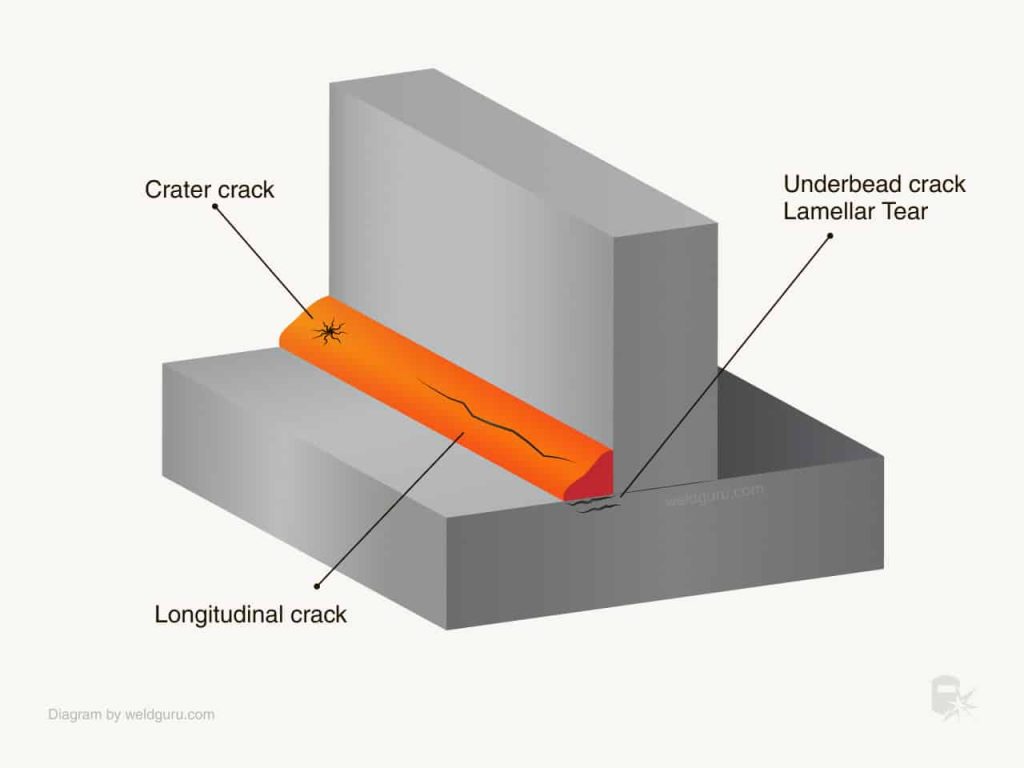
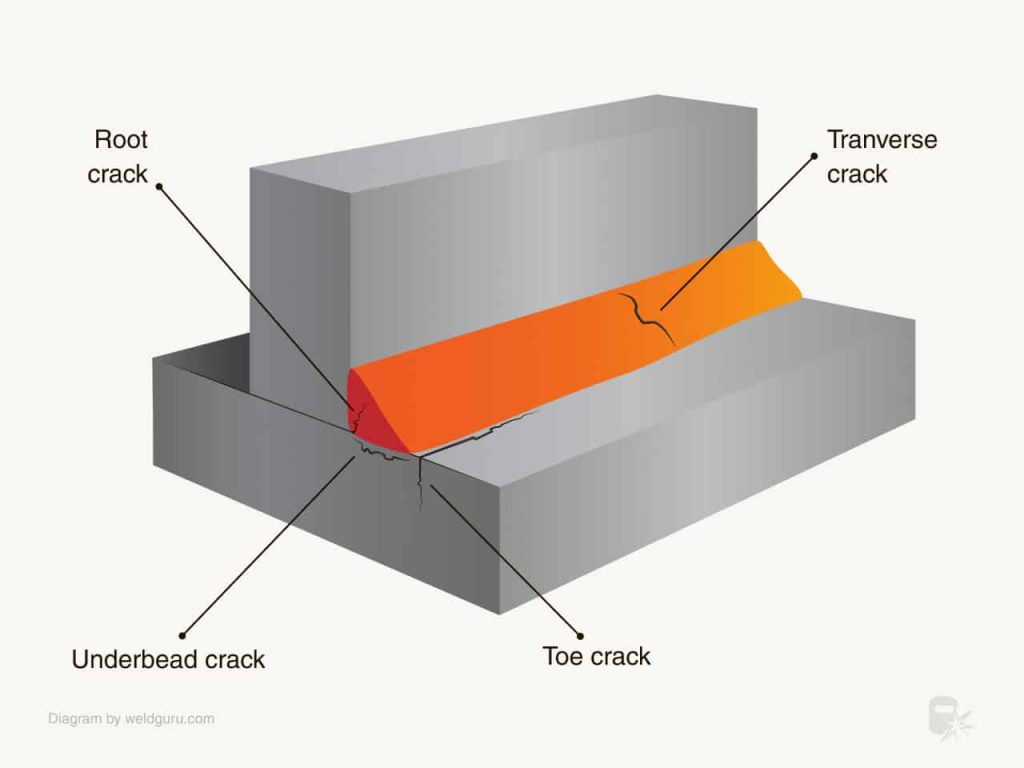
Cracking is a common concern for welders, but fret not, as there are effective measures you can take to prevent it. From selecting the right materials to ensuring proper weld design and technique, this article will guide you through the essential steps to keep those cracks at bay. So, whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting out, read on to discover practical tips and techniques that will help you achieve strong and durable welds every time.
Choose the Right Welding Technique
When it comes to welding, there are various techniques available, and choosing the right one is essential for ensuring a successful weld. Understanding the different welding techniques is the first step in making this decision.
Understand the Different Welding Techniques
Welding techniques can vary based on factors such as the type of metal being welded, the thickness of the materials, and the desired results. Some common welding techniques include MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), Stick welding, and Flux-Cored Arc Welding. Each technique has its own advantages and limitations, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of each.
Assess the Applicability of Each Technique to Your Project
After understanding the different welding techniques, you need to assess which technique is most suitable for your specific project. Consider factors such as the type of metal, the joint configuration, and the desired strength and appearance of the weld. Some techniques may be better suited for certain materials or joint designs, so take these factors into account.
Select the Most Suitable Welding Technique
Once you have assessed the applicability of each technique, it’s time to select the most suitable one for your project. Take into consideration factors such as ease of use, cost, and the availability of equipment and consumables. Remember that the right welding technique is crucial for achieving a strong and durable weld.
