Whether you are a professional welder or someone looking to learn more about the field, it is crucial to understand the safety aspects of welding.
The article “Is Welding A Safe Process?” examines the potential hazards involved in welding and highlights the necessary precautions that should be taken to ensure a safe working environment.
From protective gear to proper ventilation, this article provides valuable insights on mitigating risks and prioritizing safety in the welding world.
Potential Hazards in Welding
Welding is an advantageous and essential process in many industries. Still, it can also pose several potential hazards that must be carefully managed to ensure the safety of everyone involved. Understanding these hazards and taking proactive measures to prevent them is crucial. Let’s explore some of the main hazards associated with welding.
Electric Shock
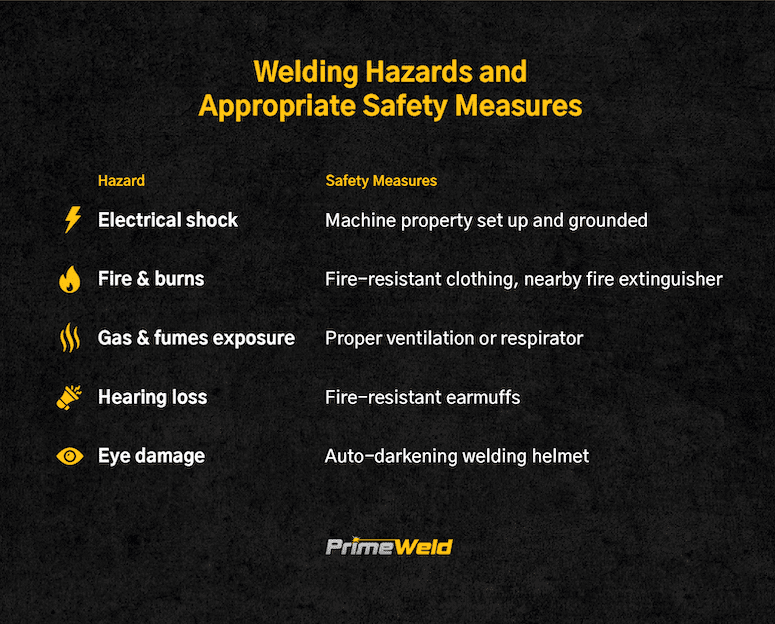
One of the most significant hazards in welding is electric shock. Welding involves high-voltage electrical currents, which can be extremely dangerous if improperly handled. Electric shocks can cause severe injuries or even be fatal.
To prevent electric shock, it is essential to ensure that all electrical equipment is properly grounded and circuits are protected with ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs). Additionally, training and education on safe work practices around electricity are vital to minimize the risk of electric shock.
Health Hazards
Welding fumes and gases can pose significant health risks if inhaled. These substances can contain toxic metals such as lead, zinc, and chromium, as well as harmful gases like ozone and nitrogen dioxide.
Prolonged exposure to welding fumes and gases can cause various health issues, including respiratory diseases, lung cancer, and metal fume fever. Personal protective equipment (PPE) like respiratory protection and proper ventilation systems are crucial in minimizing exposure to these hazardous substances.
Fire and Explosions
Welding involves intense heat, sparks, and open flames, which create a high risk of fire and explosions. Without proper precautions, nearby flammable materials can ignite, leading to devastating consequences.
To prevent fires and explosions, it is essential to maintain a clear and safe workspace free from any combustible materials. Fire prevention measures such as the availability of fire extinguishers and fire-resistant barriers are essential for a safe welding environment.
Eye Injuries
Another potential hazard in welding is eye injuries. Intense light, radiation, and molten metal sparks emitted during welding can cause severe damage to the eyes.
Welders must always wear appropriate eye protection, such as welding helmets and face shields, to shield their eyes from harmful UV rays, infrared radiation, and flying debris. Regular eye check-ups and prompt treatment of any eye injuries are crucial in ensuring long-term eye health.
Burns and Heat-related Injuries
Welding involves working with extremely high temperatures, which can cause burns and heat-related injuries if proper precautions are not taken.
Welders must always wear protective clothing, including flame-resistant jackets, gloves, and appropriate footwear to minimize the risk of thermal burns. Safe work practices, such as keeping a safe distance from hot surfaces and using heat-resistant barriers, are crucial in preventing heat-related injuries.
Fumes and Gases
As mentioned earlier, welding fumes and gases can be harmful to health. In addition to respiratory issues, prolonged exposure to these substances can cause skin disorders.
Welders must wear appropriate protective clothing, including long-sleeved shirts, pants, and gloves, to minimize skin exposure to welding fumes and chemicals. Regular skin checks and prompt skin irritation or burns treatment are essential.
