Welding is a fascinating process that seamlessly joins metal together, but it can pose significant risks without proper protection.
This article explores the hazards that arise when welding without the necessary safety measures.
From the dangers of inhaling toxic fumes to the risk of severe burns and eye injuries, we shed light on why ensuring adequate protection is crucial for welders everywhere.
So, please grab a cup of coffee and join us as we navigate the hazardous world of welding without proper protection.
Health Hazards of Welding Without Proper Protection
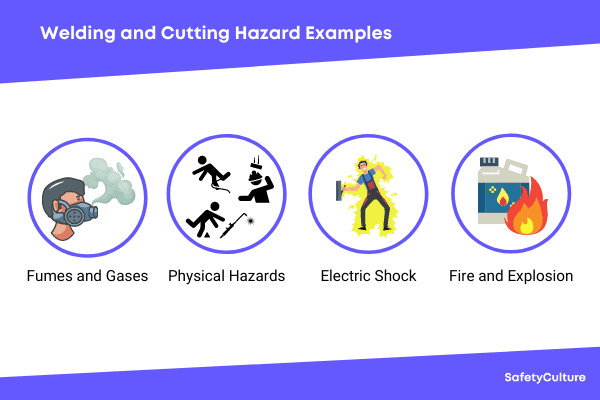
Welding, as essential as it is in many industries, poses several health hazards without the necessary protective measures. The inhalation of harmful fumes and gases is one of the primary dangers welders face.
During welding, various toxic substances are released into the air, including metal fumes, ozone, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide. Without proper protection, these fumes and gases can enter your respiratory system, leading to respiratory problems, lung infections, and long-term health issues.
Exposure to toxic metals is another risk welders face when not adequately protected. Welding involves the melting and joining of metals, and this process can release toxic metals such as lead, cadmium, and chromium.
These metals can be absorbed into your body through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, posing significant health risks. Prolonged exposure to these toxic metals can lead to severe illnesses, including neurological disorders, kidney damage, and cancer.
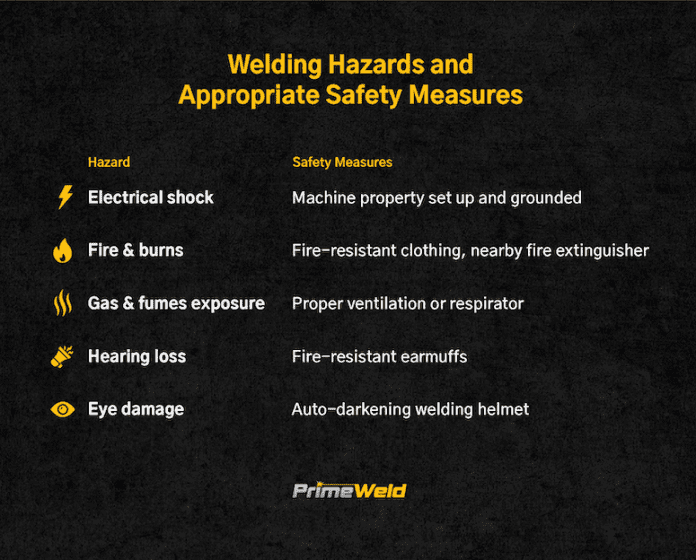
The eyes and face are particularly vulnerable during welding, making eye and face injuries a significant concern. Welding produces intense light and sparks that can cause burns, corneal injuries, and foreign object damage if not adequately protected.
In addition, the ultraviolet and infrared radiation emitted during the welding process can result in eye diseases, such as welder’s flash or “arc eye,” which can cause temporary or even permanent vision loss. Appropriate eye protection prevents these injuries, such as welding helmets and safety goggles.
Skin burns and irritations are common among welders who do not use proper protection. The heat generated during welding can cause burns and blisters if the skin comes into contact with hot metals, sparks, or UV radiation.
Moreover, the chemicals present in welding fumes can irritate and damage the skin, leading to dermatitis or other skin conditions. Wearing flame-resistant clothing gloves and maintaining a barrier cream, welders can safeguard their skin from these potentially painful and long-lasting injuries.
Fire and Explosion Hazards
Welding without proper protection can also create fire and explosion hazards. Ignition of flammable materials is a significant concern in welding environments where combustible substances are present.
