When it comes to arc welding, choosing the right shade of welding helmet can make all the difference in ensuring your safety and getting the job done effectively. With a wide range of helmet shades available, it can be overwhelming to know which one is best suited for arc welding. In this article, we’ll break down the different shade options and provide you with the insights you need to make an informed decision. So, whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting out, join us as we shed some light on the importance of selecting the right shade of welding helmet for arc welding.
Importance of Choosing the Right Shade
Protecting Your Eyes and Face
When it comes to arc welding, protecting your eyes and face is of utmost importance. Arc welding produces intense light and heat, which can be harmful to your eyes and skin. The right shade of welding helmet acts as a protective shield, blocking harmful ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) rays emitted during the welding process. These rays can cause serious damage to your eyes, including welding flash burns, cataracts, and other vision problems. Additionally, the right welding helmet shade protects your face from sparks, spatter, and flying debris, ensuring your safety while welding.
Ensuring Proper Visibility
While protecting your eyes and face is crucial, ensuring proper visibility is equally important. The right shade of welding helmet allows you to see clearly while welding. It reduces the brightness of the welding arc to a comfortable level, preventing eye strain and fatigue. Welding with the correct shade ensures that you can see your workpiece and welding joint clearly, allowing for accurate and precise welding. Adequate visibility also improves overall safety, as it enables you to detect potential hazards and maintain control over the welding process.
Preventing Welding-Related Injuries
Choosing the right shade of welding helmet is not only important for protecting your eyes and ensuring visibility but also crucial in preventing welding-related injuries. When you wear an appropriate shade, it minimizes the risk of accidents caused by impaired vision. Accurate and clear vision reduces the chances of welding defects, such as improper bead placement, lack of fusion, or incomplete penetration. By preventing these defects, you avoid potential structural weaknesses in your welds, ensuring the strength and integrity of your finished work. Furthermore, a properly shaded welding helmet shields your face from sparks, spatter, and hot metal fragments, reducing the risk of burns and other injuries.
Understanding Arc Welding
Definition and Process
Arc welding is a welding technique that uses an electric arc to join metal pieces together. It involves creating an intense arc of electricity between an electrode and the workpiece, causing the metals to melt and fuse together. The electric arc generates high heat, which melts the parent metals and creates a pool of molten metal. As the pool cools and solidifies, it forms a strong and durable weld joint. Arc welding is widely used in industries such as construction, fabrication, automotive, and shipbuilding, due to its versatility and ability to weld a wide variety of metals.
Types of Arc Welding
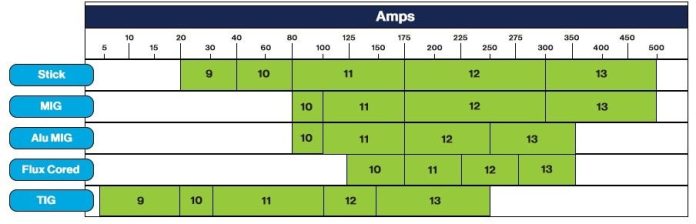
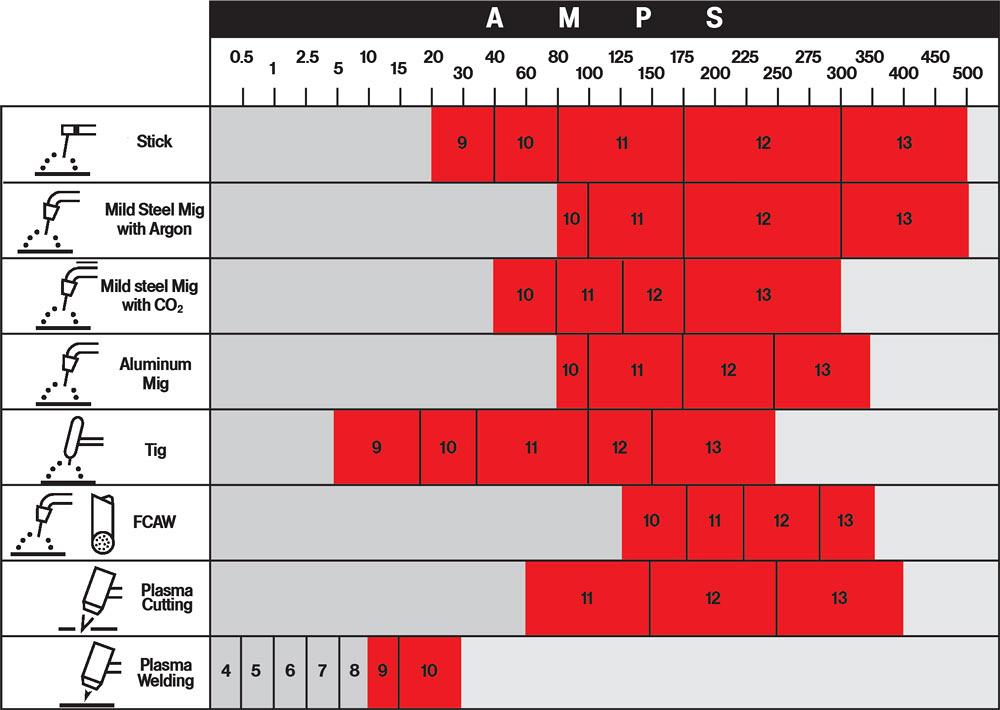
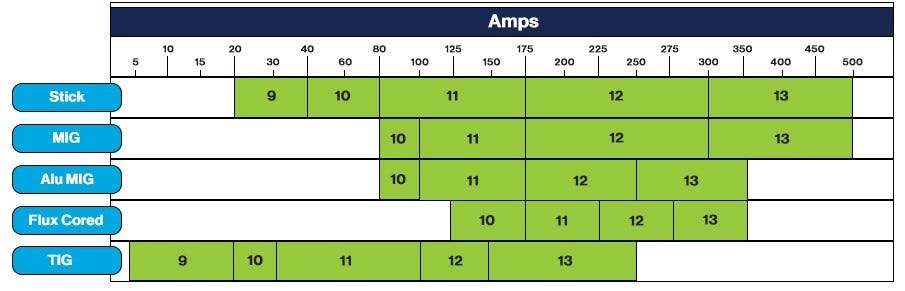
