Curious about the wonders of welding gloves? Look no further! In this article, we uncover the secrets behind how these essential hand protectors shield us from harm in the world of welding. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or someone who’s simply fascinated by the trade, join us as we unravel the remarkable ways in which welding gloves keep our hands safe during intense heat, sparks, and potential hazards. Get ready to be amazed at the incredible science behind this underrated but crucial piece of safety equipment.
Protection against heat and flames
Thick and durable materials
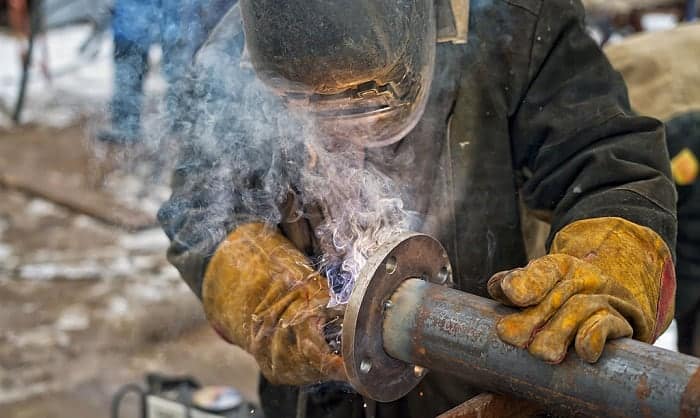
Welding involves high temperatures that can cause severe burns if not properly protected. That’s why welding gloves are made with thick and durable materials that can withstand intense heat and flames. These materials, such as leather or specialized heat-resistant fabrics, act as a barrier between your hands and the extreme temperatures present during welding. The thickness of the gloves ensures that the heat doesn’t penetrate through and reach your skin, keeping your hands safe and comfortable.
Insulated layers
In addition to being thick and durable, welding gloves often feature insulated layers. These layers provide an extra level of protection against heat by adding a barrier between your hands and the source of heat. Insulation helps to reduce the amount of heat conducted through the gloves, keeping your hands cool and minimizing the risk of burns or discomfort. This is especially beneficial during long welding sessions, where the heat exposure can be prolonged. The insulation also helps to regulate the temperature inside the gloves, preventing excessive sweating and maintaining a comfortable environment for your hands.
Flame-resistant properties
Apart from heat, welding also involves the risk of flames and sparks. Welding gloves are designed with flame-resistant properties that prevent the gloves from catching fire. This is essential for protecting your hands from burns and ensuring that any stray sparks or flames won’t ignite your gloves and cause further injuries. The flame-resistant materials used in welding gloves are specially treated to withstand exposure to flames without melting or burning, providing you with the necessary protection and peace of mind during welding operations.
Protection against electric shocks
Insulating materials
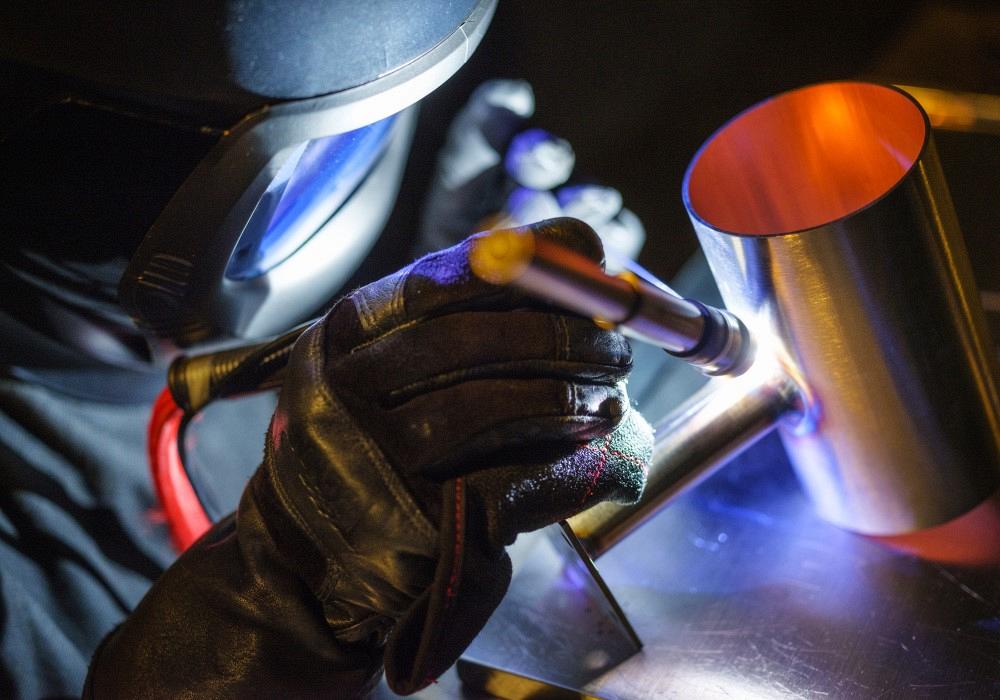