Noise Exposure
Welding can produce high noise levels, harming hearing if not adequately controlled. Prolonged exposure to excessive noise can lead to permanent hearing loss.
Welders should wear hearing protection devices like earmuffs or earplugs when working in noisy environments. Regular hearing checks and periodic breaks from noise exposure protect welders’ hearing health.
Preventive Measures
Implementing preventive measures is crucial to address the potential hazards in welding effectively. The risk of accidents and injuries can be significantly reduced by prioritizing safety and following established guidelines and regulations. Here are some preventive measures that all welders and employers should consider:
Training and Education
Proper training and education are fundamental in promoting welding safety. Welders should undergo comprehensive training on welding techniques, potential hazards, and safe work practices before operating equipment. Ongoing education and training programs should also be encouraged to ensure welders are updated with the latest safety standards and practices.
Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is vital in safeguarding welders from potential hazards. Welders must wear appropriate PPE, including welding helmets and face shields, protective clothing, respiratory protection, gloves, and appropriate footwear. Employers should provide the necessary PPE and ensure it is properly maintained and regularly inspected for defects.
Safe Work Practices
Establishing and implementing safe work practices is essential in preventing accidents and injuries. Welders should be trained on safe welding techniques, proper handling and storage of equipment, and the importance of keeping the workspace clean and free from hazards. Adhering to safety procedures, such as avoiding shortcuts and rushing tasks, is critical in maintaining a safe working environment.
Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial in minimizing exposure to welding fumes and gases. Adequate ventilation systems, such as local exhaust systems, should be installed in welding areas to effectively capture and remove harmful airborne contaminants. Regular maintenance and inspections of ventilation systems are necessary to ensure optimal functioning.
Fire Prevention Measures
Fire prevention should be a top priority in welding environments. Implementing fire prevention measures, such as maintaining transparent workspaces, removing flammable materials, and having fire extinguishers readily available, can significantly reduce the risk of fires and explosions. Regular fire drills and training on fire emergency procedures should also be conducted to ensure that all personnel is prepared during a fire.
Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is of utmost importance in welding operations. Ensuring that all electrical equipment is properly grounded and protected with ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) can significantly reduce the risk of electric shock. Welders should receive training on safe work practices around electricity, such as not working with wet hands and avoiding contact with overhead power lines.
These preventive measures can create a safer welding environment, minimizing the risk of accidents, injuries, and long-term health issues.
Welding Safety Standards and Regulations
To ensure welding safety, various organizations have established standards and regulations that outline best practices and guidelines. Adhering to these standards is crucial in maintaining a safe working environment. Here are three key organizations that focus on welding safety standards:
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
OSHA is a federal agency that sets and enforces workplace safety and health regulations in the United States. OSHA provides guidelines specific to welding operations, including safety requirements, hazard communication, and personal protective equipment. Employers should familiarize themselves with OSHA standards to ensure compliance and the well-being of their workers.
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
ANSI is a private, non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for various industries, including welding. ANSI standards cover a wide range of topics related to welding safety, such as welding qualifications, fire prevention, and ventilation requirements. Following ANSI standards can help ensure high safety in welding operations.
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
NFPA is an international organization focusing on fire prevention and safety standards in various industries, including welding. NFPA standards provide guidelines for fire prevention, protection, and safety measures in welding operations. Following NFPA standards can significantly enhance the fire safety aspects of welding processes.
By adhering to these standards and regulations, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to maintaining a safe and healthy work environment for their welders.
Risk Assessment and Job Hazard Analysis
Before commencing any welding project, conducting a thorough risk assessment and job hazard analysis is essential. This process helps identify potential hazards, evaluate risk levels, and develop appropriate safety procedures. Here are the critical steps involved in risk assessment and job hazard analysis:
Identifying Potential Hazards
The first step in a risk assessment is to identify potential hazards associated with the welding operation. This includes evaluating risks related to electric shock, health hazards, fire and explosions, eye injuries, burns and heat-related injuries, fumes and gases, and noise exposure. Identifying specific hazards allows for tailored preventive measures to be put in place.
Evaluating Risk Levels
Once potential hazards are identified, the next step is to assess the risk levels associated with each hazard. This involves evaluating the likelihood of an incident occurring and the severity of the potential consequences. Risk levels help prioritize preventive measures and allocate resources accordingly.
Developing Safety Procedures
Based on the risk assessment and hazard analysis, appropriate safety procedures should be developed and documented. These procedures may include step-by-step instructions on safe work practices, emergency response plans, and guidelines for properly using personal protective equipment. Regular updates and reviews of safety procedures ensure that they remain relevant and practical.
