Arc welding is a vital technique used in a multitude of industries, from construction to automotive manufacturing. However, one crucial aspect that often goes unnoticed is determining the appropriate shade level for arc welding. With our eyes being the gateway to the world around us, protecting them during this high-intensity process is paramount. In this article, we explore the different shade levels typically recommended for various types of arc welding, ensuring that you have all the necessary information to ensure your safety and productivity.
Factors to Consider for Selecting Shade Level
When it comes to selecting the appropriate shade level for arc welding, there are several factors that need to be taken into consideration. Each factor plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and comfort of the welder. By understanding these factors, welders can make informed decisions about shade level selection that ultimately enhance their welding experience and protect their vision.
Type of Welding Process
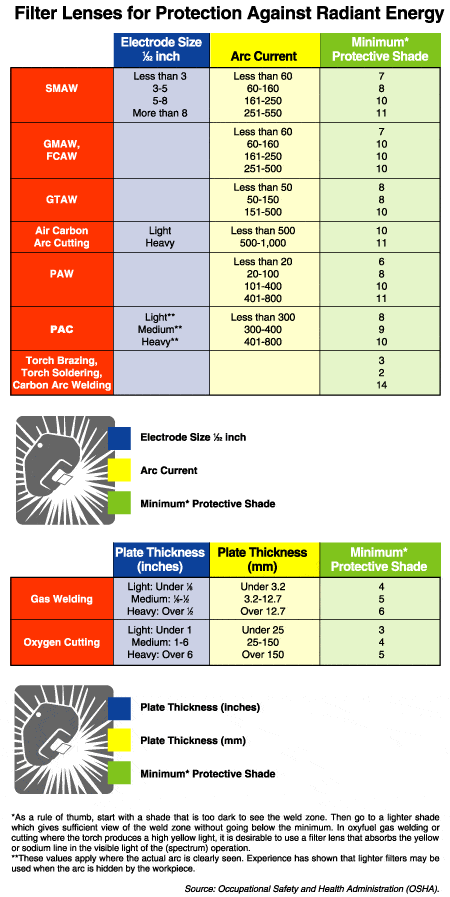
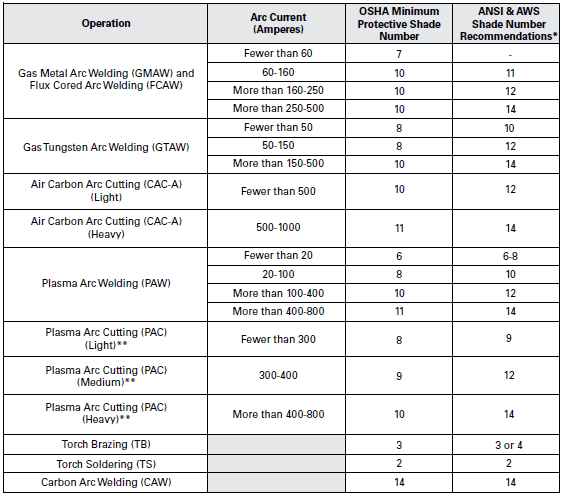
The type of welding process being used greatly influences the shade level needed for optimal protection. Different welding processes emit different levels of brightness and UV radiation. For example, Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) typically requires a higher shade level due to the intense brightness and sparks produced during the process. On the other hand, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG) requires a lower shade level since it generates a more focused and dimmer arc. Understanding the specific characteristics of each welding process is essential in determining the appropriate shade level to use.
Electrode Diameter and Amperage
The electrode diameter and amperage used in the welding process also affect the ideal shade level. As a general rule, larger electrode diameters and higher amperages result in a brighter arc and increased UV radiation. In such cases, a higher shade level is required to adequately protect the welder’s eyes. Conversely, smaller electrode diameters and lower amperages produce a less intense arc and may warrant the use of a lower shade level.