Electric shocks are another hazard that welders face while working. Welding gloves offer protection against electric shocks by utilizing insulating materials. These materials have high electrical resistance, which means that they do not conduct electricity effectively. When wearing properly insulated gloves, the electrical current from welding machines or other equipment is less likely to pass through your hands and into your body, reducing the risk of electric shock. Insulating materials effectively block the flow of electrical energy, ensuring that you can work safely without the fear of being electrocuted.
Electrically non-conductive properties
In addition to using insulating materials, welding gloves also possess electrically non-conductive properties. This means that they do not allow electricity to flow through them easily. Even if there is a small amount of moisture or conductive material on the gloves’ surface, the electrically non-conductive properties eliminate or greatly diminish the chances of a dangerous electrical shock. Welding gloves act as a protective shield, preventing electrical current from reaching your hands and minimizing the risk of severe injuries or even fatalities that can result from electrocution.
This image is property of waterwelders.com.
Protection against sparks and spatter
Highly resistant materials
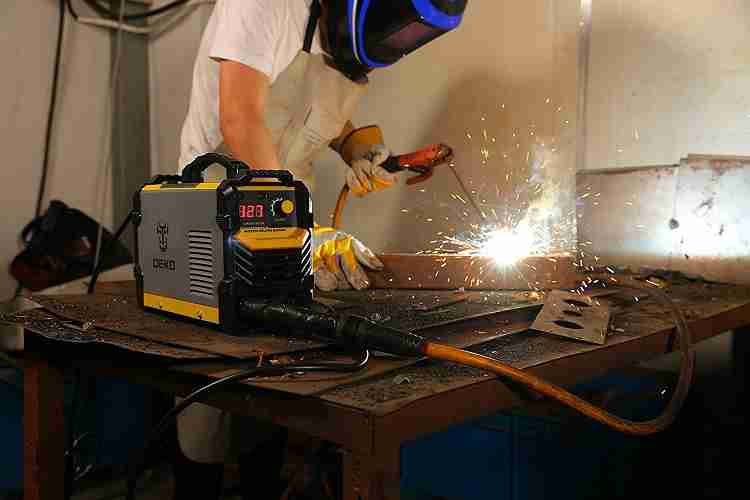
When welding, sparks and molten metal spatter can fly in various directions. To protect your hands from these potential hazards, welding gloves are made from highly resistant materials. These materials have the ability to withstand sparks and spatter, preventing them from penetrating through the gloves and causing burns or other injuries to your hands. The high resistance of these materials provides a reliable barrier, ensuring that your hands remain safe even in the presence of intense sparks and spatter. This is particularly crucial when working with metals that produce a larger amount of sparks, as it minimizes the risk of burns and other injuries.
Extended cuffs
To provide further protection against sparks and spatter, welding gloves often feature extended cuffs. These cuffs are designed to cover a portion of your forearm, offering a shielded area that prevents sparks and molten metal from making contact with your skin. The extended cuffs are typically made from the same highly resistant materials as the gloves themselves, ensuring consistent protection throughout your hands and forearms. By extending the coverage area, welding gloves with extended cuffs minimize the risk of burns or other injuries that can occur when sparks or spatter find their way past the wrist area of standard gloves.
