In the world of Welding, it’s essential to prioritize safety to avoid potential harm. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting, knowing how to prevent burns is crucial.
This article explores tips and techniques to protect you while working with hot metals and intense heat.
From the proper protective gear to practicing safe handling, you’ll discover practical ways to minimize the risk of burns and ensure a successful welding experience.
So, let’s dive in and learn how to stay burn-free while welding!
Wearing Protective Clothing
Wear a Welding Helmet
When it comes to preventing burns while Welding, wearing a welding helmet is of utmost importance. A welding helmet protects your face, neck, and eyes from sparks, radiation, and heat generated during Welding.
Choose a helmet that meets safety standards and provides adequate coverage. Additionally, consider opting for a helmet with an auto-darkening feature, which adjusts the lens shade according to the welding arc’s intensity, providing better visibility and reducing eye strain.
Use Proper Eye and Face Protection
In addition to a welding helmet, it is crucial to use proper eye and face protection. Welding activities expose your eyes and face to harmful arc radiation and sparks.
Therefore, wearing safety glasses or goggles with side shields will provide additional protection. These safety glasses should have a shade that suits the welding process. Moreover, wearing a face shield with safety glasses will offer complete eye and face protection.
Wear Fire-resistant Clothing
Wearing fire-resistant clothing is essential to protect yourself from potential burns. Welding involves intense heat, flying sparks, and molten metal, which can cause severe injuries if they come into contact with your clothing.
Opt for flame-resistant clothing made of cotton, leather, or wool. Avoid wearing synthetic fabrics as they melt when exposed to high temperatures. It is also recommended to wear long sleeves, pants, and closed-toe shoes to minimize skin exposure.
Wear Welding Gloves
To safeguard your hands from burns, welding gloves are a must. Welding gloves are designed to withstand the high temperatures and sparks associated with Welding.
They are typically made of leather and provide ample dexterity and heat resistance. Ensure that the gloves fit properly and cover your hands and wrists completely. Remember, hands are particularly vulnerable to burns, so investing in a good pair of welding gloves is crucial for your safety.
Use Protective Footwear
Protective footwear plays a significant role in preventing foot injuries and burns while welding. Sparks, welding slag, and heavy objects can potentially cause harm to your feet, so it is essential to wear steel-toe boots or shoes.
These protect your toes from falling objects, while the sturdy construction and heat-resistant materials shield your feet from sparks and molten metal. Having slip-resistant soles on your footwear also ensures stability and reduces the risk of falls in the work area.
Taking Precautions in the Workplace
Maintain a Clean and Organized Workspace
To minimize accidents and potential burn hazards, it is essential to maintain a clean and organized workspace. Cluttered work areas increase the risk of tripping, falling, and inadvertently coming into contact with hot or sharp objects.
Regularly clean up debris, remove flammable materials, and clear pathways to ensure easy movement around the workspace. This will help prevent accidents and make it easier to identify potential hazards and maintain a safe working environment.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial for welding safety. Welding generates various hazardous fumes, gases, and smoke that can be harmful if inhaled. Ensure your workspace has good ventilation to minimize exposure to these harmful substances.
If working indoors, consider using mechanical ventilation systems, such as fans or exhaust systems, to remove fumes and maintain air quality effectively. Outdoors or in open areas can also help disperse potentially harmful fumes.
Use Fire-resistant Materials
Using fire-resistant materials in your welding workspace is essential to prevent fire spread and minimize burn risks. Fire-resistant materials, such as welding blankets, barriers, or fire-resistant curtains, are designed to withstand the high temperatures and sparks associated with Welding.
These materials provide a protective barrier between the welding operation and surrounding flammable objects, reducing the risk of fires. Additionally, always have fire extinguishers readily available in case of emergencies.
Keep Flammable Materials Away
Keep flammable materials away from the welding area to maintain a safe working environment. Sparks and high temperatures can ignite nearby flammable substances, leading to fires or explosions.