There are several different types of arc welding, each with its own specific characteristics and requirements. The most common types of arc welding include Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), and Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW). SMAW, also known as stick welding, uses a consumable electrode coated in flux to create the arc. GMAW, also referred to as MIG welding, uses a continuous wire electrode and shielding gas. GTAW, often called TIG welding, utilizes a non-consumable tungsten electrode and shielding gas. Each type of arc welding has different light intensity and heat generation, requiring specific shade recommendations for optimal safety and visibility.
Light Intensity and Heat Generation
Arc welding produces extremely bright light and intense heat, which can be hazardous to the eyes and skin. The brightness of the welding arc is expressed as light intensity or luminous intensity and is measured in candelas per square meter (cd/m²). The higher the light intensity, the darker shade of welding helmet is required to ensure safe visibility. The heat generated during arc welding is measured in amperes (A). Higher amperage levels generate more heat, necessitating a higher shade level to protect against thermal radiation. Understanding the light intensity and heat generation of each type of arc welding is essential in determining the appropriate shade level for welding helmets.
Factors to Consider
Welding Amperage
One of the key factors to consider when choosing the right shade for your welding helmet is the welding amperage. As mentioned earlier, the amperage level directly corresponds to the heat generated during arc welding. Higher amperage levels produce more intense heat, requiring a darker shade of welding helmet to protect against thermal radiation. It is important to refer to welding standards and guidelines to determine the recommended shade range based on the specific amperage levels you will be working with.
Material Thickness
The thickness of the materials you will be welding also influences the shade level of your welding helmet. Thicker materials generally require higher amperage levels, which produce more intense heat and brighter light. Consequently, a darker shade of welding helmet is necessary to protect against the increased light intensity and heat generation. Conversely, thinner materials may require a lower shade level, as they typically require lower amperage levels and generate less heat and light.
Electrode Type
The type of electrode you use in your arc welding process can also impact the shade level of your welding helmet. Different electrodes require different amperage levels for optimal weld quality and penetration. For instance, electrodes with higher amperage requirements generate more heat and light, necessitating a darker shade of welding helmet. Consult the electrode manufacturer’s recommendations to determine the appropriate shade range based on the specific electrode type you will be using.
Personal Preference
While it is essential to consider factors such as welding amperage, material thickness, and electrode type, personal preference also plays a role in choosing the right shade for your welding helmet. Some individuals may find certain shade levels more comfortable to work with, based on their eye sensitivity and personal comfort. It is crucial to find a shade level that offers adequate protection and visibility while also taking into account your own comfort and preferences.