Metal Thickness and Joint Configuration
Metal thickness and joint configuration play a significant role in determining the necessary shade level for welding. Thicker metals tend to reflect more light and require a darker shade level to prevent excessive glare. Similarly, joint configurations that obstruct the welder’s line of sight may necessitate a higher shade level to ensure clear vision. Assessing the metal thickness and joint configuration is crucial in selecting the optimal shade level for the welding task at hand.
Welding Position
The welding position, whether it is overhead, horizontal, or vertical, influences the choice of shade level. Certain positions may cause the arc to be closer to the welder’s face, resulting in increased light exposure. In such cases, a higher shade level is necessary to mitigate the potential risks to the welder’s eyes. Taking the welding position into account enables welders to select the correct shade level for maximum safety and visibility.
Personal Preference and Comfort
Personal preference and comfort also play a role in shade level selection. While safety and protection should always be the top priority, individual welders may have personal preferences when it comes to the darkness of their helmet’s shade level. Some may find higher shade levels uncomfortable or restrictive, while others may prefer a darker shade for added protection and reduced eye strain. Finding the right balance between safety and personal comfort is important in ensuring a positive welding experience.
Arc Current
The arc current, or the amount of electrical current flowing through the welder’s arc, is another critical factor to consider. Higher arc currents generally result in a brighter and more intense arc. As a result, a higher shade level is necessary to shield the welder’s eyes from the excessive brightness. Conversely, lower arc currents may allow for the use of a lighter shade level. Monitoring and adjusting the shade level based on the arc current helps maintain optimal visibility and safety during welding.
Arc Voltage
Similar to arc current, the arc voltage also affects the brightness and intensity of the welding arc. Higher arc voltages typically produce a brighter arc and necessitate a higher shade level for eye protection. Conversely, lower arc voltages may allow for a lighter shade level. Welders should be aware of the arc voltage and adjust their shade level accordingly to ensure their safety and visual clarity.
Lighting Conditions
The lighting conditions in the welding environment influence the selection of shade level. Bright ambient lighting may necessitate the use of a darker shade level to prevent excessive glare and improve visibility. Conversely, welding in darker or low-light environments may require a lighter shade level to compensate for reduced visibility. Considering the lighting conditions is essential in achieving the appropriate shade level for optimal safety and performance.
Welder’s Experience and Skill Level
The welder’s experience and skill level should also be taken into account when selecting the shade level. Novice welders may require a higher shade level to compensate for potential errors or lack of experience in maintaining proper arc positioning. As welders gain more experience and proficiency, they may be able to work with lighter shade levels while still ensuring their safety. Evaluating the welder’s experience and skill level is crucial in determining the appropriate shade level for a successful welding operation.
Safety Regulations and Standards
Compliance with safety regulations and standards is of utmost importance in the welding industry. Different regions and organizations may have specific guidelines and requirements regarding shade level selection. Welders must familiarize themselves with these regulations and ensure that their shade level choices align with the prescribed safety standards. Adhering to safety regulations and standards not only protects the welder but also contributes to a culture of safety within the welding industry.
Types of Shade Levels
When it comes to shade levels for welding helmets, there are various options available, each designed for specific welding applications. It is crucial for welders to understand the different shade levels and their respective purposes to ensure adequate eye protection.