Clear the area of substances like solvents, oils, greases, or other flammable liquids. Store them in designated areas away from the welding workspace. Keeping flammable materials at a safe distance significantly reduces the risk of burns and other workplace accidents.
Use Welding Screens or Curtains
Using welding screens or curtains is an effective way to protect yourself and others in the vicinity from harmful sparks and radiation. These screens act as a barrier, minimizing the spread of sparks and containing the welding process.
You can effectively create designated welding zones by setting up appropriate welding screens or curtains, keeping the surrounding area safe. These screens are typically durable and fire-resistant, ensuring reliable protection and additional safety.
Using Safety Equipment
Use Welding Curtains or Shields
Welding curtains or shields are essential safety equipment that helps protect against stray sparks, molten metal, and radiant heat. These portable safety devices create a barrier between the welding area and the surrounding workspace, reducing the risk of burns and fires.
Welding curtains are flame-resistant and provide a transparent view of the work area while keeping others safe. Shields can cover specific objects or areas that need protection from the welding process.
Utilize Welding Blankets or Pads
Welding blankets or pads are crucial safety tools that protect nearby objects or surfaces from sparks, heat, and molten metal. These fire-resistant blankets are placed over the objects or surfaces that need shielding, preventing damage or potential fires.
Welding pads, on the other hand, provide a cushioned surface for resting hot welding equipment or tools. By efficiently using welding blankets or pads, you can minimize the risk of burns and ensure the safety of your work environment.
Have a Fire Extinguisher Nearby
A fire extinguisher within reach is vital for any welding workspace. Welding involves high temperatures, sparks, and potential fire hazards, so preparing for emergencies is crucial.
Make sure that the fire extinguisher is easily accessible and that everyone in the workspace knows its location. Regularly inspect and maintain the fire extinguisher to ensure its functionality. Familiarize yourself with the proper use of the fire extinguisher and educate others, enabling quick and effective response in case of a fire.
Use a Welding Fume Extractor
Welding fume extractors are essential for removing hazardous fumes and particles generated during Welding. Inhaling these fumes can cause serious health issues like respiratory problems and long-term lung damage.
A fume extractor helps to capture and filter out these harmful contaminants, improving air quality and maintaining a safe working environment. When selecting a fume extractor, consider the size of your workspace and the type of Welding being performed to ensure optimal effectiveness.
Keep a First Aid Kit Ready
Accidents can happen despite taking all necessary precautions. That’s why you must always have a well-stocked first aid kit in your welding workspace. A proper first aid kit should include burn dressings, sterile bandages, antiseptic solutions, adhesive tapes, scissors, and gloves.
Familiarize yourself with the first aid kit’s contents and know how to administer basic first aid, such as treating minor burns and cuts. Prompt and appropriate first aid can make a significant difference in the outcome of an injury.
Working with Proper Technique
Follow Welding Safety Procedures
Following welding safety procedures is critical to prevent burns and ensure a safe working environment. Before starting any welding task, familiarize yourself with the safety procedures outlined by your employer or welding standards.
These may include wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, conducting pre-weld inspections, properly grounding workpieces, and using safe welding techniques. Adhering to these procedures significantly reduces the risk of burns and promotes overall workplace safety.
Opt for Spot Welding Instead of Continuous Welding
Opting for spot welding instead of continuous Welding can help minimize the potential for burns. Spot welding involves joining metal pieces by creating a series of small welds rather than one continuous weld.
This technique reduces the overall heat exposure and the likelihood of overheating the surrounding areas. By strategically planning and executing spot welding, you can control the heat distribution and minimize the burn risk, ensuring the weld joint’s integrity.
Avoid Welding on Wet or Damp Surfaces
Welding on wet surfaces can be extremely dangerous and should be avoided. When water comes into contact with hot welding surfaces, it can instantly vaporize and expand, causing an explosion.
Additionally, welding on wet surfaces can produce steam, which may lead to severe burns. It is essential to ensure that the work area is dry and moisture-free before starting any welding activity. Always inspect the surfaces and surrounding areas to guarantee a safe working environment.
