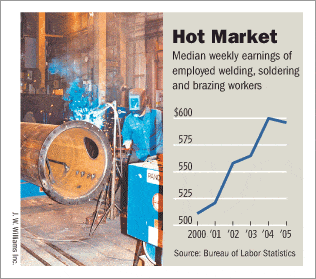
You’re curious about the prospects of Welding and whether it’s in high demand in 2023.
Well, the good news is that Welding is experiencing a surge in popularity and opportunities.
As industries continue to advance and infrastructure development remains a priority, the need for skilled welders is rising.
From construction to manufacturing, welding expertise is sought after in various sectors. So, if you’re considering a career in Welding, the signs point toward a bright and promising future.
Overview of Welding Industry
Statistics on the size of the Welding Industry
The welding industry is crucial in various fields, including construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure development.
According to recent statistics, the welding industry is experiencing significant growth and is expected to continue to be in high demand in the coming years.
2023, the global welding market is projected to reach $27.22 billion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2018 to 2023. These numbers indicate the substantial size and potential of the welding industry.
Factors Influencing the Demand for Welders
Several factors contribute to the growing demand for welders in the industry. One significant factor is the increasing need for welding professionals due to the expansion of various industries.
The continued development of infrastructure, the manufacturing sector, and oil and gas exploration drive the demand for skilled welders. Additionally, the retirement of experienced welders and the lack of new entrants into the field have contributed to the shortage of qualified welders, increasing the demand for welding professionals.
Advantages and Opportunities in Welding
Job Security and Salary Potential
One of the significant advantages of pursuing a career in Welding is the job security it offers. With the high demand for skilled welders, individuals with expertise in this field can expect a stable career path and ample employment opportunities.
Welders are essential in the construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure sectors, ensuring a steady demand for their skills.
Moreover, Welding offers excellent salary potential. Skilled welders can earn competitive wages, especially with experience and further specialization.
Welding professionals who obtain certifications and acquire additional skills can command higher salaries, making it an attractive career choice for individuals seeking financial stability and growth.
Diverse Range of Industries and Applications
Welding presents an array of opportunities in various industries and applications. From construction and manufacturing to automotive and aerospace, Welding is indispensable in many sectors.
Skilled welders have the advantage of being able to apply their expertise across a multitude of industries, allowing for career versatility and adaptability. This diversity provides opportunities for personal and professional growth, enabling welders to explore different fields and broaden their skill sets.
Global Demand for Skilled Welders
The demand for skilled welders extends beyond national boundaries in today’s globalized world. Many countries face a shortage of qualified welders, creating a global demand for these professionals.
This opens up opportunities for welders to work internationally and gain exposure to new cultures, practices, and industries. The ability to work globally not only enhances career prospects but also enriches personal and professional experiences.
Industries with a High Demand for Welders
Construction and Infrastructure
The construction and infrastructure sectors are significant contributors to the demand for welders. Welding plays a fundamental role in the construction of buildings, bridges, highways, and other infrastructure projects.
Skilled welders are responsible for joining structural components, ensuring the strength and integrity of these critical structures. With the steady growth in construction and infrastructure development, the demand for welders in this sector remains consistently high.
Manufacturing and Fabrication
Manufacturing and fabrication industries heavily rely on welding to produce goods and equipment. Welders are involved in manufacturing processes, such as assembling metal components, welding repairs, and quality control, ensuring the final product’s durability and functionality.
From automotive to electronics, the manufacturing industry offers numerous opportunities for welders to apply their skills and contribute to producing essential goods.
Shipbuilding and Offshore Industries
The shipbuilding and offshore industries require skilled welders for various tasks, including the construction and repair of ships, offshore platforms, and pipelines.
Welding is essential for joining metal structures and ensuring their strength, reliability, and safety, especially in challenging marine environments. With the increasing demand for energy resources and maritime transportation, the need for qualified welders in these industries is expected to remain high.
Oil and Gas Sector
The oil and gas sector is another industry that relies heavily on welding expertise. Welders are essential for constructing and maintaining pipelines, oil rigs, refineries, and storage tanks.
Welding professionals in this sector are responsible for ensuring the integrity and safety of these critical facilities. As the energy demand continues to grow, so does the need for skilled welders in the oil and gas industry.