Prepare the Materials Properly
Proper preparation of the materials is essential for achieving a high-quality weld. This involves cleaning the surfaces to be welded, removing any contaminants or oxides, ensuring proper fit-up of the joint, and using appropriate clamping or fixturing techniques.
Clean the Surfaces to be Welded
Before welding, ensure that the surfaces to be welded are clean and free from any dirt, rust, paint, or other contaminants. Use a wire brush, grinding wheel, or chemical cleaner to remove any debris and create a clean surface for welding. This will help achieve better adhesion and prevent defects in the weld.
Remove Any Contaminants or Oxides
In addition to cleaning the surfaces, it’s important to remove any contaminants or oxides that may be present. These can hinder the welding process and lead to weak welds or cracks. Use a suitable cleaning method, such as wire brushing, grinding, or chemical cleaning, to eliminate any impurities and ensure a clean weld joint.
Ensure Proper Fit-Up of the Joint
Proper fit-up of the joint is crucial for achieving a strong weld. Ensure that the parts to be welded are aligned correctly and that there are no gaps or misalignments. Proper fit-up ensures full penetration of the weld and helps prevent defects such as lack of fusion or incomplete penetration.
Use Appropriate Clamping or Fixturing Techniques
Using appropriate clamping or fixturing techniques can help hold the parts in place and maintain proper alignment during the welding process. This is especially important for complex or large structures where precise alignment is critical. Proper clamping or fixturing techniques ensure uniform heat distribution and help prevent distortion or warping of the welded joint.