Use Correct Welding Settings
Using the correct welding settings plays a crucial role in preventing burns and ensuring the quality of your welds. Improper settings can lead to excessive heat, increased sparks, and an increased risk of burns.
Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and welding standards to determine the appropriate settings for the specific welding process and materials. Maintaining proper arc length, electrode angle, and travel speed is essential for optimal weld quality and safety.
Take Breaks to Reduce Fatigue
Fatigue can negatively impact your focus, coordination, and overall safety while Welding. Regular breaks allow you to rest and recharge, reducing the likelihood of making mistakes or being inattentive.
Working for extended periods without breaks can increase the risk of accidents and burn injuries. Listen to your body and take breaks as needed. Stay hydrated, stretch, and relax during your breaks to minimize fatigue and maintain your focus during welding tasks.
Maintaining Equipment and Tools
Regularly Inspect and Maintain Welding Equipment
Regular inspection and maintenance of your welding equipment ensures safe and efficient operation. Inspect the welding machine, cables, hoses, and other components regularly for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
Promptly address any issues by repairing or replacing the damaged parts. Clean and lubricate the welding machine and its components as the manufacturer recommends. Maintaining your equipment properly reduces the risk of malfunctions, electrical hazards, and potential burns.
Keep Your Tools in Good Condition
In addition to the welding equipment, maintaining your welding tools in good condition is equally important. Sharp and well-maintained tools help prevent accidents resulting from slips or improper usage.
Keep your tools clean, regularly check their integrity, and replace damaged or worn-out parts. Properly storing your tools in designated areas also helps prevent accidents and ensures they are easily accessible when needed. By keeping your tools in good condition, you enhance your safety while working with them.
Ensure Proper Grounding of Workpieces
Proper grounding of workpieces is essential for electrical safety during Welding. Grounding helps prevent electrical shocks and fires caused by stray currents. Ensure the welding machine is properly grounded according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Additionally, make sure the workpiece being welded is also appropriately grounded. An insufficient or faulty ground connection can result in electrical hazards and potential burns. Regularly inspect the grounding connections and cables to ensure their integrity and effectiveness.
Avoid Overheating Equipment
Overheating welding equipment can lead to malfunctions, electrical hazards, and potential burn injuries. Excessive heat can cause damage to the welding machine, compromising its performance and safety features.
Avoid overusing the equipment continuously without giving it sufficient time to cool down. Monitor the temperature of the equipment during operation and follow the recommended duty cycle provided by the manufacturer. By preventing overheating, you extend the lifespan of your equipment and maintain a safe welding environment.
Use Tools Specifically Designed for Welding
Using tools designed explicitly for Welding is essential for your safety and the quality of your work. Welding tools are designed to withstand the demands of the welding process and provide enhanced safety features.
Using non-specialized tools can compromise your safety and lead to accidents or burns. Invest in high-quality welding tools, such as welding hammers, chipping hammers, wire brushes, and pliers, to ensure optimal performance and minimize the risk of injuries or equipment failures.
Being Mindful of Surroundings
Be Aware of Nearby Hazards and Obstructions
Awareness of your surroundings is critical to preventing accidents and burns while welding. Be mindful of potential hazards, such as overhead obstructions, uneven surfaces, or nearby combustible materials.
By identifying potential hazards beforehand, you can take appropriate measures to mitigate risks and promote a safe working environment. Regularly inspect the workspace, remove obstructions or debris, and mark hazardous zones or objects to prevent accidents and burns.
Secure Cables and Hoses to Prevent Tripping
Cables and hoses are vital components of the welding setup but can pose a tripping hazard if improperly secured. Ensure cables and hoses are neatly organized and adequately protected to avoid entanglement or accidental tugging.
Use cable covers or guards to prevent trip hazards and safeguard your welding leads. Routinely inspect cables and hoses for any signs of damage and replace them if necessary. Properly securing cables and hoses minimizes the risk of falls and subsequent burns.