Technological Advancements Impacting Welding Demand
Automation and Robotics
Technological advancements, such as automation and robotics, have revolutionized the welding industry. Automated welding systems and robotic welders are increasingly utilized in various sectors, enhancing productivity, precision, and efficiency.
These advancements have impacted the demand for welders, with a shift towards higher-skilled roles focused on programming and operating automated welding machines. Welders with expertise in automation and robotics can enjoy increased job opportunities and better job prospects in the evolving welding industry.
Digitalization and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Digitalization and the Internet of Things (IoT) have also influenced the welding industry. Integrating digital sensors, data analytics, and connectivity has led to more intelligent and efficient welding processes.
Welding equipment and machines can now be monitored and controlled remotely, improving productivity and reducing downtime. As digitalization advances, welders with knowledge of IoT and digital welding technologies will play a crucial role in meeting the industry’s evolving demands.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D Printing, has gained significant traction in various industries. This technology utilizes welding processes, such as metal deposition, to create complex three-dimensional objects layer by layer.
As 3D Printing becomes increasingly adopted, the demand for welders skilled in additive manufacturing processes will likely grow. Welders capable of operating 3D printing equipment and manipulating various materials will have unique opportunities in this emerging field.
Welding Simulations and Augmented Reality (AR)
Welding simulations and augmented reality (AR) are revolutionizing training and skill development in the welding industry. These technologies allow welders to practice and improve their techniques in virtual environments, reducing the need for physical equipment and minimizing material waste.
Welders proficient in using welding simulations and AR can enhance their expertise without the limitations of real-world constraints, positioning themselves at the forefront of technological advancements in Welding.
Skills Required for High-Demand Welding Jobs
Proficiency in Various Welding Techniques
Welders must be proficient in various welding techniques to meet the demands of different applications and industries. These techniques include shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), tungsten inert gas welding (TIG), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW), among others.
Welders with diverse skill sets who can adapt to different welding techniques have a competitive advantage in a high-demand job market.
Knowledge of Different Metals and Alloys
A thorough understanding of various metals and alloys is essential for welders to select the appropriate materials and welding methods for different applications. Each metal has distinct properties and requires specific techniques for optimal weld quality.
Welders knowledgeable about different metals and alloys can deliver precise and high-quality welds, making them invaluable assets to industries with specific material requirements.
Certifications and Qualifications
Certifications and qualifications are essential for welders to establish credibility and enhance their employability. Welding certifications, such as those issued by the American Welding Society (AWS), validate a welder’s competence and adherence to industry standards.
Additionally, obtaining specialized qualifications, such as Certified Welding Inspector (CWI) or Certified Welding Supervisor (CWS), can open doors to supervisory and managerial positions. Continuous education and certification help welders stay competitive and thrive in the high-demand welding job market.
Ability to Read Blueprints and Technical Drawings
The ability to read and interpret blueprints and technical drawings is crucial for welders to understand welding specifications, joinery requirements, and project plans.
Welders who can accurately translate these technical documents into precise welds and fabrications contribute to successful projects. Mastering blueprint reading sets welders apart and demonstrates their attention to detail and technical proficiency.
Public Perception and Workforce Challenges
Lack of Skilled Welders
Despite the high demand for welders, one of the significant challenges faced by the welding industry is the lack of skilled professionals.
The retirement of experienced welders and a decrease in new entrants into the profession have created a shortage of qualified personnel. As a result, industries struggle to find proficient welders, leading to project delays and increased costs. Addressing and bridging this skills gap ensures the industry’s sustained growth.
Aging Workforce and Retirement
Like many other sectors, the welding industry is experiencing an aging workforce. Many skilled welders are approaching retirement age, creating a significant talent gap. As these experienced professionals exit the industry, there is a pressing need to attract and train the next generation of welders.
By promoting Welding as a rewarding career choice and offering comprehensive training programs, the industry can mitigate the challenges of an aging workforce and ensure a continuous supply of skilled welders.
Promoting the Image of Welding Careers
Public perception of welding careers plays a crucial role in attracting new talent and addressing the shortage of skilled welders.