By following a systematic approach to risk assessment and job hazard analysis, organizations can proactively manage potential hazards and ensure the safety of their welding operations.
Health Effects of Welding
While welding is an essential process, it can have adverse health effects if proper precautions are not taken. Understanding these health effects is crucial for welders to protect themselves and for employers to implement necessary preventive measures. Here are some of the leading health effects associated with welding:
Fume Fever
Fume fever, or “metal fume fever,” is a common health effect of welding. The inhalation of certain metal fumes, such as zinc, aluminum, and copper oxide, causes it. Symptoms include flu-like symptoms like fever, chills, headache, and muscle aches. The best way to prevent fume fever is by using proper ventilation systems and wearing respiratory protection.
Lung Cancer
Prolonged exposure to welding fumes can increase the risk of developing lung cancer. Welding fumes often contain carcinogenic substances such as chromium, nickel, and arsenic. Proper respiratory protection and ventilation are crucial in minimizing the risk of lung cancer in welders.
Pneumonia
Inhalation of certain welding fumes and gases can lead to pneumonia. Gases like ozone and nitrogen dioxide, often generated during welding, can irritate the lungs, making them more susceptible to bacterial or viral infections. Adequate respiratory protection and ventilation systems are necessary to prevent pneumonia.
Respiratory Diseases
Welders risk developing various respiratory diseases due to inhaling welding fumes and gases. These diseases include chronic bronchitis, asthma, and occupational lung diseases. Proper respiratory protection, such as powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) or supplied air systems, can help prevent respiratory diseases.
Skin Disorders
Exposure to certain welding fumes and chemicals can also cause skin disorders. Skin irritation, burns, and allergic reactions are joint in welders who come into contact with substances like solvents, fluxes, or metal dust. Wearing appropriate protective clothing, such as gloves and long-sleeved shirts, and practicing good hygiene are essential in protecting the skin.
Understanding these health effects and taking appropriate preventive measures is crucial for welders to ensure their long-term health and well-being.
Protecting Against Electric Shock
Electric shock is one of the most significant hazards in welding, but fortunately, there are several ways to protect against it. By implementing the following measures, welders can minimize the risk of electric shock:
Insulation and Grounding
Ensuring all electrical equipment, including welding machines, cables, and power sources, is properly insulated and grounded is essential. Insulation prevents accidental contact with live wires, while grounding provides a safe path for electrical current in case of a fault. Regular checks of insulation and grounding systems should be conducted to ensure their effectiveness.
Use of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs)
Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) protect against electric shock by monitoring the flow of electrical current. They automatically interrupt or “trip” the circuit if any abnormality, such as a ground fault or current leakage, is detected. GFCIs should be installed in all electrical circuits used for welding to provide additional protection.
Safe Work Practices Around Electricity
Welders should be trained on safe work practices to minimize the risk of electric shock. This includes avoiding contact with energized parts, using non-conductive tools and equipment, and wearing appropriate insulated gloves when working with electrical equipment. Regular inspections of electrical equipment should also be conducted to identify potential issues.
Avoiding Overhead Power Lines
When welding outdoors, it is essential to be mindful of overhead power lines. Contact with power lines can result in electric shock or electrocution. Welders should always maintain a safe distance from power lines and prevent accidental contact, such as erecting barriers or using non-conductive materials.
By implementing these protective measures, welders can significantly reduce the risk of electric shock, ensuring a safer working environment.