Recommended Shade Guide
Shade Range Specifications
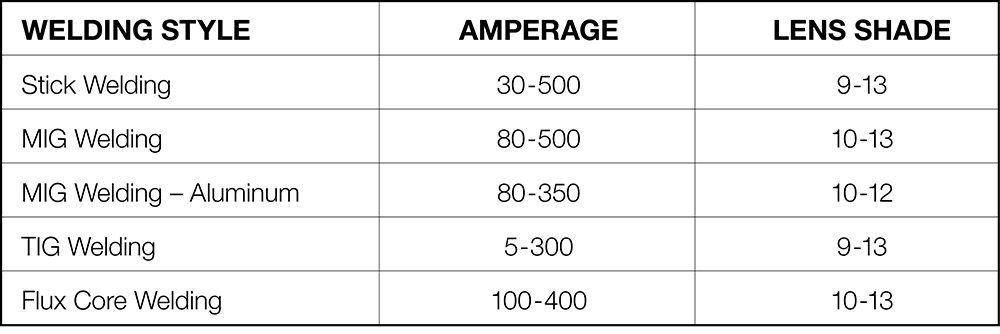
The recommended shade range for welding helmets is typically indicated by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards provide guidelines for selecting the appropriate shade level based on the specific welding process and conditions. The shade range is often expressed as a range of numbers, such as shade 8-13, indicating that the helmet can be adjusted within that range. It is important to ensure that your welding helmet meets the ANSI and ISO standards and provides the necessary shade range for your arc welding applications.
Different Shades for Different Applications
Different arc welding processes may require different shade levels to ensure optimal safety and visibility. For instance, SMAW, which produces a lower light intensity compared to other welding processes, may require a shade range of 8-12. On the other hand, GMAW and GTAW, which generate higher light intensity, may require a shade range of 10-13 or even higher. Understanding the specific shade requirements for each welding process enables you to choose the right helmet for the job.
Specific Shade Recommendations
While general shade range specifications provide a starting point, it is important to consider specific shade recommendations based on the welding amperage, material thickness, electrode type, and personal preference discussed earlier. Consulting welding experts, manufacturers, and industry guidelines can provide valuable insights into the recommended shade levels for specific welding applications. It is crucial to accurately assess the factors involved in your welding process to ensure the appropriate shade level for your welding helmet.
Types of Welding Helmets
Passive Welding Helmets
Passive welding helmets, also known as traditional welding helmets, feature a fixed shade lens. These helmets are typically made of durable, heat-resistant materials and provide reliable protection against harmful UV and IR rays. Passive welding helmets are less expensive than auto-darkening helmets and are suitable for welders who require a fixed shade level for their specific welding applications. They do not require batteries or electronic components, making them more straightforward and reliable in operation.
Auto-Darkening Welding Helmets
Auto-darkening welding helmets, as the name suggests, utilize an electronic system that automatically adjusts the shade level of the lens in response to the welding arc. These helmets feature a liquid crystal display (LCD) and sensors that detect the light intensity of the arc. When the arc is struck, the sensors signal the LCD to darken the lens to the appropriate shade level. Auto-darkening welding helmets offer the flexibility of adjusting the shade level within a specific range, providing optimal visibility and protection during welding. They eliminate the need for constantly flipping the helmet up and down, increasing efficiency and convenience.
Features to Look for in a Welding Helmet
When choosing a welding helmet, there are several features to consider to ensure maximum comfort, protection, and functionality. Some key features to look for include a lightweight and ergonomic design for prolonged use, adjustable headgear for a customized fit, a large view area for improved visibility, and a reliable lens that meets the necessary safety standards. Additionally, consider the helmet’s response time, which determines how quickly the lens switches from the light state to the darkened state when the arc is struck. An adjustable sensitivity control and delay function can also be valuable features, allowing you to fine-tune the helmet’s response to your specific welding requirements.
Choosing the Right Shade for Different Types of Arc Welding
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Shielded Metal Arc Welding, commonly known as SMAW or stick welding, typically requires a shade range of 8-12. SMAW produces a lower light intensity compared to other arc welding processes, making a shade 8 helmet suitable for most welding applications. However, situations that involve higher amperage levels or prolonged exposure to the welding arc may require a darker shade, such as shade 10-12.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Gas Metal Arc Welding, also referred to as GMAW or MIG welding, generates a higher light intensity compared to SMAW. A shade range of 10-13 is commonly recommended for GMAW. The specific shade level required within that range depends on factors such as welding amperage, material thickness, and personal preference. Higher amperage levels or thicker materials may require a darker shade within the recommended range.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, known as GTAW or TIG welding, produces a high-intensity arc that requires a shade range of 10-14. GTAW typically involves working with thinner materials and lower amperage levels, resulting in a higher shade requirement for optimum visibility and protection. Depending on the specific welding conditions and requirements, a shade level within the recommended range should be selected.