Sparks, slag, or hot metal fragments can ignite nearby flammable materials, leading to fires or explosions that endanger the welder and those working there. Proper fire safety precautions, including keeping the work area clear of flammable materials and using fire-resistant curtains or shields, are crucial in preventing these hazardous situations.
In specific environments, welding may also create explosive atmospheres. When welding in confined spaces or areas with flammable gases, vapors, or dust, the heat and sparks generated during the process can ignite the surrounding atmosphere, resulting in an explosion. It is vital tocontinually assess the work environment and identify potential explosive atmosphere risks before starting any welding activities.
Employing adequate ventilation systems and using appropriate explosion-proof equipment is essential in preventing these hazardous scenarios.
Electrical Hazards
Working with electricity adds another layer of risk when proper protection is not utilized. Electric shock is a significant hazard for welders when they come into contact with live electrical components or equipment.
The powerful electrical currents used in welding can cause severe injuries or even death if not handled safely. Wearing proper electrical insulation gloves and being mindful of electrical safety protocols can help prevent electric shock incidents.
Electrocution, the lethal consequence of electric shock, poses a grave threat to welders. Without proper protection and safety measures, the risk of fatal electrocution increases significantly.
To avoid this, welders must ensure that equipment, tools, and cables are properly grounded and that all electrical connections are secure. Additionally, proper training on electrical safety practices is vital in reducing the likelihood of electrocution accidents.
Radiation Hazards
Welding can expose individuals to various types of radiation, resulting in potential long-term health consequences. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, emitted during the welding process, can cause damage to the skin and eyes.
Overexposure to UV radiation without proper protection can lead to sunburn-like symptoms, including redness, peeling, and skin cancer. Therefore, wearing protective clothing, including welding helmets and gloves with UV filters, is crucial in shielding the body from harmful UV radiation.
Infrared (IR) radiation, also emitted during welding, can cause thermal burns to the skin, leading to pain, blistering, and scarring. Prolonged exposure to IR radiation without adequate protection can result in severe tissue damage and long-lasting effects.
Wearing flame-resistant clothing and using heat-shielding materials can effectively minimize the risks associated with exposure to infrared radiation.
Noise Hazards
The constant exposure to loud noise puts welders at risk of hearing loss and tinnitus. The high noise levels generated by welding equipment and processes can cause irreversible damage to the inner ear over time.
This can result in a gradual decline in hearing ability and, in extreme cases, complete deafness. Additionally, welders may experience tinnitus, a persistent ringing or buzzing sound in the ears, which can be distressing and negatively impact their quality of life. Proper hearing protection, such as earmuffs or earplugs, is essential in preventing noise-related hearing damage.
Physical Hazards
Working in welding environments exposes individuals to several physical hazards, including falling objects. Welding often involves working at elevated heights or in areas with heavy materials. The risk of falling objects causing head injuries, fractures, or other serious accidents increases without proper protection. Wearing hard hats and implementing proper storage and securing practices for materials is essential in minimizing the potential dangers of falling objects.
Slips and trips are also common physical hazards in welding environments. Oil, water, or debris on the ground poses a significant risk to the welder and others in the area. Slippery surfaces can easily lead to falls, resulting in injuries ranging from sprains to more severe fractures.
Maintaining clean and dry workspaces, using anti-slip mats, and wearing appropriate footwear with good traction are effective measures to prevent slip and trip incidents.
Respiratory Hazards
Inhaling welding fumes can cause respiratory system irritation, leading to various health issues. The release of metal fumes, gases, and hazardous chemicals during the welding process is a primary cause of respiratory problems among welders.
Short-term exposure to these substances can result in symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Prolonged exposure can lead to chronic conditions such as bronchitis, asthma, or lung cancer. Proper respiratory protection equipment, including respirators and ventilation systems, minimizes the risks associated with inhaling welding fumes.
Lung infections are another concern for welders who do not take proper precautions. The inhalation of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, in welding fumes can lead to respiratory infections and other pulmonary conditions.
These infections can range from mild respiratory illnesses to severe and potentially life-threatening diseases. Ensuring proper ventilation and maintaining good respiratory hygiene can help reduce the likelihood of contracting lung infections.