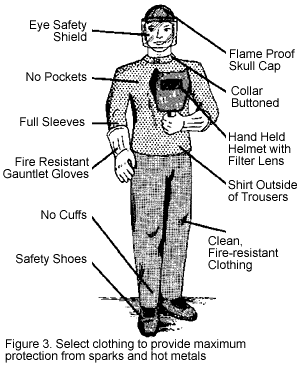
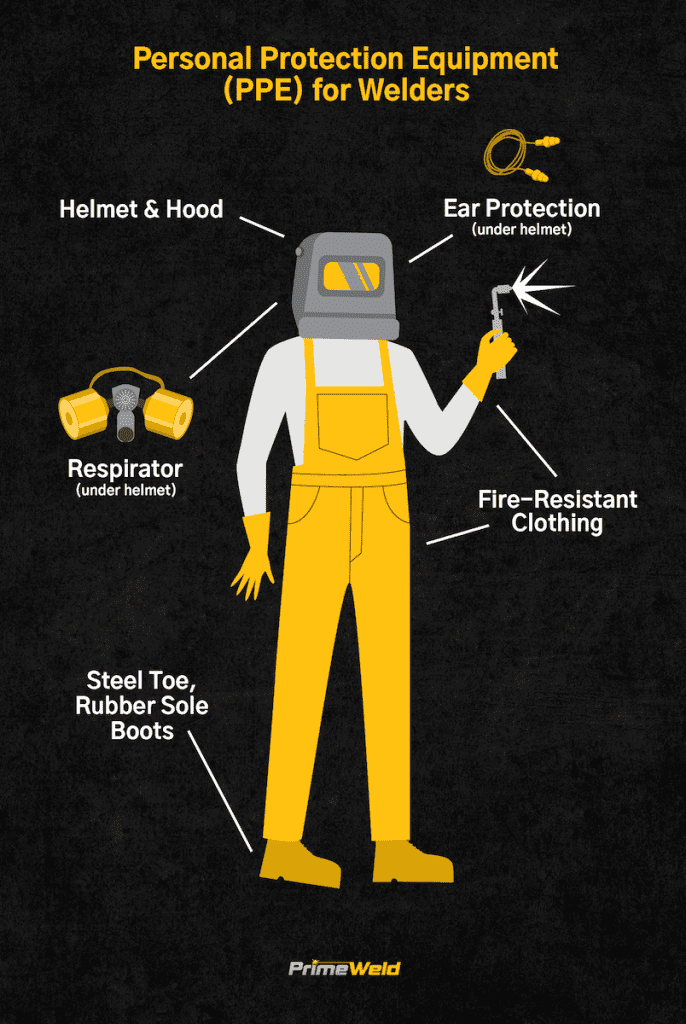
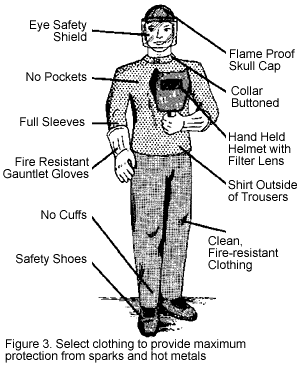
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a crucial component of welding safety. Welders should use the following PPE items to protect themselves from potential hazards:
Welding Helmets and Face Shields
Welding helmets and face shields protect the eyes and face from intense light, radiation, and flying debris. They should have a proper shade lens that filters harmful UV and infrared radiation. Welders should wear helmets and face shields at all times during welding operations.
Protective Clothing
Welders should wear flame-resistant clothing made of leather or denim to protect the body from sparks, molten metal, and thermal hazards. Clothing should cover the arms, legs, and torso completely. Ensuring that clothing is not worn under protective gear is crucial, as it may catch fire.
Respiratory Protection
To protect against welding fumes and gases, respiratory protection is essential. Depending on the level of exposure, welders should wear respirators, such as disposable masks or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs), equipped with appropriate filters. The respirator should be properly fit-tested and worn throughout welding operations.
Gloves and Hand Protection
Welders’ hands are vulnerable to burns, cuts, and injuries from sharp objects. Heat-resistant gloves made of leather or other flame-resistant materials should be worn to protect against thermal hazards. Gloves should be appropriately fitted for dexterity and grip while ensuring complete hand protection.
Foot Protection
Appropriate footwear protects the feet from falling objects, sparks, and electrical hazards. Welders should wear steel-toed boots or shoes made of flame-resistant materials. The footwear should have non-slip soles to prevent accidental slips and falls in the work area.
Proper training, regular inspection, and maintenance of personal protective equipment are vital to ensure their effectiveness in protecting welders from potential hazards.
Safe Work Practices
In addition to using personal protective equipment, following safe work practices is essential in maintaining a safe working environment during welding operations. The following practices should be implemented:
Proper Ventilation and Local Exhaust Systems
Adequate ventilation and local exhaust systems are crucial in removing welding fumes and gases from the working area. Properly designed ventilation systems ensure the continuous flow of fresh air, reducing the risk of hazardous exposure. Regular inspections and proper maintenance of ventilation systems are necessary to keep them functioning effectively.
Safe Storage and Handling of Compressed Gases
Compressed gases, such as oxygen and acetylene, are commonly used in welding operations. Proper storage and handling of these gases are essential to prevent accidents and leaks. Gas cylinders should be securely stored in well-ventilated areas, away from heat sources or flammable materials. Handling of gas cylinders should follow established guidelines to avoid damage or injury.
Avoidance of Confined Spaces
Working in confined spaces like tanks or vessels can pose severe risks to welders. Lack of oxygen, accumulation of toxic gases, and limited escape routes are common hazards in confined spaces. Adequate training, proper permits, and monitoring systems are necessary to ensure the safety of welders working in confined spaces.
