In the world of welding, there’s a wide range of pay scales depending on several factors, such as experience, location, and specialization.
However, have you ever wondered who the lowest-paid welder is?
This article aims to explore the answer to that question, shedding light on the challenges faced by these individuals and offering insights into the industry as a whole.
So, let’s embark on a journey to discover the reality of the lowest-paid welder.
Factors Affecting Welder Salaries
When determining a welder’s salary, several factors come into play. Your level of experience, the location where you work, the type of industry you are in, your education and certification, and your union membership all contribute to how much you can earn in this profession. Let’s explore each of these factors in more detail.
Level of Experience
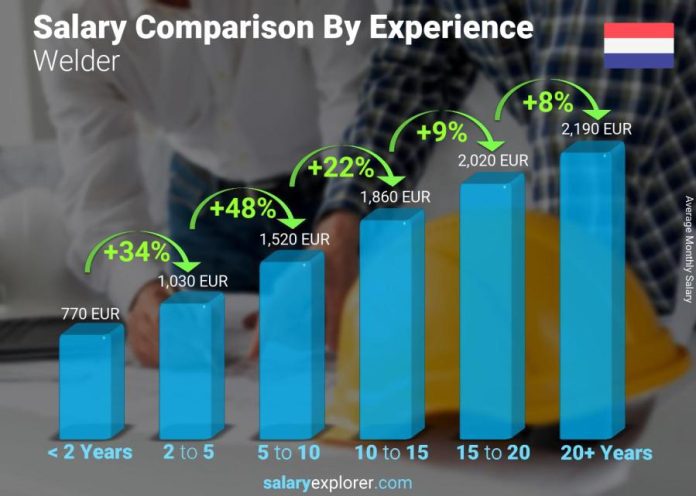
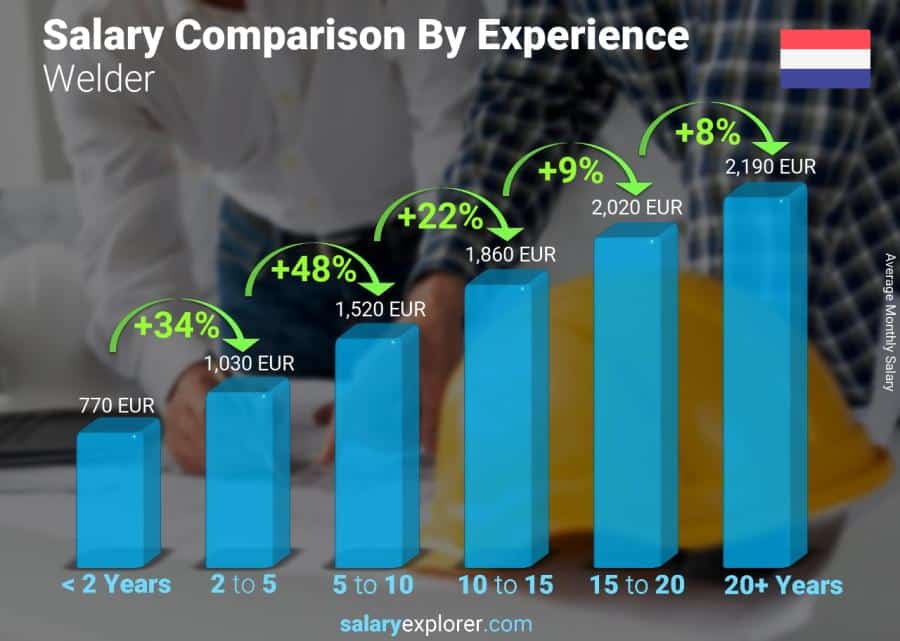
One of the main factors determining a welder’s salary is their experience level. As with any profession, the more experience you have, the higher your earning potential.
Entry-level welders typically earn less than those with several years of experience. As you gain more knowledge and skills through on-the-job training and years of practice, your value as a welder increases, and so does your salary.