Reinforced stitching
To enhance the overall durability and resistance of welding gloves, they often incorporate reinforced stitching. The seams of the gloves, particularly in high-stress areas, are reinforced with extra stitching to ensure that the gloves hold up well against the demands of welding work. Reinforced stitching prevents the gloves from tearing or coming apart, even when subjected to heavy use or contact with sharp objects. This feature not only extends the lifespan of the gloves but also contributes to their ability to protect your hands effectively from sparks and spatter. The reinforced stitching maintains the integrity of the gloves, keeping your hands safe throughout your welding tasks.
Protection against cuts and abrasion
Cut-resistant materials
Apart from protecting against heat and flames, welding gloves also provide defense against cuts and abrasions. These gloves are often made with cut-resistant materials that can withstand contact with sharp objects or rough surfaces commonly encountered during welding operations. The cut-resistant materials used in welding gloves are specifically designed to prevent blades, metal edges, or abrasive surfaces from penetrating through the gloves and causing injuries to your hands. This aspect of protection is especially important when handling sharp tools, using cutting equipment, or working in environments with sharp edges or rough metal surfaces.
Reinforced palm and finger areas
To enhance the resistance to cuts and abrasions, welding gloves typically have reinforced palm and finger areas. These reinforced sections provide an additional layer of protection, as they are built with extra layers of durable material or specialized padding. The reinforced palm and finger areas ensure that the most vulnerable parts of your hands are shielded from sharp edges or abrasive surfaces. Whether you’re handling rough materials or operating equipment that requires a firm grip, the reinforced areas of welding gloves offer the necessary protection and peace of mind. They help minimize the risk of cuts, scrapes, or other injuries that can result from direct contact with sharp objects.
Enhanced grip
Maintaining a secure grip on welding tools and equipment is crucial for safety and efficiency. Welding gloves often incorporate features that enhance grip to prevent accidental slips or drops. These gloves may have textured surfaces on the palm and fingers, providing improved friction and allowing for a better hold on tools, materials, or welding electrodes. The enhanced grip ensures that you can handle objects with confidence and reduced risk of accidents. By avoiding dropped tools or materials, you can minimize potential hazards in the welding environment and maintain a smooth workflow without compromising safety.
This image is property of www.safeopedia.com.
Protection against chemicals and oils
Chemical-resistant materials
Welding often involves exposure to various chemicals and oils, which can be harmful to the skin. Welding gloves offer protection against these hazards by utilizing chemical-resistant materials. These materials possess properties that make them resistant to the corrosive effects of chemicals commonly found in welding processes. Chemical-resistant welding gloves prevent harmful substances from coming into direct contact with your skin, reducing the risk of chemical burns, irritations, or other adverse reactions. Whether you’re handling chemicals directly or working in an environment where chemical splash or contamination is possible, using chemical-resistant welding gloves provides an important layer of defense.
Non-absorbent properties
In addition to being chemically resistant, welding gloves also have non-absorbent properties. This means that they do not absorb liquids, including oils and chemicals. Non-absorbent gloves help to prevent the penetration of harmful substances into the gloves’ material, ensuring that your hands stay protected and that the gloves themselves remain in good condition. The non-absorbent properties also make it easier to clean the gloves after use by simply wiping off any spilled chemicals or oils. By keeping your hands shielded from potentially hazardous liquids, non-absorbent welding gloves contribute to a safer and more hygienic working environment.
Protection against impact and puncture
Impact-resistant padding or reinforcement
Welding tasks sometimes involve situations where impact protection is necessary. Welding gloves may incorporate impact-resistant padding or reinforcement in specific areas to safeguard your hands against potential injuries caused by heavy objects or accidental impacts. The padding or reinforcement is strategically placed, typically on the back of the hand or knuckle areas, to absorb and dissipate the force of impact, reducing the risk of fractures, contusions, or other trauma. This feature is especially important when handling heavy tools or during operations where objects are prone to falling or being dropped. Impact-resistant welding gloves provide an additional layer of protection to ensure your hands remain safe from potential impacts.
Puncture-resistant materials
In some welding tasks, there is a risk of puncture injuries from sharp objects or debris. Welding gloves often incorporate puncture-resistant materials, such as multiple layers of strong fabric or specialized inserts, to minimize the likelihood of punctures. These materials provide robust resistance against penetration by sharp objects, offering reliable protection for your hands during welding operations. Whether you’re working with metal fragments, wires, or other sharp materials, puncture-resistant welding gloves help prevent injuries and maintain your hands’ safety.