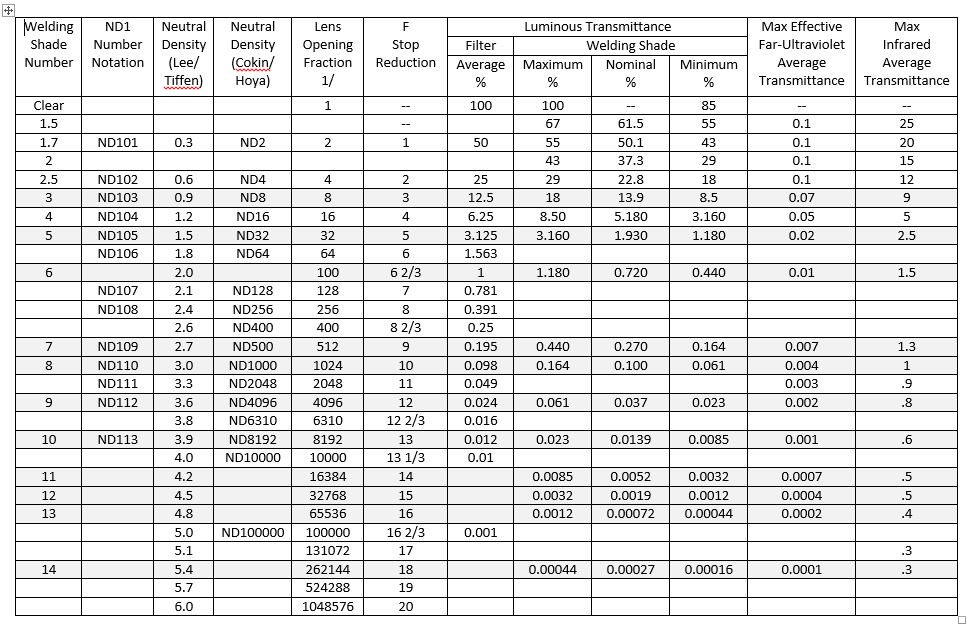
Shade Level 8-10
Shade levels 8-10 are commonly used for cutting and low amperage welding processes. These shade levels allow enough light transmission to provide a clear view of the workspace while still protecting the eyes from harmful radiation. They are suitable for applications such as plasma cutting, oxy-fuel welding, and light-duty welding tasks.
Shade Level 11-12
Shade levels 11-12 are typically used for general welding tasks and offer enhanced eye protection. These shade levels provide moderate light transmission, allowing welders to have a reasonably clear view of their workpieces while reducing the intensity of the arc. Shade levels 11-12 are suitable for Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG), and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW).
Shade Level 13-14
Shade levels 13-14 are recommended for high amperage welding applications. These shade levels significantly reduce light transmission, shielding the eyes from intense arc brightness and UV radiation. Welders engaged in heavy-duty welding processes, such as overhead welding or higher amperage processes, should consider using shade levels 13-14 for optimum eye protection.
Shade Level Above 14
Some specialized welding applications, such as atomic hydrogen welding, require shade levels above 14. These extremely dark shade levels provide maximum protection from the intense brightness and UV radiation associated with such processes. Welders engaged in these unique applications should consult industry standards and guidelines to determine the precise shade level requirements.
This image is property of www.millerwelds.com.
Effects of Inadequate Shade Level
Using an inadequate shade level during welding can have detrimental effects on both the welder’s health and the quality of the weld. Failing to provide adequate eye protection exposes the welder to various risks and may result in severe consequences.
Eye Strain and Fatigue
Insufficient shade levels can lead to eye strain and fatigue during prolonged welding sessions. The intense brightness of the arc forces the eyes to work harder to focus, resulting in eye strain and discomfort. Over time, this can lead to headaches, blurred vision, and decreased overall performance.
Arc Eye (Photokeratitis)
Arc eye, also known as photokeratitis, is a painful condition caused by exposure to intense ultraviolet (UV) radiation from arc welding. Insufficient shade levels fail to filter out the harmful UV radiation, resulting in damage to the surface of the eye. Symptoms of arc eye include eye redness, tearing, sensitivity to light, and a gritty sensation. While the condition is usually temporary, it can be extremely painful and may require medical treatment.
Retinal Damage
Inadequate shade levels can also result in long-term retinal damage. The intense arc brightness and UV radiation can cause phototoxicity, a condition where the retina sustains harm due to excessive exposure to light. Prolonged or repeated exposure to UV radiation without the proper shade level can lead to irreversible damage to the retina and vision loss over time.
Reduced Welding Quality and Accuracy
Using an inappropriate shade level can have a direct impact on the quality and accuracy of the weld. Insufficient eye protection limits the welder’s ability to clearly see the weld pool, resulting in inconsistent and flawed welds. Adequate shade levels are crucial for maintaining visibility of the welding area, ensuring accurate weld placement, and achieving desired weld quality.