Location
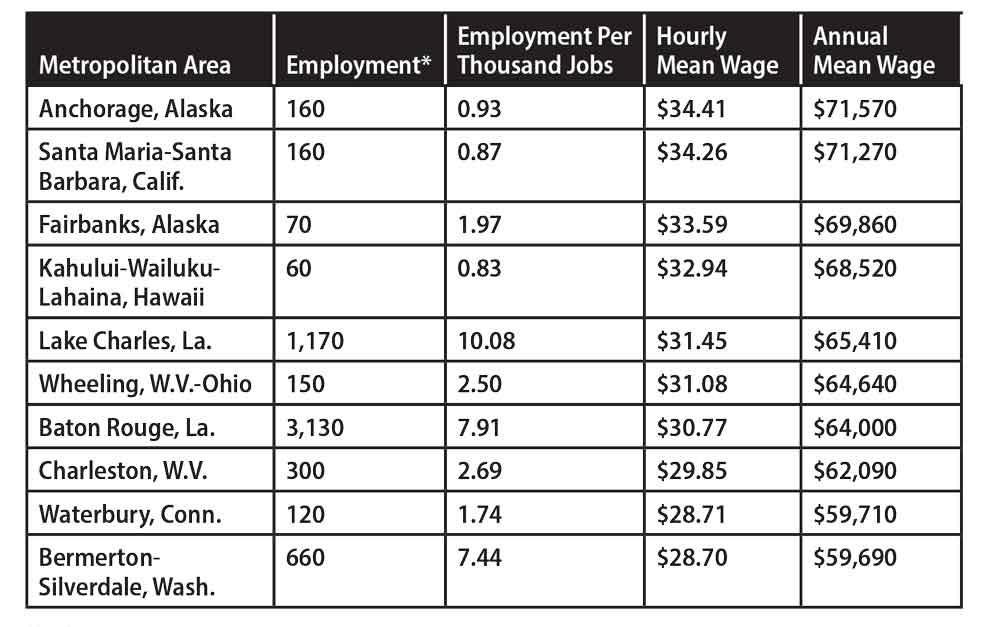
Another significant factor that affects welder salaries is the location where you work. The demand for welders can vary significantly depending on your region or state. Welders working in highly populated areas with a solid industrial presence often have more opportunities and higher salaries than those in less populated or rural areas.
Additionally, the cost of living in different locations can also impact the wage rates for welders. Researching and considering the average salary and cost of living in a particular area is essential before pursuing a welding career there.
Type of Industry
The industry in which a welder works can also greatly influence their salaries. Various industries require welding services; some may offer higher salaries than others.
It’s essential to consider the specific demands and requirements of the industry you are interested in. Some industries, such as construction, manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and oil and gas, are known to have a high demand for skilled welders, resulting in potentially higher salaries.
Education and Certification
Education and certification also play a vital role in determining a welder’s salary. While a high school diploma is usually the minimum requirement to become a welder, further education and specialized certifications can significantly increase earning potential.
Pursuing post-secondary education, such as a welding certificate or degree program, can provide you with more advanced skills and knowledge, making you more attractive to employers. Additionally, obtaining industry-recognized certifications, such as those offered by the American Welding Society (AWS), can demonstrate your expertise and result in higher-paying job opportunities.
Union Membership
Being a member of a union can have a significant impact on a welder’s salary. Unions negotiate collective bargaining agreements on behalf of their members, which can include provisions for higher wages, better benefits, and improved working conditions.
Unionized welders often enjoy more job security and access to training programs that can enhance their skills and earning potential. However, it’s important to note that not all welders are part of a union, and the decision to join one should be based on personal preferences and circumstances.
Government and Private Sector Welding Jobs
Welding jobs can be found in both the government and private sectors. Let’s explore the opportunities available in each sector.
Federal Government Jobs
The federal government provides numerous welding job opportunities, primarily through agencies such as the Department of Defense (DOD), the Department of Transportation (DOT), and the Department of Energy (DOE).
These agencies require welding services for various purposes, including infrastructure maintenance, aircraft and vehicle manufacturing and maintenance, and energy-related projects. Welders working for the federal government often receive competitive salaries, ample benefits, and opportunities for career advancement.