Keep a Safe Distance from Flammable Materials
Maintaining a safe distance from flammable materials is essential to prevent fires and burns. Sparks, welding slag, or hot welding equipment can ignite nearby flammable substances, leading to potentially hazardous situations.
When setting up your welding workspace, ensure that flammable materials are kept at a safe distance or stored in designated areas away from the welding process. This eliminates the risk of accidental ignition and maintains a controlled environment for welding operations.
Weld in Well-lit Areas
Welding in well-lit areas is crucial for maintaining visibility and reducing the risk of accidents or burns. Insufficient lighting can lead to errors in judgment, misalignment of welds, or unintentionally coming into contact with hot surfaces.
Ensure that your work area is adequately illuminated, particularly in the vicinity of the Welding. This ensures clear visibility of the workpiece, welding equipment, and potential hazards, enabling you to work safely and efficiently.
Work in a Controlled Environment
Working in a controlled environment helps ensure optimum safety while Welding. Set up your workspace in an area designated for welding activities whenever possible. This controlled environment allows you to implement safety measures effectively, such as proper ventilation, fire prevention, and controlled access.
Additionally, working in a controlled environment minimizes the potential for distractions or interference from unrelated tasks, allowing you to focus on your welding tasks and reduce the risk of burns.
Seeking Proper Training and Supervision
Undergo Proper Welding Training
Proper welding training is essential for preventing burns and ensuring safe welding practices. Proper training helps you understand the potential risks involved in Welding and teaches you techniques to minimize those risks.
Enroll in a reputable welding training program or apprenticeship to learn about welding safety procedures, proper equipment usage, and welding techniques. By gaining the necessary knowledge and skills through training, you significantly reduce the likelihood of burns and create a safer work environment.
Get Certified if Required
If required by your employment or local regulations, obtaining welding certification is essential. Certification ensures you possess the necessary skills and knowledge to safely and effectively perform welding tasks.
Certification programs typically involve passing written exams and practical demonstrations to demonstrate your proficiency in welding techniques and safety protocols. By obtaining certification, you demonstrate your commitment to maintaining high safety standards and increase your employability within the welding industry.
Work under Supervision or Guidance
Especially for novice welders, working under the direct supervision or guidance of experienced welders is highly recommended. Seasoned welders can provide valuable insights, share expertise, and guide you through proper welding techniques and safety practices.
They can identify potential hazards, offer recommendations for improvement, and ensure that you follow correct procedures. Working under supervision enhances your skills and promotes a safer work environment by mitigating potential risks early on.
Stay Updated with Safety Guidelines
The field of Welding is constantly evolving, and safety guidelines are regularly updated to address new risks and challenges. It is crucial to stay informed and updated with the latest safety guidelines and regulations about Welding.
Reference resources such as industry publications, safety websites, and welding standards organizations to remain current with best practices and safety recommendations. Stay informed; you can continuously improve your safety practices and reduce the risk of burns and other welding-related injuries.
Learn Emergency Response Protocols
Being prepared for emergencies and knowing how to respond appropriately is crucial in any workplace. Learning emergency response protocols empowers you to take swift and effective action in case of accidents, fires, or other hazardous situations.
Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures, such as evacuation routes, fire alarm locations, and contacts. Participate in safety drills or training sessions to practice the necessary response actions. By being prepared, you can minimize the impact of emergencies and ensure the well-being of yourself and others.
Maintaining Personal Hygiene
Avoid Touching Eyes, Nose, or Mouth
You are maintaining good personal hygiene while Welding is vital to prevent infections and the potential spread of harmful substances. Avoid touching your eyes, nose, or mouth while Welding, as your hands may come into contact with welding residues, dust, or other contaminants.
Touching your face without washing your hands can lead to contamination and potential health risks. Make it a habit to refrain from touching your face and wash your hands thoroughly before and after each welding session.