Heat Hazards
Working in welding environments exposes individuals to intense heat levels, leading to heat-related hazards. Heat stress is a significant concern, especially when working in hot and humid conditions.
The high temperatures can cause the body to overheat, leading to heat exhaustion or heatstroke. Symptoms of heat stress include fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and confusion. Wearing cooling vests, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking regular breaks in shaded areas are essential in preventing heat-related illnesses.
Burns are another significant hazard when proper protection is not utilized. The high temperatures and intense energy in welding can cause severe burns if materials or equipment come into direct contact with the skin.
Moreover, sparks and spatter can also result in burn injuries if appropriate clothing, such as flame-resistant welding jackets and trousers, is not worn. Employing proper shielding techniques, wearing suitable personal protective equipment (PPE), and ensuring that any flammable materials are far from the welding area is crucial in avoiding burn incidents.
Chemical Hazards
Welding involves using various chemicals that pose significant health risks when not handled properly. Skin sensitization is a common consequence of prolonged exposure to certain welding chemicals such as solvents, degreasers, and fluxes.
Sensitized skin can react unfavorably, leading to allergic contact dermatitis, which can cause discomfort, itching, and redness. Wearing appropriate protective gloves and ensuring proper hygiene practices, such as prompt removal of chemical residues or contaminated clothing, is essential in preventing skin sensitization.
Allergic reactions are also a concern for welders who come into contact with certain welding fumes or chemicals. These allergic reactions can manifest as skin irritation, eye inflammation, or respiratory distress.
Individuals with pre-existing allergies or asthma may be more susceptible to these reactions. Identifying potential allergens, using proper respiratory protection, and seeking medical advice if any symptoms arise are vital steps in preventing or managing allergic reactions caused by welding.
Some welding fumes and chemicals are known or suspected to have carcinogenic effects, which can cause cancer. Prolonged exposure to substances such as chromium, nickel, and certain hydrocarbons present in welding fumes can increase the risk of developing various types of cancer, including lung, larynx, and bladder cancer.
Minimizing exposure through proper ventilation, utilizing fume extraction systems, and practicing good overall workplace hygiene are crucial measures in reducing the potential carcinogenic effects of welding.
General Safety Hazards
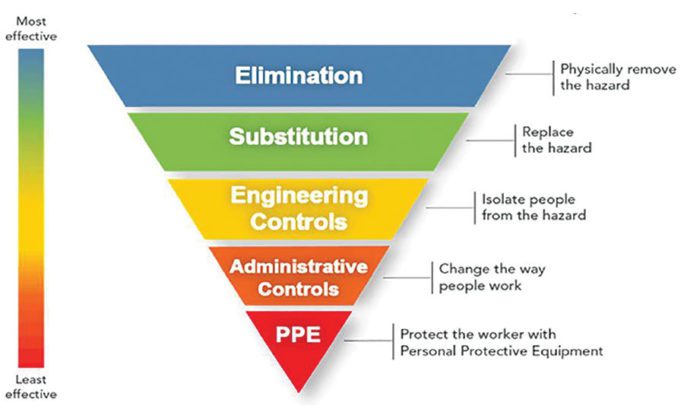
In addition to the specific hazards mentioned, welding without proper protection exposes individuals to general safety hazards. The lack of personal protective equipment (PPE) is a significant risk factor in welding environments.
Failure to wear appropriate PPE, such as welding helmets, gloves, and footwear, exposes workers to many potential injuries and health risks. Employers should ensure the provision of necessary PPE and regularly educate and remind workers about the importance of using it consistently.
Improper ventilation in welding environments can lead to the accumulation of hazardous fumes, gases, and heat, putting both the welder and others in the area at risk.
Inadequate ventilation can increase exposure to harmful substances and impair air quality, leading to respiratory issues, eye irritations, and other health problems. Proper ventilation systems, including local exhaust ventilation, must be implemented to remove contaminants and provide a safer working environment effectively.
In conclusion, welding without proper protection exposes individuals to many health hazards, ranging from respiratory problems and skin injuries to electrocution and long-term health effects.
It is imperative to prioritize safety in welding environments by wearing suitable personal protective equipment, maintaining proper ventilation, and following established safety protocols. By proactively ensuring safety measures are in place, welders can effectively mitigate the risks associated with their craft and work in a healthier and safer environment.