Control the Heat Input
Controlling the heat input during welding is crucial for achieving a high-quality weld and avoiding potential issues such as distortion, cracking, or weakened mechanical properties. Pay attention to factors such as avoiding excessive heat, maintaining proper preheating and interpass temperatures, using correct welding parameters, and controlling the welding speed.
Avoid Excessive Heat
Excessive heat can lead to numerous problems, including distortion, cracking, and reduced mechanical properties of the welded joint. It’s important to ensure that the heat input is within the recommended range for the specific material being welded. Excessive heat can be controlled by adjusting welding parameters such as amperage, voltage, or wire feed speed.
Maintain Proper Preheating and Interpass Temperatures
Preheating the base material before welding and maintaining interpass temperatures during the welding process can help prevent cracking and ensure proper fusion. Consult the welding procedure specifications or industry standards to determine the appropriate preheating and interpass temperature requirements for your specific material.
Use Correct Welding Parameters
Using correct welding parameters, such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, and electrode or wire size, is crucial for achieving a sound weld. The welding parameters may vary depending on the material thickness, joint type, and welding technique being used. Consult the welding procedure specifications or seek professional guidance to determine the optimal welding parameters for your project.
Control the Welding Speed
Controlling the welding speed is essential for achieving proper fusion and avoiding defects such as lack of penetration or incomplete fusion. Welding too fast can lead to insufficient heat input, while welding too slow can result in excessive heat and potential issues like burn-through or distortion. Find the optimal welding speed for your specific application and maintain a steady and consistent speed throughout the welding process.
Choose the Right Welding Consumables
Selecting the right welding consumables, such as welding rods, wire, or electrodes, is crucial for achieving a successful weld. The choice of consumables should be based on factors such as the base material, the welding process being used, and the joint configuration.
Select Appropriate Welding Rods, Wire, or Electrodes
Different welding processes require different types of consumables. Select the appropriate welding rods, wire, or electrodes based on the welding technique being used. Consider factors such as the tensile strength, chemical composition, and shielding requirements of the consumables.
Match the Consumables to the Base Material
Ensure that the welding consumables are compatible with the base material being welded. Matching the consumables to the base material helps achieve good weld quality and prevents issues like cracking or poor mechanical properties. Consult welding consumable manufacturers’ recommendations or industry standards for guidance on selecting the appropriate consumables for specific materials.
Consider the Welding Process and Joint Configuration
The welding process being used and the joint configuration also play a role in selecting the right consumables. Some welding processes, such as TIG or MIG welding, may require specific types of consumables. Consider the joint design, accessibility, and welding position when choosing the consumables to ensure proper deposition and efficient welding.
Ensure Proper Shielding
Proper shielding of the weld zone is essential for preventing contamination, ensuring sound welds, and achieving the desired mechanical properties. Pay attention to factors such as using sufficient shielding gas, protecting the weld pool from contamination, checking gas flow and nozzle positioning, and considering alternative shielding methods like flux or flux-cored wire.
Use Sufficient Shielding Gas
Shielding gases, such as argon or carbon dioxide, are often used to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. The choice of shielding gas depends on factors such as the welding process being used and the base material being welded. Ensure that the shielding gas flow rate is sufficient to create an effective shielding gas environment around the weld zone.
Protect the Weld Pool from Contamination
Contamination of the weld pool can lead to defects like porosity, lack of fusion, or reduced mechanical properties. Protect the weld pool by avoiding contact with air, moisture, or any other contaminants. Use welding techniques such as gas shielding or flux to prevent atmospheric contamination and maintain a clean and sound weld.
Check Gas Flow and Nozzle Positioning
Proper gas flow and nozzle positioning are crucial for effective shielding gas coverage and preventing contamination. Ensure that the gas flow rate is set correctly, and the nozzle is positioned at the appropriate distance from the weld zone. Improper gas flow or incorrect nozzle positioning can result in inadequate shielding, which may lead to welding defects.