Increased Risk of Accidents and Injuries
Failure to use the correct shade level significantly increases the risk of accidents and injuries. Without proper eye protection, welders are more likely to experience temporary visual impairments like glare, flash, and reduced depth perception. These impairments can lead to mistakes, misjudgments, and accidents, placing both the welder and those nearby at risk. Adequate shade levels are essential in preventing accidents and promoting a safe working environment.
Choosing the Right Shade Level
Selecting the appropriate shade level for arc welding involves considering a range of factors and making informed decisions in alignment with industry standards and personal preference. The following guidelines can help welders in their shade level selection process.
Referencing Industry Standards
First and foremost, welders should consult the relevant industry standards and guidelines regarding shade level selection. Organizations like the American Welding Society (AWS) provide comprehensive recommendations on shade levels for different welding processes, ensuring compliance with safety standards and minimizing the risk of eye injuries.
Welding Application Considerations
Understanding the specific welding application is crucial in determining the appropriate shade level. Consider factors such as the welding process, amperage, electrode diameter, joint configuration, and metal thickness. By evaluating these application-specific variables, welders can make more informed decisions about shade level selection.
Testing Different Shade Levels
If uncertain about the ideal shade level, it is advisable to test different options to find the most appropriate one. Welders can experiment with shades within the range recommended for their specific task and assess how well they can see the welding arc, the weld pool, and the surrounding workspace. Through trial and error, welders can identify the shade level that offers optimal visibility without compromising safety.
Adjusting Shade Level based on Feedback and Comfort
Welders should listen to their own feedback and evaluate their comfort levels with different shade levels. If the selected shade level feels restrictive, causes discomfort, or impedes visibility, adjustments may be necessary. It is crucial to strike a balance between optimal protection and personal comfort to promote safety and productivity.
Updating Shade Level with Changes in Welding Conditions
As welding conditions change, such as when the amperage or process is altered, the appropriate shade level may also need adjustment. It is essential for welders to reassess the welding conditions periodically and make necessary modifications to the shade level for ongoing eye protection.
This image is property of www.euromarc.co.nz.
Common Shade Levels for Different Welding Processes
Different welding processes have specific shade level recommendations to ensure proper eye protection. Here are some common shade level guidelines for various welding processes:
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
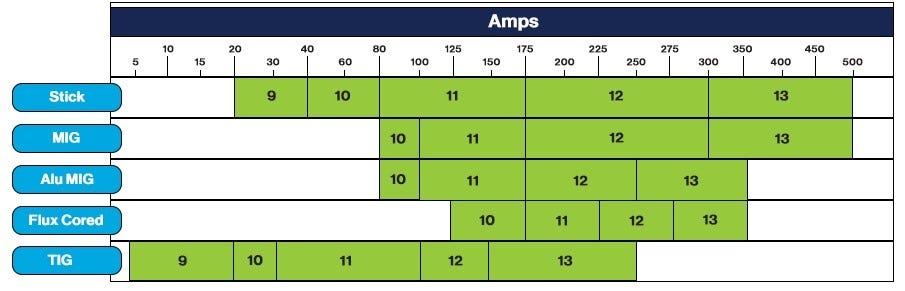
For SMAW, which is commonly referred to as stick welding, shade levels between 9 and 13 are typically recommended. The exact shade level depends on the welding application, amperage, and electrode diameter. Welders should adhere to the industry standards for SMAW shade level selection.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG)
Gas Metal Arc Welding, also known as MIG welding, generally requires shade levels ranging from 10 to 13. The specific shade level within this range depends on factors such as the welding process variant, amperage, and material thickness. Referencing industry guidelines for GMAW shade levels is essential for optimal eye protection.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Flux-Cored Arc Welding typically calls for shade levels between 10 and 14, depending on the specific variant of the process, amperage, and welding application. Welders should consult industry recommendations for FCAW shade level selection and adjust as needed based on the specific circumstances.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG)
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, commonly known as TIG welding, often requires shade levels ranging from 8 to 13. The appropriate shade level within this range depends on factors such as the welding application, amperage, and tungsten electrode size. Following industry standards for GTAW shade levels ensures optimal eye protection during TIG welding.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Submerged Arc Welding typically necessitates a higher shade level due to the intense brightness of the welding arc. Shade levels ranging from 10 to 14 are commonly recommended, depending on the specific requirements of the welding application and amperage used. Welders should consult industry guidelines and adjust the shade level accordingly for Submerged Arc Welding tasks.