State and Local Government Jobs
State and local governments offer welding job opportunities, especially in infrastructure development, public transportation, and utility maintenance.
These jobs may involve working on projects such as bridges, highways, public buildings, and water treatment facilities. Welders employed by state and local governments typically benefit from stable employment, reasonable salaries, and access to government employee benefits.
Private Sector Jobs
The private sector provides various welding job opportunities across various industries. Construction companies, manufacturing firms, agricultural companies, transportation companies, and oil and gas companies are just a few examples of private sector employers.
Welders in the private sector often have the chance to work on diverse projects and gain experience in different industries. Salaries can vary greatly depending on the specific company and industry, but private sector jobs often offer competitive pay and opportunities for career growth.
Welders in Different Industries
Now, let’s delve into the specific roles and opportunities for welders in different industries.
Construction Industry
In the construction industry, welders are crucial in joining metal components for structures such as buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects. Within the construction industry, there are several roles where welders are in high demand.
Structural Iron and Steel Workers
Structural iron and steel workers work with steel beams, columns, and other structural components. They often collaborate closely with welders to ensure these components’ secure and proper joining. Welders working as structural iron and steel workers in the construction industry can earn competitive salaries due to the nature of their work and the need for specialized skills.
Pipefitters and Steamfitters
Pipefitters and steamfitters also rely on welding skills to install and repair piping systems in various structures. Welders in this role work with different types of piping material, including steel, copper, and plastic.
They must be proficient in various welding techniques to ensure the integrity of the pipelines. Welders in pipefitting and steamfitting positions often earn higher salaries due to the specialized skills required.
Plumbers, Pipefitters, and Steamfitters
Welders specializing in plumbing, pipefitting, and steamfitting work alongside other professionals to install and repair plumbing systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
They utilize welding techniques to join pipes and ensure leak-free connections. Welders in these roles can benefit from stable employment and potential salary growth as they gain experience.
Electricians
Electricians may also need welding skills for specific tasks in the construction industry. Electricians often work with conduit systems and structural supports, which may require welding for proper installation.
While welding is not the primary focus of their role, electricians with welding skills may have an advantage in the job market and potentially earn higher salaries.
Manufacturing Industry
Welders in the manufacturing industry contribute to fabricating and assembling various products, machinery, and equipment. This industry offers diverse opportunities for welders.
Motor Vehicle Manufacturing
Motor vehicle manufacturers require welders to assemble car frames, chassis components, and other metal parts used in the manufacturing process. Welders with expertise in automotive welding techniques and materials can find rewarding careers in motor vehicle manufacturing.
Aerospace Product and Parts Manufacturing
The aerospace industry relies on welders for the fabrication and assembly of aircraft components, including wings, fuselages, and engine parts.
Aerospace manufacturing welders must meet stringent quality standards and possess advanced welding skills. The specialized nature of this industry can result in higher salaries for skilled welders.
Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing
Welders in fabricated metal product manufacturing work on various products, including structural steel, metal tanks, sheet metal components, and custom-made metal products. This sector provides opportunities for welders to apply their skills to various projects, potentially expanding their knowledge and expertise.
Machinery Manufacturing
Welders working in machinery manufacturing play a vital role in producing industrial machinery, such as heavy equipment, agricultural machinery, and machine tools.
These welders must possess strong fabrication skills and be proficient in welding techniques commonly used in machinery assembly. Welders in this industry can benefit from stable employment and potential career advancement opportunities.
Agriculture and Forestry
Welders in the agriculture and forestry industries contribute to fabricating and maintaining equipment used in farming, logging, and related activities.
Farm Equipment and Machinery Manufacturing
Farm equipment manufacturers require welders to fabricate and assemble components used in tractors, combines, and other agricultural machinery. Welders specializing in agricultural equipment manufacturing often have opportunities for stable employment and potentially higher salaries due to the specific skills required.
Agricultural Services
In agricultural services, welders may work directly for farms or agribusinesses, providing maintenance and repair services for farming equipment, irrigation systems, and storage facilities. These welders must possess a broad range of welding skills to handle diverse tasks, making their services valuable to the industry.