Consider Using Flux or Flux-Cored Wire for Shielding
In some cases, using flux or flux-cored wire can provide an alternative method for shielding the weld zone. Flux or flux-cored wire contains materials that produce a protective shield during the welding process, eliminating the need for external shielding gas. Consider using flux or flux-cored wire when appropriate, based on the welding process and material being used.
Avoid Distortion and Stress
Minimizing distortion and stress in the welded structure is crucial for maintaining its integrity and preventing potential issues such as cracking or fatigue failure. Strategies for achieving this include balancing heat input and cooling, using tack welds or temporary fixtures, employing heat sinks or backing bars, and applying the proper weld sequence.
Balance Heat Input and Cooling
Balancing heat input and cooling helps minimize distortion and stress in the weld area. Avoid sudden changes in temperature or excessive heat buildup by ensuring proper heat distribution and managing the cooling process. If necessary, use techniques such as intermittent welding or controlled post-weld cooling to control the thermal cycling and reduce the risk of distortion or stress.
Use Tack Welds or Temporary Fixtures
Tack welds or temporary fixtures can help hold the parts in the desired position during welding, reducing the risk of misalignment or distortion. These temporary attachments can be removed or ground off after the weld is completed. Use tack welds or temporary fixtures strategically to maintain alignment and achieve better weld quality.
Employ Heat Sinks or Backing Bars
In some welding applications, using heat sinks or backing bars can help control heat distribution and minimize distortion. Heat sinks or backing bars are materials that absorb or dissipate heat during welding, preventing excessive heat buildup and reducing the risk of deformation or stress. Consider using heat sinks or backing bars when appropriate, based on the welding process and joint configuration.
Apply Proper Weld Sequence
The welding sequence can also impact distortion and stress in the welded structure. Plan the order of welds strategically to evenly distribute the heat and minimize distortion. Start from the center and work towards the outer edges, or use a back-and-forth sequence to balance the heat input and control the cooling. Apply the proper weld sequence based on the specific joint configuration and consider consulting welding experts or industry guidelines for guidance.
Perform Post-Weld Treatments
Performing post-weld treatments is important for ensuring the desired mechanical properties and improving the integrity of the welded joint. Some key post-weld treatments include allowing for proper cooling and annealing, applying stress-relief heat treatment if necessary, conducting non-destructive testing (NDT), and evaluating the welding procedure and welder qualifications.
Allow for Proper Cooling and Annealing
After completion of the welding process, it’s essential to allow the weld to cool down properly. The cooling process helps relieve internal stresses and prevent cracking. Additionally, for certain materials, annealing may be necessary to further improve the mechanical properties and reduce residual stress in the weld. Follow the recommended cooling and annealing procedures based on the specific material and industry standards.
Apply Stress-Relief Heat Treatment, if Necessary
In certain cases, stress-relief heat treatment may be necessary to reduce residual stresses in the welded joint. Stress-relief heat treatment involves heating the welded structure to a specific temperature and then gradually cooling it. This process helps alleviate internal stresses and can improve the fatigue resistance and overall integrity of the weld. Consider consulting industry standards or welding specialists to determine if stress-relief heat treatment is required for your specific application.
Post-Heat or Post-Weld Heat Treatment
In addition to stress-relief treatments, post-heat or post-weld heat treatments may be necessary for specific materials or applications. These treatments involve applying controlled heating or heat cycles to the weld zone to refine the microstructure and improve the mechanical properties of the weld. Follow the recommended post-heat or post-weld heat treatment procedures based on the specific material and industry guidelines.
Perform Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as visual inspections, ultrasonic testing, or radiographic testing, can be used to evaluate the quality and integrity of the welded joint. NDT helps detect any defects or discontinuities that may compromise the structural integrity or performance of the weld. Consider conducting NDT based on the specific requirements of your project and industry standards.
Implement Quality Control Measures
Quality control measures are crucial for ensuring that the welding process and the resulting welds meet the required standards and specifications. This involves monitoring welding parameters and process variables, conducting visual and dimensional inspections, performing mechanical testing of welded joints, and evaluating the welding procedure and welder qualifications.