Common Shade Recommendations
Arc Welding Shade Chart
While the shade recommendations mentioned earlier provide general guidance for different types of arc welding, referring to an arc welding shade chart can offer more detailed and specific shade recommendations. This chart typically provides shade ranges for various welding processes, amperage levels, and material thicknesses. It is essential to ensure that the shade chart is in accordance with the ANSI and ISO standards, as well as any additional industry-specific guidelines.
Minimum Shade Recommendations
In addition to the general shade recommendations, minimum shade recommendations are important to ensure adequate eye protection. The minimum shade level varies based on the welding process and amperage level. For example, SMAW generally requires a minimum shade of 7, while GMAW and GTAW typically require a minimum shade of 8. Adhering to these minimum shade recommendations helps to prevent eye injuries and ensures safety while welding.
Additional Factors to Consider
While shade recommendations based on welding process, amperage level, and material thickness provide a good starting point, it is important to consider any additional factors specific to your welding environment or personal requirements. Factors such as ambient lighting, distance from the welding arc, and individual eye sensitivity may necessitate adjustments to the recommended shade level. Evaluating these additional factors allows you to personalize your shade choice and optimize safety and visibility during welding.
Alternative Eye Protection Options
Welding Goggles
In addition to welding helmets, welding goggles are another option for eye protection during arc welding. Welding goggles typically feature a shaded lens that can be flipped down over the eyes, similar to a welding helmet, providing protection against sparks, UV, and IR rays. Goggles are especially useful in confined spaces or situations where a welding helmet may be impractical. However, it is important to ensure that the goggles provide adequate shade level and protection for the specific welding process and conditions.
Face Shields
Face shields are an alternative option for protecting both the eyes and face during welding. They typically consist of a transparent visor that covers the entire face, protecting against sparks, spatter, and UV/IR rays. Face shields are ideal for scenarios where full-face protection is necessary, such as when working with overhead welding or in situations where additional protection is required beyond eye protection. However, they do not offer the same level of optical clarity as welding helmets or goggles, so they may not be suitable for intricate welding tasks that require precise visibility.
Welding Curtains
In some cases, welding curtains can be used to create a physical barrier between the welding area and surrounding individuals. Welding curtains are made of flame-resistant materials and are designed to block sparks, spatter, and UV/IR radiation. They are commonly used in industrial settings or workshops to partition the welding area and protect adjacent workers or bystanders. While welding curtains do not provide personal eye protection, they contribute to overall safety by reducing the risk of injuries and creating a controlled environment for welding operations.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Cleaning the Helmet
Proper maintenance of your welding helmet is essential for ensuring its optimal performance and longevity. Regularly cleaning the helmet helps to remove dirt, dust, and debris that may accumulate over time. Use a soft, dry cloth or a brush to wipe the outer surface of the helmet and the lens. Avoid using solvents or abrasive materials that could damage the helmet’s components. Additionally, check the headgear for any signs of wear or damage and replace if necessary. Clean and well-maintained helmets provide clear vision, proper protection, and comfort during welding.
Replacing Damaged Parts
In addition to regular cleaning, it is important to replace any damaged or worn-out parts of your welding helmet. This includes the lens, headgear, and other components that may deteriorate over time or after prolonged use. Damaged or scratched lenses can significantly impair visibility and compromise safety. Worn-out headgear may result in an uncomfortable fit, leading to potential distractions while welding. By regularly inspecting and replacing damaged parts, you ensure that your welding helmet continues to provide optimal protection and functionality.
Testing Helmet Functionality
To further ensure the safety and efficacy of your welding helmet, it is recommended to periodically test its functionality. This includes checking the response time of the auto-darkening feature, verifying that the lens darkens properly when the arc is struck, and ensuring that the lens returns to the light state when welding stops. Additionally, you may consider checking the fit and adjustability of the headgear to ensure maximum comfort and stability. Performing these tests allows you to identify any potential issues or malfunctions before they impact your welding safety.
Conclusion
Prioritizing safety is of paramount importance in arc welding, and choosing the right shade of welding helmet plays a crucial role in ensuring your well-being. By protecting your eyes and face, ensuring proper visibility, and preventing welding-related injuries, the right welding helmet shade enhances your safety and productivity. Understanding the different types of arc welding, factors to consider, and shade recommendations empowers you to select the most suitable helmet for your specific welding applications. Whether you opt for a passive helmet or an auto-darkening one, always consider key features, such as lightweight design, adjustability, and size of the view area, to maximize comfort and utilization. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, part replacement, and functionality testing, further enhances the lifespan and effectiveness of your welding helmet. By consistently consulting welding safety standards and personalizing your shade choice, you not only protect yourself but also promote a safe and secure welding environment. Remember, prioritizing safety is a collective responsibility, and your informed choices contribute to the overall well-being of the welding community. So, stay safe and happy welding!