Wash Hands Thoroughly before and after Welding
Proper hand hygiene is essential to prevent the transfer of contaminants and to maintain overall cleanliness. Before starting any welding activity, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water to remove any dirt, grease, or chemicals that may be present.
After completing your welding tasks, rewash your hands to eliminate any potential residues on your skin. Practicing good hand hygiene reduces the risk of contamination, safeguards your health, and promotes a hygienic work environment.
Keep Long Hair Tied Back
If you have long hair, keeping it securely tied back while welding is essential. Long hair presents a safety hazard as it can quickly come into contact with sparks, flames, or moving equipment, leading to burns or entanglement.
Opt for hairstyles that keep your hair away from your face and securely contained, such as braids, buns, or ponytails. Additionally, consider wearing a welding cap or bandana to provide extra protection and keep loose hair in place.
Avoid Loose-fitting Clothing or Jewelry
She wore loose-fitting clothing or jewelry, while Welding could pose serious safety risks. Loose clothing or jewelry can easily get caught in moving equipment, sparks, or flames, potentially causing injuries or burns.
Wearing well-fitted clothing that covers your arms, legs, and body is advisable. Remove any jewelry, such as rings, bracelets, or necklaces, before starting welding tasks to eliminate potential hazards. Choosing appropriate attire ensures your safety and minimizes the risk of accidents.
Stay Hydrated and Take Necessary Breaks
Staying hydrated and taking regular breaks are essential for maintaining your well-being and preventing fatigue while Welding. Welding in hot environments or for extended periods can lead to dehydration, which affects concentration and physical performance.
Keep a water bottle nearby and drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated throughout the day. Listen to your body and take the necessary breaks to rest and recharge. Staying hydrated and taking breaks reduces the risk of fatigue-related accidents and promotes your overall health.
Understanding Types of Burns
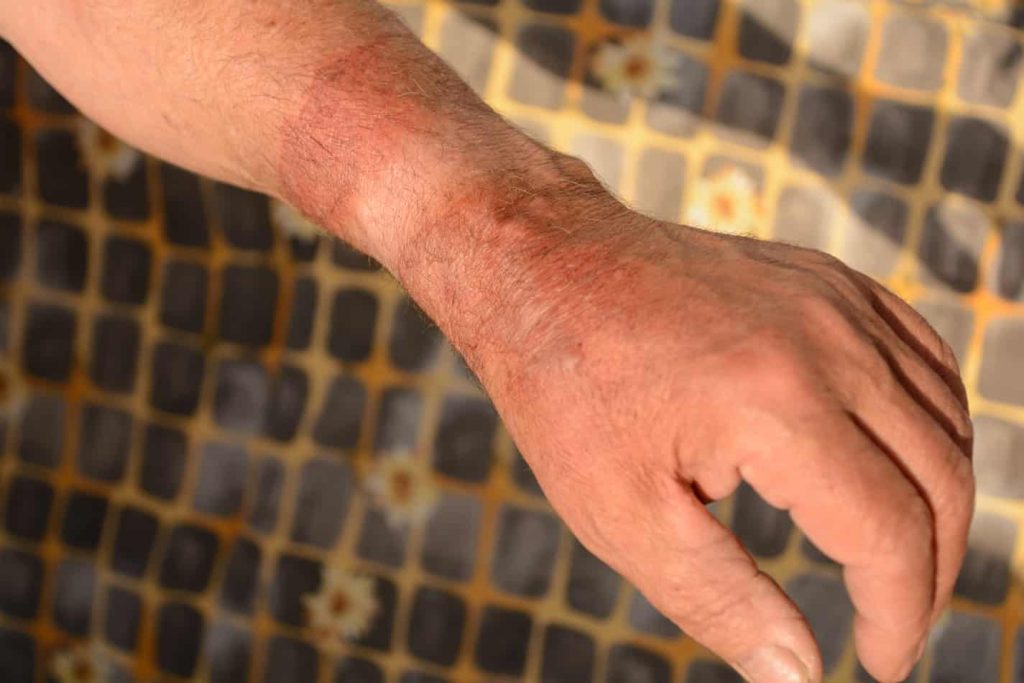
Thermal Burns
Thermal burns are one of the most common burns encountered while welding. They occur when the skin comes into direct contact with hot objects, sparks, or flames generated during welding.