Monitor Welding Parameters and Process Variables
Regular monitoring of welding parameters, such as amperage, voltage, and travel speed, helps ensure that the welding process is under control and within the specified parameters. Additionally, monitoring process variables, such as shielding gas flow rate or joint fit-up, helps detect any deviations that may affect the quality of the weld. Implement a systematic monitoring system and document the parameters and variables for quality control purposes.
Conduct Visual and Dimensional Inspections
Visual inspections of the welds are essential for detecting any visible defects, such as cracks, porosity, or lack of fusion. Regularly inspect the welds using appropriate techniques, such as visual examination or dye penetrant testing, to ensure conformity to the required standards. Additionally, conduct dimensional inspections to verify that the welded joints meet the specified dimensions and tolerances.
Perform Mechanical Testing of Welded Joints
Mechanical testing of welded joints provides valuable information about the weld’s strength, toughness, and other mechanical properties. Various testing methods, such as tensile testing, hardness testing, or impact testing, can be used to evaluate the weld’s performance under different load conditions. Conduct mechanical testing based on the specific requirements of the project and the applicable standards or codes.
Evaluate the Welding Procedure and Welder Qualifications
Regular evaluation of the welding procedure and welder qualifications helps maintain the quality and consistency of the welding process. Assess the welding procedure periodically to ensure it is up to date and in compliance with the industry standards. Additionally, verify the qualifications of the welders involved in the project, ensuring they have the necessary certifications and training to perform the welding tasks correctly.
Avoid Common Mistakes
To achieve high-quality welds, it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can compromise the integrity and performance of the weld. Some common mistakes include lack of fusion or penetration, inadequate preheating or interpass temperatures, improper joint design or weld repair, and insufficient cleaning or surface preparation.
Lack of Fusion or Penetration
Lack of fusion or penetration occurs when the weld fails to fully fuse with the base material or penetrate into the joint. This can result from insufficient heat input, improper welding technique, or inadequate joint preparation. Ensure proper heat input, use appropriate welding techniques, and prepare the joint correctly to prevent lack of fusion or penetration.
Inadequate Preheating or Interpass Temperatures
Inadequate preheating or interpass temperatures can lead to problems such as cracking or reduced mechanical properties in the weld. Follow the recommended preheating or interpass temperature requirements for the specific material and joint configuration. Inadequate temperature control can result in insufficient diffusion of hydrogen or other harmful elements and compromise the integrity of the weld.
Improper Joint Design or Weld Repair
Improper joint design or weld repair can weaken the structure and result in potential failure. Ensure that the joint design is appropriate for the intended application and provides sufficient strength and load-bearing capacity. When repairing welds, follow proper repair procedures and techniques to maintain the integrity and performance of the weld.
Insufficient Cleaning or Surface Preparation
Insufficient cleaning or surface preparation can introduce contaminants that compromise the quality of the weld. Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be welded, removing any rust, paint, or dirt. Use appropriate cleaning methods and materials for the specific base material, following industry guidelines. Insufficient cleaning can lead to defects such as porosity, lack of fusion, or reduced mechanical properties.
Seek Professional Advice
While understanding the principles and techniques of welding is important, seeking professional advice can further enhance your knowledge and skills. Consulting with welding engineers or experts can provide valuable insights and guidance for specific welding projects. Additionally, attending welding training or certification courses helps improve your expertise and keeps you updated with the latest industry developments. Make use of welding codes and standards as references and engage in continuous learning and improvement to further excel in the field of welding.
By following these comprehensive tips and techniques, you can prevent your welds from cracking and achieve high-quality and durable welds. Remember to choose the right welding technique, prepare the materials properly, control the heat input, select the appropriate welding consumables, ensure proper shielding, minimize distortion and stress, perform post-weld treatments, implement quality control measures, avoid common mistakes, and seek professional advice when needed. With practice and attention to detail, your welding skills will continue to improve, ensuring successful and reliable welds. Happy welding!