Logging and Forestry
Welders in the logging and forestry industry play a role in maintaining and repairing equipment used in timber harvesting and processing.
They may be responsible for welding and repairing machinery such as skidders, loaders, and sawmill equipment. Welders working in logging and forestry can benefit from stable employment and potentially higher wages due to the specialized nature of their work.
Transportation and Warehousing
The transportation and warehousing industry relies on welders to maintain and repair various types of vehicles, containers, and infrastructure.
Truck Transportation
Welders working in truck transportation may be employed by trucking companies or repair shops to ensure the proper functioning of trucks and trailers.
They may be responsible for welding repairs on frames, bodies, and other components and fabricating custom parts. Truck transportation welders often benefit from stable employment and opportunities for career growth.
Rail Transportation
The rail transportation industry requires welders to fabricate and maintain railway tracks, infrastructure, and rolling stock. These welders may be involved in welding rails, joining track components, and repairing locomotives and railcars.
Welders in rail transportation often face specific challenges, such as working in outdoor environments and adhering to strict safety standards. Due to their work’s specialized nature, rail transportation welders can earn competitive wages.
Water Transportation
The water transportation industry, including shipbuilding and ship repair, requires skilled welders. This industry’s welding may involve steel hull fabrication, structural welding, and repairing marine vessels. The maritime industry often offers competitive salaries and opportunities for travel and work in diverse locations.
Air Transportation
Welders in the air transportation industry contribute to aircraft fabrication, assembly, and repair. They may work for aircraft manufacturers, maintenance and repair organizations, or in specialized aviation welding facilities. Due to the aviation industry’s stringent safety requirements and high-quality standards, welders in this sector can often expect higher salaries and potential growth opportunities.
Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry presents opportunities for extraction and pipeline construction welders.
Oil and Gas Extraction
Welders in oil and gas extraction may work on offshore platforms or onshore facilities, contributing to the fabrication, maintenance, and repair of drilling equipment, pipelines, and storage tanks. The specialized skills and potentially hazardous environments in this industry can result in higher salaries for welders.
Oil and Gas Pipeline Construction
Welders involved in oil and gas pipeline construction play a crucial role in the installation and welding of pipelines used for transporting oil and gas over long distances.
These welders ensure the integrity and safety of the pipeline systems, often facing challenging working conditions and adhering to stringent quality standards. Welders in oil and gas pipeline construction can benefit from competitive salaries and potential travel opportunities.
Other Factors Affecting Welder Salaries
In addition to the abovementioned factors, several other factors can affect a welder’s salary.
Company Size
The size of the company you work for can impact your salary. Larger companies, especially those with significant financial resources and higher market share, often offer higher salaries for welders than smaller businesses.
This is due to various factors, such as the demand for skilled welders, the scale of projects, and the financial capacity to invest in employee compensation.
Employment Status
Whether you are employed as a full-time, part-time, or contract welder can affect your salary. Full-time employees generally receive more comprehensive benefits packages and job security than part-time or contract workers. However, contract welders may be more flexible and potentially earn higher hourly rates or project-based fees.
Non-Monetary Compensation
Some employers may offer non-monetary compensation in addition to salary. This can include benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and bonuses.
The value of these non-monetary benefits can significantly impact the overall compensation package and the attractiveness of a welding job.
Benefits and Vacation
Benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and vacation time can play a significant role in a welder’s overall compensation package.
Employers who offer comprehensive benefits and generous vacation policies can enhance the attractiveness of a welding job, even if the base salary is slightly lower than that offered by other employers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, several factors influence a welder’s salary.
Factors such as level of experience, location, type of industry, education and certification, union membership, company size, employment status, and non-monetary compensation all play a role in determining how much a welder can earn.
It is essential to consider these factors when choosing a welding career path and seeking career advancement opportunities.
By understanding the various factors that affect welder salaries, you can make informed decisions about your education, training, and job choices, ultimately maximizing your earning potential in this fulfilling and essential profession.