Many individuals are unaware of the numerous opportunities and benefits welding offers. Raising awareness about the advantages, stability, and potential for growth in the welding industry can help dispel misconceptions and encourage more people to consider pursuing a career in Welding.
Training and Education Initiatives
To meet the demand for skilled welders, investing in training and education initiatives is essential. Providing comprehensive and accessible training programs, both in vocational schools and through apprenticeships, can impart the necessary skills and knowledge to aspiring welders.
Collaborating with educational institutions and industry organizations to develop curricula aligned with industry needs ensures welders are adequately equipped to meet current and future workforce demands.
Demand for Specialized Welding Jobs
Underwater Welding and Pipeline Construction
Underwater Welding is a specialized field that requires welders to perform welds in challenging subsea environments.
These welders must possess advanced diving skills and be trained in specific welding techniques suitable for underwater conditions. With the growing focus on offshore energy exploration and pipeline construction, there is a consistent demand for skilled underwater welders capable of ensuring the integrity and safety of underwater structures.
Aerospace and Aviation Welding
The aerospace and aviation industries have stringent requirements for quality and safety. Welding plays a crucial role in the construction and maintenance of aircraft, spacecraft, and related components.
Welders in this industry must meet strict standards and possess specialized skills in working with lightweight materials and alloys prevalent in aerospace applications. The demand for aerospace and aviation welders remains high due to ongoing advancements in these industries.
Nuclear Power Plant Welding
Nuclear power plants require precise, high-quality welds to maintain the safety and efficiency of their systems. Welders working in nuclear power plants must adhere to stringent regulations and possess specialized knowledge of working with radioactive materials and components.
The demand for skilled nuclear power plant welders is expected to remain significant as existing plants require maintenance and new plants are constructed to meet the growing energy needs.
Custom Furniture and Artistic Welding
Welding also presents unique opportunities in custom furniture and artistic applications. Welders skilled in artistic Welding can create intricate and visually appealing metalwork, including sculptures, furniture, and decorative pieces.
This niche market offers creative outlets for welders, allowing them to combine their technical skills with artistic expression. The demand for custom furniture and artistic Welding is driven by individuals seeking one-of-a-kind, handcrafted pieces for their homes and businesses.
Future Outlook and Opportunities in Welding
Growth in Infrastructure Projects
The future of the welding industry is promising, with significant growth anticipated in infrastructure projects worldwide.
From the development of smart cities to transportation network expansion, infrastructure investments will drive the demand for skilled welders. Welders will play a crucial role in constructing bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure components, ensuring the safety and longevity of these essential structures.
Renewable Energy and Green Technologies
The increasing focus on renewable energy and green technologies will create substantial opportunities for welders.
The construction and maintenance of wind farms, solar energy installations, and other sustainable energy infrastructure will require skilled welders to handle specialized welding tasks. Welders with knowledge of green technologies and sustainable practices will be in high demand as the world transitions to cleaner and more environmentally friendly energy sources.
Advancements in Space Exploration
Advancements in space exploration and the growing commercial space industry offer exciting prospects for welders. Welding is essential in constructing space vehicles, spacecraft components, and space station modules.
As space exploration expands and commercial space travel becomes more accessible, welders with expertise in aerospace welding and space-grade materials will find themselves at the forefront of this rapidly evolving field.
Increasing Importance of Maintenance and Repair
As industries grow and evolve, the need for maintenance and repair becomes increasingly critical. Welders skilled in maintenance and repair processes will play a vital role in ensuring the longevity and functionality of various structures and equipment.
From repairing infrastructure to maintaining industrial machinery, welders proficient in repair work will find ample opportunities as the emphasis on sustainability and efficient resource utilization continues to grow.
Conclusion
The welding industry is in high demand and offers numerous advantages and opportunities for those considering a career. With job security, competitive salaries, and versatile job prospects across various industries, Welding presents an attractive option for individuals seeking a stable and rewarding career.
Infrastructure development, technological advancements, and increasing global demand for skilled welders fuel the industry’s growth. However, addressing challenges such as the shortage of skilled welders, an aging workforce, and public perception remains essential for the industry’s sustained success.
By investing in education and training initiatives, promoting welding careers, and adapting to technological advancements, the welding industry can forge a bright future filled with exciting opportunities.