Adherence to Safety Procedures
Adhering to established safety procedures is critical in maintaining a safe working environment. Welders should follow approved work procedures, such as pre-welding inspections, equipment, and weld quality checks. Any deviations or abnormalities should be reported promptly to supervisors. Regular safety meetings and reminders promote a safety-conscious work culture.
Regular Equipment Maintenance
Regular maintenance of welding equipment is necessary to ensure its safe and optimal functioning. Welding machines, cables, and accessories should be inspected regularly for defects, worn-out parts, or loose connections. Any malfunctioning or damaged equipment should be repaired or replaced promptly to prevent accidents or injuries.
By incorporating these safe work practices into daily welding operations, organizations can create a safer working environment and minimize the risk of accidents.
Education and Training
Education and training play a vital role in promoting welding safety. Along with technical skills, welders should receive comprehensive education and training on the potential hazards of welding and the necessary precautions. The following aspects of education and training are essential:
Understanding Welding Hazards
Welders should have a thorough understanding of the potential hazards associated with welding. This includes knowledge of the health effects of welding fumes and gases, the risks of electric shock, fire, and explosion hazards, and the importance of personal protective equipment. Understanding these hazards allows for better risk management and preventive measures.
Training on Safe Work Practices
Proper training on safe work practices is crucial for welders to minimize the risk of accidents and injuries. This includes training on the safe use of welding equipment, proper handling and storage of materials, and maintaining a clean and organized work area. Ongoing training ensures welders are updated with the latest safety standards and practices.
Qualifications and Certification
Obtaining the proper qualifications and certification is essential to promoting welding safety. Welders should undergo formal training programs and pass certification exams to demonstrate their competency in welding techniques and safety practices. Certified welders assure employers that their workers have the necessary skills and knowledge to work safely.
Continuous Professional Development
Continuing education and professional development are essential for welders to enhance their skills and stay updated on the latest developments in welding safety. Attending seminars, workshops, and industry conferences provide opportunities for learning and networking. Continuous professional development ensures welders are equipped to tackle new challenges and advancements in the field.
By investing in education and training, organizations can empower welders with the knowledge and skills necessary to work safely and effectively.
Establishing a Safety Culture
Organizations must establish a strong safety culture to sustain a safe working environment for welders. Safety culture involves a collective commitment to safety, where everyone, from management to employees, prioritizes safety in all aspects of their work. Here are some critical aspects of establishing a safety culture:
Leadership and Management Commitment
Leadership and management are crucial in setting the tone for a safety culture. By demonstrating a solid commitment to safety through their words and actions, leaders inspire employees to prioritize safety. Allocating resources for safety initiatives, conducting regular safety meetings, and leading by example are essential aspects of leadership commitment.
Employee Involvement and Engagement
Involving employees in safety-related decisions and activities fosters a sense of ownership and engagement. Employees should be encouraged to identify potential hazards, report near misses or incidents, and participate in safety training and initiatives. Regular safety meetings, feedback sessions, and recognition for safe practices promote employee involvement and create a positive safety culture.
Regular Safety Inspections
Regular safety inspections are necessary to identify potential hazards and rectify any unsafe conditions promptly. Inspections should cover all aspects of welding operations, including equipment, work areas, ventilation systems, and personal protective equipment. Conducting inspections at regular intervals and addressing identified issues enhances workplace safety.
Incident Reporting and Investigation
Establishing a robust incident reporting and investigation system is crucial in learning from accidents, near misses, or safety incidents.
Encouraging prompt reporting of incidents, conducting thorough investigations, and implementing corrective actions ensure that similar incidents are prevented in the future. Transparent communication about incidents fosters a culture of openness and continuous improvement.
Safety Audits and Reviews
Periodic safety audits and reviews help evaluate safety programs’ effectiveness and identify improvement areas. External audits conducted by independent safety professionals can provide valuable insights and ensure compliance with established safety standards and regulations. Regular internal reviews ensure that safety programs remain relevant and aligned with evolving industry practices.
By incorporating these elements into their organizational culture, companies can create a robust safety framework that protects welders and the overall work environment.
In conclusion, welding is a crucial process in various industries but comes with inherent hazards. Electric shock, health risks, fires and explosions, eye injuries, burns, fumes and gases, and noise exposure are potential hazards that must be addressed. Implementing preventive measures, following safety standards and regulations, conducting risk assessments, and providing proper education and training are essential. Protecting against electric shock, using personal protective equipment, practicing safe work practices, and establishing a safety culture further ensure the well-being of welders. By prioritizing safety at every step, organizations can create a safer working environment for all involved in the welding process.