Thermally-induced burns can vary in severity, depending on the temperature and duration of exposure. It is essential to treat thermal burns promptly to minimize pain and promote healing. Cooling the burn with cold water, covering it with a clean cloth, and seeking medical attention if necessary are essential steps for managing thermal burns effectively.
Electric Arc Burns
Electric arc burns are specific burns caused by the electric arc produced during Welding. An electric arc discharges electric current through the air, generating intense heat and bright light. Arc burns can occur when the electric arc comes into contact with the skin, resulting in burn injuries.
These burns can be deep and severe, requiring immediate medical attention. Preventing electric arc burns involves using appropriate personal protective equipment, maintaining a safe distance from the arc, and following safe welding practices.
Radiation Burns
Radiation burns occur due to exposure to the intense ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation emitted during Welding. Prolonged UV and IR radiation exposure can cause skin reddening, sunburn-like symptoms, and even long-term damage.
To protect against radiation burns, wearing proper eye and face protection, such as welding helmets with UV and IR filters is crucial. Additionally, ensuring proper ventilation and reducing exposure time can minimize the risk of radiation burns.
Chemical Burns
Chemical burns can occur when the skin or eyes come into contact with hazardous chemicals or substances commonly used in Welding, such as acids, alkalis, or solvents. These burns can be excruciating and may cause severe tissue damage.
Preventing chemical burns involves appropriately handling and storing hazardous chemicals, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, and following safety regulations and guidelines. In case of a chemical burn, it is essential to immediately flush the affected area with clean water and seek immediate medical attention.
Friction Burns
Friction burns can occur due to the rapid movement of objects across the skin’s surface during welding tasks. These burns are characterized by heat generated from friction and are often superficial but can be painful.
Friction burns commonly occur when skin comes into contact with rapidly spinning wire brushes or abrasive materials. Wearing appropriate gloves and protective clothing can help prevent friction burns. In case of a friction burn, cool the affected area, clean it gently, and apply a sterile bandage to protect against infection.
First Aid for Welding Burns
Remove Heat Source
When a burn occurs during Welding, the first step is to remove the heat source as quickly as possible. Switch off the welding machine or move away from the hot object, causing the burn. Eliminating the heat source prevents further damage to the affected area and begins cooling the burn.
Cool the Burn with Cold Water
After removing the heat source, cool the burned area with cold water for 10 to 20 minutes. Avoid ice or icy water, as extreme cold can damage the burned skin further.
Burn cooling helps alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and minimize tissue damage. Continue running cold water over the burn until medical attention is sought or the pain subsides.
Cover the Burn with a Clean, Dry Cloth
Once the burn has been cooled with water, gently cover it with a clean, dry cloth or sterile dressing. This protective covering helps prevent infection and further damage to the burned area.
Avoid using adhesive bandages directly on the burn; they can stick to the skin and cause more pain during removal. Covering the burn also provides a barrier against contaminants in the environment.
Seek Medical Attention if Necessary
Depending on the severity and extent of the burn, it may be necessary to seek medical attention. Superficial burns can often be managed with first aid and self-care, while more severe burns require immediate medical attention.
If a burn appears deep, covers a large body area, or is accompanied by other symptoms like difficulty breathing or signs of shock, it is essential to seek immediate medical assistance.
Follow First Aid Guidelines
When providing first aid for welding burns, following appropriate first aid guidelines is essential.
The steps mentioned above are general guidelines for initial burn care, but each burn is unique, and the severity may require specific treatments or professional medical evaluation.
Stay with the individual and monitor their condition until medical help arrives. By following first aid guidelines and ensuring prompt medical attention when needed, you can provide the best care for burn injuries while welding.