Factors Affecting Shade Level Visibility and Perception
While selecting the appropriate shade level is crucial for eye protection, several factors can affect the visibility and perception of the shade level. Being aware of these factors helps welders optimize their visual clarity and enhances their overall welding experience.
Lens Coatings and Filters
Different lens coatings and filters can affect how welders perceive the shade level. Anti-glare coatings and filters can reduce glare and improve visibility. Additionally, some coatings offer enhanced color recognition, making it easier to see the workpiece and weld pool. Selecting high-quality lenses with suitable coatings and filters can enhance the overall visibility and perception of the shade level.
Ambient Lighting Conditions
The ambient lighting conditions in the welding environment influence how welders perceive the shade level and their overall visibility. Bright lighting conditions may cause the shade level to appear less effective, resulting in increased eye strain. Similarly, low-light conditions may make the shade level appear darker than intended, potentially hindering visibility. Being aware of the ambient lighting conditions helps welders adjust their shade level preferences accordingly.
Welding Helmet Design and Fit
The design and fit of the welding helmet can impact how welders perceive the shade level. Comfortable and well-fitting helmets ensure that the lens is positioned correctly in front of the eyes, allowing for optimal visibility and clarity. Proper helmet design and fit contribute to a better overall perception of the shade level and enhance the welder’s ability to perform their tasks effectively.
Personal Health Conditions (e.g., Vision, Color Blindness)
Individual welders may have personal health conditions that affect their vision or color perception. It is essential for welders to consider any underlying health conditions, such as vision impairments or color blindness, when selecting their shade level. Adjusting the shade level to accommodate these conditions ensures optimal visibility and reduces the risk of errors or accidents.
This image is property of vseyewear.com.
Technological Advancements in Auto-Darkening Helmets
Technological advancements have revolutionized the welding industry, particularly in the development of auto-darkening helmets. These helmets offer a range of features that enhance both productivity and safety for welders.
Variable Shade Level Selection
Auto-darkening helmets allow welders to select and adjust the shade level according to their specific needs and preferences. This flexibility ensures optimal eye protection while maintaining visibility of the welding area and workpiece. Welders can easily switch between shade levels without the need for manual adjustments or changing lenses.
Sensitivity and Delay Adjustments
Auto-darkening helmets provide precise control over sensitivity and delay settings. Sensitivity adjustments allow welders to fine-tune the helmet’s response to arc brightness, preventing any interruption or delay in darkening when the welding arc ignites. Delay adjustments help control the transition time from the darkened state back to the clear state, allowing for seamless visibility in between welds.
Enhanced Optical Clarity
Modern auto-darkening helmets feature enhanced optical clarity, improving the welder’s overall visibility. High-quality lenses allow for accurate color recognition, sharper contrast, and reduced distortion. This clarity enhances the welder’s ability to see the weld pool, workpiece, and surroundings, resulting in improved welding accuracy and quality.
Integration of Grind Mode
Many auto-darkening helmets now include a grind mode feature. Grind mode allows welders to switch to a light shade level specifically designed for grinding applications. This eliminates the need for changing helmets or lenses when transitioning between welding and grinding tasks, enhancing convenience and productivity.