This image is property of constructioninformer.com.
Protection against cold temperatures
Insulated lining
Welding work may also take place in cold environments, which can be uncomfortable and pose specific risks to your hands. To protect against cold temperatures, welding gloves are often equipped with insulated linings. These linings trap body heat and act as a thermal barrier, preventing the cold from reaching your hands. The insulated lining works to keep your hands warm and comfortable, even in freezing conditions, allowing you to focus on your work without the distraction of numb or chilled hands. This feature is especially beneficial when performing welding tasks outdoors or in refrigerated areas where exposure to cold temperatures is unavoidable.
Thermal-resistant properties
Alongside the insulated lining, welding gloves possess thermal-resistant properties. These properties enable the gloves to resist damage or degradation when exposed to extreme temperature variations. Thermal-resistant welding gloves are designed to maintain their form, integrity, and protective qualities under conditions of both extreme heat and cold. This ensures that the gloves remain functional and effective in protecting your hands, regardless of the thermal environment. With thermal-resistant welding gloves, you can perform your welding tasks confidently and without concerns about the gloves losing their protective capabilities due to temperature extremes.
Comfort and flexibility
Ergonomic design
Welding gloves are not just about protection; they also prioritize your comfort and flexibility while working. Many welding gloves feature an ergonomic design that contours to the natural shape of your hands. This design consideration ensures a snug and comfortable fit, allowing you to maintain dexterity and tactile sensitivity while wearing the gloves. The ergonomic design also reduces fatigue and hand strain, as it eliminates unnecessary bulk or friction that can impede your movements. By providing a comfortable and ergonomic fit, welding gloves enable you to work for extended periods without discomfort and with improved control over your welding tools.
Flexible materials
To enhance flexibility and ease of movement, welding gloves are often constructed with flexible materials. These materials allow your hands to move naturally and without restrictions, ensuring that you have the freedom to perform welding tasks with precision and agility. The flexibility of welding gloves is particularly important when it comes to ergonomic movements and fine adjustments required during welding processes. By maintaining flexibility, the gloves provide a seamless extension of your hands, allowing you to work comfortably and efficiently without compromising safety or control.
Pre-curved fingers
Another feature that contributes to comfort and flexibility in welding gloves is the inclusion of pre-curved fingers. Pre-curved fingers mimic the natural position of your fingers, eliminating the need to exert extra force or strain to grip tools or operate equipment. This ergonomic design detail prevents hand fatigue and allows for more natural and effortless movements. With pre-curved fingers, the gloves conform to the natural contours of your hand, enhancing overall comfort and ensuring that your hands can perform intricate tasks and delicate maneuvers with ease.
This image is property of cdn.thefabricator.com.
Durability and longevity
Quality stitching
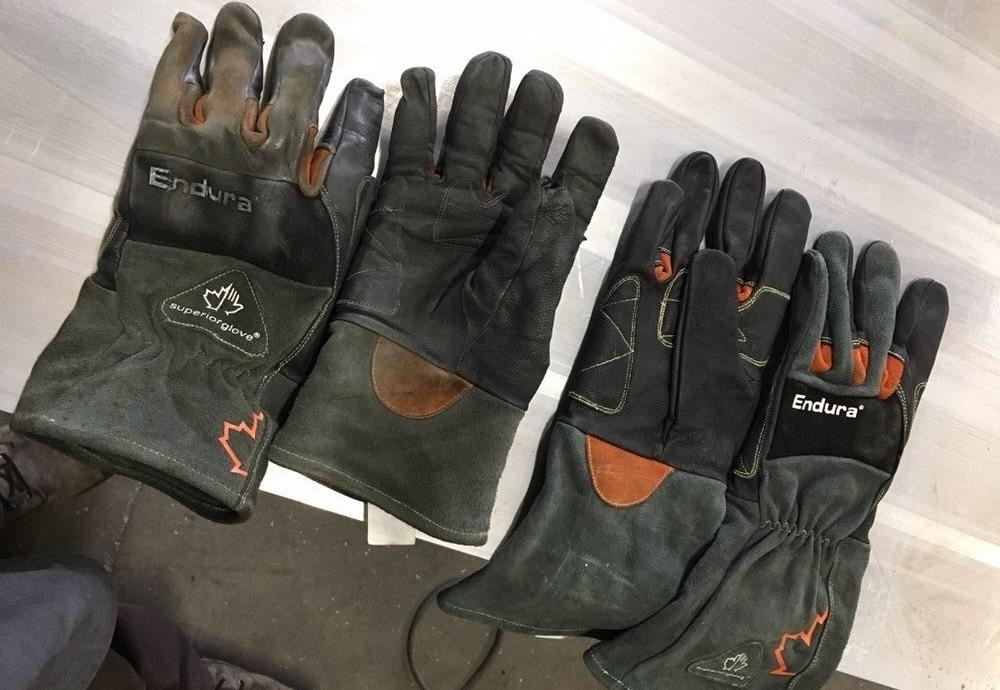
Welding gloves need to withstand the rigorous demands of the welding environment and extensive use. To ensure durability and longevity, welding gloves feature quality stitching. The stitching on welding gloves is designed to be strong, resistant to heat, and able to withstand heavy-duty usage. Quality stitching creates secure seams that keep the gloves intact and prevent them from coming apart, even under challenging conditions. With reliable stitching, welding gloves can withstand repeated wear and tear, maintain their protective properties, and offer long-lasting performance throughout numerous welding projects.
