding. Limiting the exposure time to high noise levels and taking regular breaks in quieter areas can also help reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss.
1.5 Electromagnetic Radiation Exposure
In addition to the risks mentioned above, welding also exposes workers to electromagnetic radiation. This radiation, emitted by the welding arc, can penetrate the body and potentially cause harm. Although the long-term effects of electromagnetic radiation exposure in welding are still uncertain, precautionary measures should be taken to minimize the risk.
To reduce electromagnetic radiation exposure, welders should stand as far away from the welding arc as possible without compromising the quality of their work. Ensuring that the work area is properly shielded and using welding curtains or screens can also provide additional protection.
Safety Risks of Welding
2.1 Burns and Fires
Welding involves working with highly heated metal and sparks, making burns and fires a significant safety risk. Accidental contact with hot metal, sparks, or direct exposure to flames can cause severe burns. Additionally, sparks or stray heat can ignite flammable materials in the surrounding area, leading to fires or explosions.
To prevent burns and fires, it is essential to follow proper welding procedures and maintain good housekeeping practices in the workspace. This includes removing flammable materials and ensuring that fire extinguishers are readily accessible. Wearing flame-resistant clothing and using appropriate welding tools and accessories can also minimize the risk of burns and fires.
2.2 Electrical Hazards
Welding requires the use of electrical equipment, which introduces the risk of electrical hazards. Contact with live electrical components or faulty equipment can result in electric shocks or electrocution. The high currents used in welding can be particularly dangerous and potentially fatal.
To reduce the risk of electrical hazards, it is vital to ensure that all welding equipment is properly grounded and regularly inspected for faults or damage. Following safe work practices, such as not touching the electrode or workpiece with bare hands and using insulated gloves, can also prevent electrical accidents.
2.3 Falling Objects
Welding often involves working at heights or in elevated positions, which increases the risk of falling objects. Tools, equipment, or even debris can accidentally fall from above and cause injuries or accidents. Being struck by falling objects can lead to severe head injuries, fractures, or other bodily harm.
To prevent falling objects, it is crucial to secure all tools and equipment properly when working at heights. Setting up barricades or safety nets can also provide additional protection. Additionally, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as helmets, safety glasses, and steel-toe boots, can reduce the risk of injuries caused by falling objects.
2.4 Welding Fumes and Gases
The fumes and gases generated during welding not only pose health risks but also safety risks. Certain welding processes produce flammable gases, such as hydrogen or acetylene, which can ignite if not properly controlled. High concentrations of welding fumes can also create an oxygen-deficient atmosphere, increasing the risk of suffocation.
To mitigate the safety risks associated with welding fumes and gases, it is crucial to work in well-ventilated areas or use local exhaust ventilation systems. Proper monitoring of flammable gas concentrations and ensuring the availability of adequate oxygen levels in the working environment is also essential. Regular maintenance and inspection of welding equipment can further prevent leaks or malfunctions that may lead to hazardous gas buildup.
2.5 Noise Hazards
As mentioned earlier, excessive noise levels during welding can not only impact health but also pose safety risks. The loud noise generated by welding can distract workers, impair communication, and compromise their situational awareness. This can increase the likelihood of accidents or other safety hazards.
To address noise hazards, it is important to implement effective hearing conservation programs in the workplace. This includes providing appropriate hearing protection to all workers exposed to high noise levels and conducting regular hearing tests to monitor any changes in their hearing health. Creating designated quiet areas for breaks or discussions can also help reduce noise-related safety risks.
Prevention of Health and Safety Risks
3.1 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
One of the most effective ways to prevent health and safety risks in welding is by using personal protective equipment (PPE). PPE includes items such as welding helmets, goggles, gloves, aprons, and respirators. By wearing the appropriate PPE, welders can protect themselves from the hazards associated with welding.
It is important to select PPE that is specifically designed for welding and meets the necessary safety standards. Regular inspection and replacement of damaged or worn-out PPE is also crucial to ensure its effectiveness. Proper training and education on the correct use and maintenance of PPE should be provided to all workers.
3.2 Ventilation and Extraction Systems
Ensuring adequate ventilation and extraction systems in the workplace is another important preventive measure. These systems help remove welding fumes, gases, and other airborne contaminants, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and maintaining a safe working environment.
Regular inspection and maintenance of ventilation and extraction systems are essential to ensure their effectiveness. Proper placement of exhaust hoods or localized extraction systems can help capture and remove contaminants effectively. Adequate airflow and the use of air purifiers or filters can further enhance the efficiency of these systems.
3.3 Training and Education
Proper training and education are crucial for the prevention of health and safety risks in welding. Workers should receive comprehensive training on safe welding practices, hazard identification, emergency procedures, and the proper use of equipment and protective gear.
Regular educational sessions and refresher courses should be conducted to keep workers updated on the latest safety protocols and techniques. Creating a culture of awareness and accountability through training programs can help foster a safe working environment.
3.4 Proper Equipment Maintenance
Regular maintenance and inspection of welding equipment are essential to ensure its safe and efficient operation. Faulty or damaged equipment can increase the risk of accidents, fires, or other hazards. Scheduled maintenance checks, including electrical grounding testing and gas leak detection, can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
It is also important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for equipment maintenance and ensure that only qualified personnel handle repairs or modifications. Regular calibration of welding machines can further enhance their performance and safety.
3.5 Regular Health Check-ups
Lastly, regular health check-ups are crucial for the early detection and prevention of any health issues related to welding. These check-ups should include examinations of the eyes, respiratory system, skin, and hearing. Early detection of any abnormalities or changes can lead to timely interventions and prevent further complications.
Employers should provide access to regular health assessments and encourage workers to undergo these check-ups. Creating awareness about the importance of health surveillance and offering appropriate medical support and guidance can go a long way in promoting the overall well-being of welders.
In conclusion, welding comes with its fair share of health and safety risks. By understanding these risks, implementing preventive measures, and prioritizing safety in the workplace, we can ensure a healthier and safer environment for all welders. Remember, your health and well-being should always be a top priority, so take the necessary precautions and protect yourself from the potential hazards of welding.