You’ve just finished welding a joint, and now comes the critical question: How do you know if your weld is strong enough?
Ensuring the strength and integrity of a weld is crucial to constructing reliable structures and machinery.
This article will guide you through four key indicators to determine the strength of your weld, giving you the confidence and peace of mind that your welded joint is up to the task.
Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting your journey in the welding world, understanding how to assess the strength of your weld is a valuable skill that will contribute to your success in the field.
So, let’s explore the factors that determine the strength of a weld and equip you with the knowledge to make informed judgments about your work.
Understanding Weld Strength
When it comes to welding, understanding the strength of your welds is crucial for ensuring the integrity and reliability of your structures and projects. Weld strength refers to the ability of a weld joint to withstand applied loads, resist deformation, and maintain its structural integrity under various conditions.
To assess the strength of a weld, several factors can be considered, as well as various testing methods that can be employed. This article will explore the factors affecting weld strength, common weld strength test methods, welding standards and codes, consulting welding experts, welding training and certification, and quality control measures.
Factors Affecting Weld Strength
Several factors can significantly impact the strength of a weld. Understanding these factors is essential for producing strong and durable welds. One of the critical factors is the metallurgical properties of the parent materials and the weld filler metal.
These materials’ composition, grain structure, and mechanical properties can influence the strength of the resulting weld joint.
Another critical factor is the joint design and preparation. Proper joint design and preparation ensure that the weld joint can effectively distribute loads and minimize stress concentrations.
The choice of welding process also plays a significant role in weld strength. Different welding processes have varying heat inputs, cooling rates, and potential for defects, all of which can affect the strength of the weld.
Common Weld Strength Test Methods
Several test methods are commonly used to determine the strength of a weld. These methods can be categorized into three main types: visual inspection, non-destructive, and destructive testing.
Visual Inspection
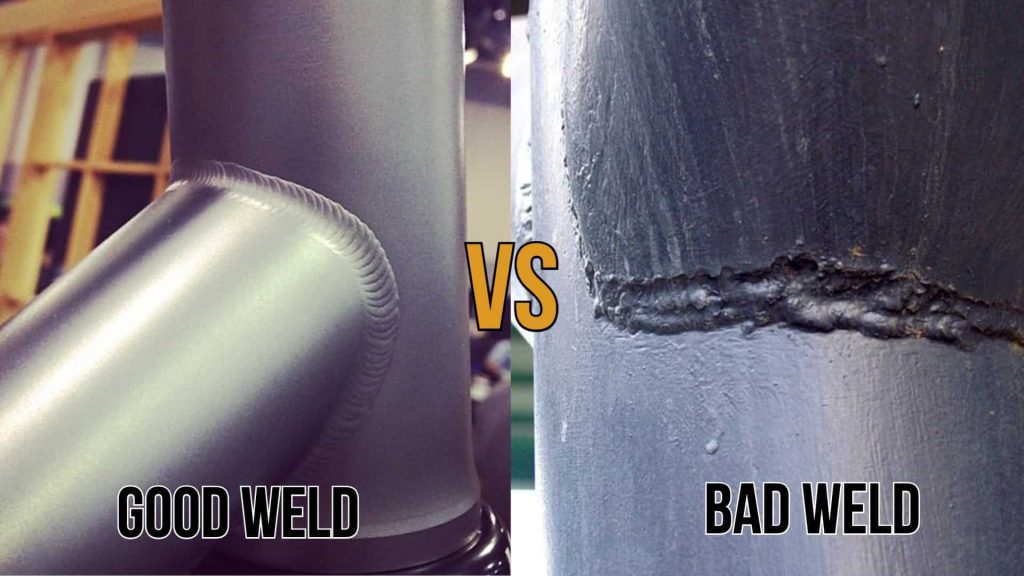
Visual inspection is the simplest and most basic method of assessing weld strength. It involves examining the weld joint with the naked eye to identify any visible defects or discontinuities. Two essential aspects of visual inspection for evaluating weld strength are checking for adequate penetration and examining weld profiles.
Checking for Adequate Penetration
Adequate penetration refers to the depth to which the weld filler material has fused with the parent materials. Insufficient penetration can weaken the weld and lead to joint failure. Visual inspection helps confirm the penetration depth and ensure its adequacy.
Examining Weld Profiles
The shape and appearance of a weld, known as its profile, can provide valuable insights into its strength. Specific profiles, such as concave or convex shapes, can indicate problems like underfill or undercut, which may affect the weld’s strength.
Visual inspection helps identify any irregularities in the weld profile and allows for appropriate corrective measures to be taken if necessary.
Non-Destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods are used to assess the properties of a weld without causing any damage to the tested component. These methods are commonly employed in industries where the integrity of welds is critical.
Using Dye Penetrant Testing
Dye penetrant testing, also known as liquid penetrant testing, involves applying a colored liquid (dye) to the surface of the weld and allowing it to penetrate any surface-breaking defects. Excess dye is removed, and a developer is applied to make the indications visible. This method can detect surface cracks, porosity, and other discontinuities affecting weld strength.
Performing Magnetic Particle Inspection
Magnetic particle inspection (MPI) is a non-destructive testing method to detect surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
By applying a magnetic field and introducing magnetic particles onto the surface of the weld, any defects will create magnetic flux leakage, making them visible under suitable lighting conditions. MPI effectively detects cracks, lack of fusion, and other defects that can compromise the strength of a weld.