High-quality materials
The use of high-quality materials is another key factor that contributes to the durability and longevity of welding gloves. High-quality materials, such as premium leather or advanced synthetic fabrics, are selected for their strength and resilience. These materials are able to withstand the rigors of welding work, including exposure to heat, flames, sparks, chemicals, and abrasions, without deteriorating or losing their protective qualities. By using high-quality materials, welding gloves are built to last and provide reliable protection over an extended period, ensuring that your hands remain safe throughout your welding endeavors.
Reinforced areas
To further enhance the durability of welding gloves, specific areas prone to higher wear or stress are reinforced. These areas typically include the fingertips, palm, and thumb, which are subject to frequent contact with rough surfaces, sharp objects, or tools. Reinforced sections of welding gloves are often made with multiple layers of durable material or reinforced with additional padding or inserts. The reinforcement adds an extra layer of protection against wear and tear, extending the lifespan of the gloves. By reinforcing these vulnerable areas, welding gloves are better equipped to withstand the demands of the welding environment and ensure their longevity in providing optimal hand protection.
Considerations for different welding processes
MIG and TIG welding
For MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding processes, welding gloves require specific features to accommodate the nature of these tasks. MIG and TIG welding gloves are usually thinner and more dexterous than gloves designed for other welding processes. The thinner materials allow for better tactile sensitivity, enabling welders to have precise control over the welding gun and wire. These gloves are often made from heat-resistant and non-conductive materials to protect against intense heat and electric shocks. Additionally, MIG and TIG welding gloves might have extended cuffs to shield the wrist and lower forearm from heat, sparks, and spatter.
Stick welding
Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), involves a flux-coated electrode that creates an arc with the metal being welded. Stick welding gloves need to provide excellent heat resistance, as they are subjected to high temperatures and intense sparks. These gloves are often made from thick and durable materials that can withstand the heat generated during the process. They may also feature extended cuffs and reinforced areas for additional protection against sparks and spatter. Grip enhancement is also a crucial consideration, as stick welding requires a firm grip on the electrode holder and welding rod.
Plasma cutting
Plasma cutting, used to cut through metal with the help of an electrically conductive gas and high-powered plasma torch, also requires specialized gloves. Plasma cutting gloves must provide protection against heat, sparks, and potential electric shocks. They are typically made from heat-resistant materials and feature reinforced areas to withstand the intense conditions created by the plasma cutting process. Additionally, these gloves often incorporate cut-resistant materials, as the use of the plasma torch can create sharp or abrasive edges that pose a risk of cuts or abrasions. The gloves’ design prioritizes flexibility and a secure grip to ensure optimal control over the plasma cutting torch.
This image is property of cdn.thefabricator.com.