Smart Helmet Features for Productivity and Safety
Some auto-darkening helmets incorporate smart features such as Bluetooth connectivity, arc sensing technology, and compatibility with welding data management systems. These features allow for seamless integration with other welding equipment and enable welders to monitor and analyze their welding parameters. Smart helmet features enhance both productivity and safety by providing real-time data and facilitating process optimization.
Training and Education on Shade Level Selection
Proper training and education are vital components of effective shade level selection. By providing welders with comprehensive instruction and knowledge, organizations can ensure that workers are equipped to make informed decisions about shade levels and prioritize eye health and safety.
Importance of Proper Training
Proper training is essential to educate welders about the potential risks associated with inadequate shade levels and to instill safe welding practices. Training programs should cover the fundamentals of shade level selection, industry guidelines, and the effects of excessive exposure to arc light. By emphasizing the importance of eye protection, employers can create a culture of safety and reduce the risk of eye injuries.
Educating Welders on Shade Level Guidelines
Welders should receive education on the shade level guidelines recommended for their specific welding processes and applications. They should be familiarized with the factors that influence shade level selection, including welding process, amperage, electrode diameter, joint configuration, and metal thickness. This education ensures that welders make informed decisions about shade levels based on industry standards and best practices.
Continuous Learning and Updates
The welding industry is constantly evolving, and new information about shade level selection and eye protection emerges regularly. Continuous learning and updates on industry standards, advancements in technology, and best practices should be emphasized. Employers and welders should stay informed about the latest developments in shade level guidelines to ensure ongoing eye health and safety.
Promoting Eye Health and Safety Awareness
Promoting eye health and safety awareness among welders is crucial for reducing the risk of eye injuries. Organizations should foster a culture that prioritizes eye safety and encourages open dialogue about eye protection measures. Regular safety meetings, signage, and reminders can help reinforce the importance of shade level selection and provide ongoing support and resources for welders.
This image is property of image.thefabricator.com.
Periodic Eye Examinations and Protection
In addition to shade level selection, welders should consider other measures to protect their eyes and maintain their visual health. Periodic eye examinations and the use of suitable eye protection equipment are essential components of a comprehensive eye care routine.
Eye Examinations for Welders
Welders should undergo regular eye examinations to monitor their visual health. Eye examinations can detect any early signs of eye conditions or injuries caused by welding. Optometrists and ophthalmologists with experience in occupational eye health can provide valuable insights and recommendations specific to welding-related eye care.
Prescription Eyeglasses and Filters
For welders requiring vision correction, prescription eyeglasses with appropriate filters should be used in conjunction with welding helmets. These glasses provide personalized eye protection, ensuring optimal visual acuity and shade level customization. It is crucial to consult with an eye care professional specializing in occupational eye health to determine the most suitable eyeglasses and filters for welding tasks.
Importance of Eye Protection Measures
In addition to shade level selection, welders must utilize other eye protection measures to minimize the risk of eye injuries. Safety glasses, goggles, or face shields can provide an additional layer of protection from welding debris, sparks, and flying particles. Welders should wear these forms of eye protection whenever necessary, regardless of the shade level of their welding helmet.
Routine Maintenance of Welding Helmets and Lenses
Routine maintenance of welding helmets and lenses is essential for ensuring optimal performance and eye protection. Regular cleaning of lenses, inspection for scratches or cracks, and replacement of damaged parts should be conducted to maintain clear visibility. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for helmet maintenance and lens replacement prolongs the lifespan of the equipment and ensures continued eye safety.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate shade level for arc welding is a critical aspect of maintaining eye health and safety. By considering factors such as the welding process, electrode diameter and amperage, metal thickness and joint configuration, welding position, personal preferences, and other influencing factors, welders can make informed decisions about the shade level that suits their specific needs. Applying industry standards, staying updated on advancements in auto-darkening helmet technology, and prioritizing training and eye health education contribute to the overall safety and well-being of welders. By adopting a proactive approach to shade level selection and eye protection, welders can continue to carry out their work with maximum safety, accuracy, and comfort.
This image is property of weldknowledge.files.wordpress.com.