Ultrasonic Testing for Weld Integrity
Ultrasonic testing (UT) utilizes high-frequency sound waves to assess the integrity of a weld. A transducer emits ultrasonic waves into the weld, and the reflections or echoes from internal defects or boundaries are analyzed to determine their size, location, and orientation. UT is widely used for detecting subsurface defects such as cracks, lack of fusion, and inclusions that may affect weld strength.
Destructive Testing
Destructive testing involves subjecting a weld joint to controlled forces or conditions that cause it to fail. While this approach may destroy the weld, it provides valuable information about its strength and performance under specific conditions.
Tensile Strength Test
The tensile strength test is among the most common destructive tests for assessing weld strength. It involves gradually increasing tension to a standardized specimen, either as a weld coupon or a section of the welded component, until the weld joint fractures. The maximum load attained during this test is recorded and used to determine the ultimate tensile strength of the weld.
Bend Test
The bend test evaluates the ductility and soundness of a weld joint by subjecting it to a bending force. A section of the weld or a prepared specimen is bent to a specific angle, typically 180 degrees or more, until a crack appears or the weld fractures.
This test assesses the weld’s ability to withstand bending loads and identifies any defects that may affect its strength, such as lack of fusion or cracks.
Charpy Impact Test
The Charpy impact test measures the ability of a weld to absorb energy under impact loading conditions. A pendulum or hammer strikes a notched specimen, and the energy required to fracture the specimen is recorded. This test provides information about the weld’s toughness and resistance to sudden impact, which are crucial factors in determining its strength.
Welding Standards and Codes
Welding standards and codes play a significant role in ensuring weld strength and overall weld quality. These standards provide guidelines and specifications for various aspects of welding, including joint design, welding processes, and testing requirements.
Understanding Welding Codes and Standards
Welding codes and standards, such as the American Welding Society (AWS) codes, provide a set of rules and criteria that must be followed to achieve weld quality and strength. These codes cover everything from welder qualifications and materials to inspection and testing procedures. Understanding and adhering to these codes is essential for producing welds that meet the required standards.
Referencing Code Requirements for Weld Strength
When determining the strength requirements for a particular weld, it is crucial to reference the applicable welding code or standard. These codes specify the minimum strength and quality requirements for welds based on load conditions, materials, and intended application. By consulting the relevant code requirements, welders can ensure that their welds meet the necessary strength criteria.
Consulting Welding Experts
In complex welding projects or when faced with challenging weld strength assessments, seeking advice from certified welding inspectors and consulting structural engineers can be beneficial.
Seeking Advice from Certified Welding Inspectors
Certified welding inspectors (CWIs) are experienced professionals who have demonstrated their knowledge and expertise in welding inspection.
These individuals can provide valuable insights into weld strength and advise on appropriate testing methods and corrective actions for any identified defects. Consulting a CWI can help ensure that welds meet the required strength standards and contribute to the overall safety and reliability of the structure.
Consulting Structural Engineers
Structural engineers are experts in designing and analyzing structures. Their expertise extends to evaluating weld strength and can be invaluable in complex projects or situations where the consequences of weld failure are significant.
By engaging a structural engineer, you can benefit from their knowledge and experience in assessing weld strength, identifying potential weak points, and recommending appropriate design modifications or reinforcement measures to ensure adequate strength.
Welding Training and Certification
Proper welder training and certification are vital for producing solid and reliable welds. Welders must undergo comprehensive training programs that cover theoretical knowledge, practical techniques, and safety practices to develop the necessary skills for successful welding.
Importance of Proper Welder Training
Welder training is essential for understanding welding processes, joint design, metallurgy, and other factors contributing to weld strength. Proper training equips welders with the knowledge and skills to produce high-quality welds that meet strength requirements and withstand various loads and environmental conditions.
Additionally, welders should be trained in recognizing and addressing welding defects to ensure the integrity of the weld joint.
Understanding Welder Certification Levels
Welder certification is a process through which an individual’s welding skills are assessed and verified by an authorized certification body. Certification levels are typically based on the welding process, material type, joint configuration, and position.
By achieving certification, welders demonstrate their proficiency in producing welds that meet the required strength and quality standards. Working with certified welders ensures that the welds are performed by skilled individuals with the necessary expertise to achieve the desired weld strength.
Quality Control Measures
Implementing effective quality control measures ensures consistent weld strength and overall weld quality.
Quality control measures encompass various procedures and processes that monitor, verify, and document the quality of welds throughout the fabrication and construction phases.
Implementing Welding Procedure Specifications
Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) are detailed documents that outline the specific welding parameters and requirements for a given weld joint.
A well-defined WPS ensures that the welding process is carried out consistently, with appropriate heat inputs, welding techniques, and other vital factors contributing to weld strength. Adhering to approved WPSs helps maintain weld quality and ensures that the weld joint meets the desired strength standards.
Adopting Quality Control Plans
A quality control plan (QCP) is a comprehensive document that outlines the procedures, responsibilities, and processes for ensuring the quality of welds. It encompasses activities such as welder qualifications, inspection procedures, testing requirements, and documentation.
By adopting a QCP, organizations can systematically monitor and control the quality of welds, thereby enhancing weld strength and maintaining compliance with relevant codes and standards.
Conclusion
Assessing weld strength is crucial for ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of welded structures and projects.
By understanding the factors affecting weld strength, employing appropriate testing methods, adhering to welding standards and codes, consulting welding experts, undergoing proper training and certification, and implementing effective quality control measures, you can achieve welds with the necessary strength and quality.
Remember, strong welds contribute to the long-term durability and success of your projects while promoting overall safety and reliability.
Developing a comprehensive understanding of weld strength is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning, staying up-to-date with industry advancements, and seeking professional guidance when needed.